Abstract
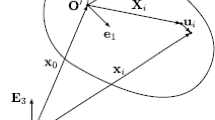
Employing the floating frame of reference formulation in the topology optimization of dynamically loaded components of flexible multibody systems seems to be a natural choice. In this formulation the deformation of flexible bodies is approximated by global shape functions, which are commonly obtained from finite element models using model reduction techniques. For topology optimization these finite element models can be parameterized using the solid isotropic material with penalization (SIMP) approach. However, little is known about the interplay of model reduction and SIMP parameterization. Also securing the model reduction quality despite major changes of the design during the optimization has not been addressed yet. Thus, using the examples of a flexible frame and a slider-crank mechanism this work discusses the proper choice of the model reduction technique in the topology optimization of flexible multibody systems.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albers A, Ottnad J, Weiler H, Häußler P (2007) Methods for lightweight design of mechanical components in humanoid robots. In: IEEE-RAS international conference on humanoid robots, Pittsburg, Pennsylvania, USA
Antoulas A (2005) Approximation of large-scale dynamical systems. SIAM, Philadelphia
Antoulas A, Beattie C, Gugercin S (2010) Interpolatory model reduction of large-scale dynamical systems. In: Mohammadpour J, Grigoriadis K (eds) Efficient modeling and control of large-scale systems. Springer, Berlin, pp 3–59
Antoulas AC, Sorensen DC (2001) Approximation of large-scale dynamical systems: An overview. Int J Appl Math Comput Sci 11(5):1093–1121
Bathe KJ (1996) Finite element procedures. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River
Bendsøe M (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution Problem. Struct Multidiscip Optim 1:193–202
Bendsøe M, Sigmund O (2003) Topology optimization - theory methods and applications. Springer, Berlin
Brüls O, Lemaire E , Duysinx P, Eberhard P (2011) Optimization of multibody systems and their structural components. In: Multibody dynamics, Springer Netherlands, pp 49–68
Burkhardt M, Seifried R, Eberhard P (2014) Aspects of symbolic formulations in flexible multibody systems. J Comput Nonlinear Dyn. 9(4)
Craig R, Bampton M (1968) Coupling of substructures for dynamic analyses. AIAA J 6(7):1313–1319
Craig R, Kurdila A (2006) Fundamentals of Structural Dynamics. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Dietz S (1999) Vibration and fatigue analysis of vehicle systems using component modes. VDI Fortschritt-Berichte, Reihe 12, Nr. VDI-Verlag, Düsseldorf
Ewins D (1995) Modal Testing: Theory and Practice. Taunton Research Studies
Fehr J (2011) Automated and error-controlled model reduction in elastic multibody systems, dissertation schriften aus dem institut für technische und numerische mechanik der universität stuttgart, vol 21. Shaker Verlag, Aachen
Grimme E (1997) Krylov projection method for model reduction. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Phd thesis
Häußler P, Emmrich D, Müller O, Ilzhöfer B, Nowicki L, Albers A (2001) Automated topology optimization of flexible components in hybrid finite element multibody systems using ADAMS/Flex and MSC. construct. In: ADAMS European User’s Conference, Berchtesgaden, Germany, 14th-15th November
Häußler P, Minx J, Emmrich D (2004) Topology optimization of dynamically loaded parts in mechanical systems: coupling of MBS, FEM and structural optimization. Wiesbaden, Germany
Held A, Seifried R (2013) Gradient-based optimization of flexible multibody systems using the absolute nodal coordinate formulation. In: Proceedings of the ECCOMAS thematic conference multibody dynamics 2013, Zagreb, Croatia, 1-4 July
Hurty WC (1965) Dynamic analysis of structural systems using component modes. AIAA J 3:678–685
Kang B, Park G (2005) Optimization of flexible multibody dynamic systems using the equivalent static load method. AIAA J 43(4):846–852
Kurz T, Burkhardt M, Eberhard P (2011) Systems with constraint equations in the symbolic multibody simulation software neweul-M 2. In: Samin JC, Fisette P (eds) Proceedings of the ECCOMAS thematic conference on multibody dynamics. Brussels, Belgium, p 2011
Kurz T, Eberhard P, Henninger C, Schiehlen W (2010) From Neweul to Neweul-M 2: symbolical equations of motion for multibody system analysis and synthesis. Multibody Sys Dyn 24(1):25–41
Moghadasi A (2013) Modeling and analyzing the influence of bearing loads in the topology Optimization of flexible multibody systems. Institute of Engineering and Computational Mechanics, University of Stuttgart
Nowakowski C, Fehr J, Fischer M, Eberhard P (2012) Model-Order reduction in elastic multibody systems using the floating Frame of reference formulation. In: Proceedings MATHMOD 2012 - 7th Vienna International Conference on Mathematical Modelling, Vienna Austria
Olhoff N, Du J (2005) Topological design of continuum structures subjected to forced vibration. In: 6th World congresses of structural and multidisciplinary optimization
Pedersen N (2000) Maximization of eigenvalues using topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 20:2–11
Saad J (2003) Iterative methods for sparse linear systems. SIAM, Philadelphia
Schwertassek R, Wallrapp O, Shabana AA (1999) Flexible multibody simulation and choice of shape functions. Nonlinear Dynamics 20(4):361–380
Schwertassek R, Wallrapp O (1999). Dynamik flexibler Mehrkörpersysteme (in German) Vieweg, Braunschweig
Seifried R (2013) Dynamics of underactuated multibody systems - modeling. Springer, Berlin
Seifried R, Held A (2012) Optimal design of lightweight machines using flexible multibody system dynamics. In: Proceedings of the ASME 2012 international design engineering technical conferences (IDETC/CI 2012). Chicago, IL, USA
Shabana AA (1997) Flexible multibody dynamics: review of past and recent developements. Multibody Sys Dyn 1:189–222
Shabana AA (2005) Dynamics of multibody systems. Cambridge University Press, New York
Sigmund O (2007) Morphology-based black and white filters for topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 33:401–424
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes - A new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24:359– 373
Tromme E, Brüls O, Emonds-Alt J, Bruyneel M, Virlez G, Duysinx P (2013) Discussion on the optimization problem formulation of flexible components in multibody systems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48 (6):1189–1206
Volkwein S (2006) Model reduction using proper orthogonal decomposition. http://www.uni-graz.at/imawww/volkwein/POD.pdf. In: Accessed 30 March 2012
Wallrapp O (1993) Standard Input Data of Flexible Bodies for Multibody System Codes. Report IB 515-93-04, DLR. Institute for Robotics and System Dynamics, Oberpfaffenhofen
Wehage RA, Haug EJ (1981) Generalized coordinate partitioning in dynamic analysis of mechanical systems. Tech rep. College of Engineering, University of Iowa
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the German Research Foundation (DFG) for financial support of the project within the Cluster of Excellence in Simulation Technology (EXC 310/2) at the University of Stuttgart.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Held, A., Nowakowski, C., Moghadasi, A. et al. On the influence of model reduction techniques in topology optimization of flexible multibody systems using the floating frame of reference approach. Struct Multidisc Optim 53, 67–80 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1302-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1302-4