Abstract
Objective
Angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2) is a potent regulator of vascular permeability and inflammation in acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Genetic variants in the Ang-2 gene may lead to altered activities of Ang-2 (or ANGPT2) gene. The aim of this study was to assess if genetic variants of Ang-2 are associated with the risk of ARDS.
Design
Unmatched, case-control study nested within a prospectively enrolled cohort.
Setting
Intensive care units (ICU) of an academic medical center.
Patients
About 1,529 critically ill patients with risk factors for ARDS consecutively admitted to the ICUs from 1999 to 2006. Cases were 449 patients who developed ARDS and controls were 1,080 subjects who did not developed ARDS.
Intervention
None.
Measurements and results
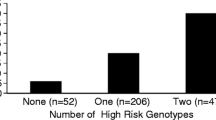
Nine tagging SNPs (tSNPs) spanning the entire Ang-2 gene were genotyped in all patients. The results were analyzed using logistic regression models, adjusting for covariates. The variant T allele of one tSNP (rs2515475) was significantly associated with increased risk of ARDS (ORadjusted = 1.28; P = 0.042). This association was stronger in subjects with extrapulmonary injuries (ORadjusted = 1.79; P = 0.004). Haplotype TT in block 2 containing the T allele of the rs2515475 was also significantly associated with higher risk of ARDS (ORadjusted = 1.42; P = 0.009), particularly in subjects with extrapulmonary injuries (ORadjusted = 1.90; P = 0.004).
Conclusion
Common genetic variation in the Ang-2 gene may be associated with increased risk of ARDS, especially among patients with extrapulmonary injuries.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Piantadosi CA, Schwartz DA (2004) The acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ann Intern Med 141:460–470
Ware LB, Matthay MA (2000) The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 342:1334–1349
Andrews P, Azoulay E, Antonelli M, Brochard L, Brun-Buisson C, De Backer D, Dobb G, Fagon JY, Gerlach H, Groeneveld J, Macrae D, Mancebo J, Metnitz P, Nava S, Pugin J, Pinsky M, Radermacher P, Richard C (2007) Year in review in intensive care medicine, 2006. II. Infections and sepsis, haemodynamics, elderly, invasive and noninvasive mechanical ventilation, weaning, ARDS. Intensive Care Med 33:214–229
Orfanos SE, Mavrommati I, Korovesi I, Roussos C (2004) Pulmonary endothelium in acute lung injury: from basic science to the critically ill. Intensive Care Med 30:1702–1714
Maniatis NA, Orfanos SE (2008) The endothelium in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Curr Opin Crit Care 14:22–30
McDonald DM (2001) Angiogenesis and remodeling of airway vasculature in chronic inflammation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:S39–S45
Koh GY, Kim I, Kwak HJ, Yun MJ, Leem JC (2002) Biomedical significance of endothelial cell specific growth factor, angiopoietin. Exp Mol Med 34:1–11
Maisonpierre PC, Suri C, Jones PF, Bartunkova S, Wiegand SJ, Radziejewski C, Compton D, McClain J, Aldrich TH, Papadopoulos N, Daly TJ, Davis S, Sato TN, Yancopoulos GD (1997) Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis. Science 277:55–60
Fiedler U, Augustin HG (2006) Angiopoietins: a link between angiogenesis and inflammation. Trends Immunol 27:552–558
Roviezzo F, Tsigkos S, Kotanidou A, Bucci M, Brancaleone V, Cirino G, Papapetropoulos A (2005) Angiopoietin-2 causes inflammation in vivo by promoting vascular leakage. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 314:738–744
Rondaij MG, Bierings R, Kragt A, van Mourik JA, Voorberg J (2006) Dynamics and plasticity of Weibel-Palade bodies in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:1002–1007
Bhandari V, Choo-Wing R, Lee CG, Zhu Z, Nedrelow JH, Chupp GL, Zhang X, Matthay MA, Ware LB, Homer RJ, Lee PJ, Geick A, de Fougerolles AR, Elias JA (2006) Hyperoxia causes angiopoietin 2-mediated acute lung injury and necrotic cell death. Nat Med 12:1286–1293
Parikh SM, Mammoto T, Schultz A, Yuan HT, Christiani D, Karumanchi SA, Sukhatme VP (2006) Excess circulating angiopoietin-2 may contribute to pulmonary vascular leak in sepsis in humans. PLoS Med 3:e46
Orfanos SE, Kotanidou A, Glynos C, Athanasiou C, Tsigkos S, Dimopoulou I, Sotiropoulou C, Zakynthinos S, Armaganidis A, Papapetropoulos A, Roussos C (2007) Angiopoietin-2 is increased in severe sepsis: correlation with inflammatory mediators. Crit Care Med 35:199–206
Gallagher DC, Parikh SM, Balonov K, Miller A, Gautam S, Talmor D, Sukhatme VP (2008) Circulating angiopoietin 2 correlates with mortality in a surgical population with acute lung injury/adult respiratory distress syndrome. Shock 29:656–661
Ward EG, Grosios K, Markham AF, Jones PF (2001) Genomic structures of the human angiopoietins show polymorphism in angiopoietin-2. Cytogenet Cell Genet 94:147–154
International HapMap Consortium (2005) A haplotype map of the human genome. Nature 437:1299–1320
Hegen A, Koidl S, Weindel K, Marme D, Augustin HG, Fiedler U (2004) Expression of angiopoietin-2 in endothelial cells is controlled by positive and negative regulatory promoter elements. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:1803–1809
Pauling MH, Vu TH (2004) Mechanisms and regulation of lung vascular development. Curr Top Dev Biol 64:73–99
Konac E, Onen HI, Metindir J, Alp E, Biri AA, Ekmekci A (2007) Lack of association between −460 C/T and 936 C/T of the vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin-2 exon 4 G/A polymorphisms and ovarian, cervical, and endometrial cancers. DNA Cell Biol 26:453–463
Dunai G, Vasarhelyi B, Szabo M, Hajdu J, Meszaros G, Tulassay T, Treszl A (2008) Published genetic variants in retinopathy of prematurity: random forest analysis suggests a negligible contribution to risk and severity. Curr Eye Res 33:501–505
Menezes SL, Bozza PT, Neto HC, Laranjeira AP, Negri EM, Capelozzi VL, Zin WA, Rocco PR (2005) Pulmonary and extrapulmonary acute lung injury: inflammatory and ultrastructural analyses. J Appl Physiol 98:1777–1783
Riva DR, Oliveira MB, Rzezinski AF, Rangel G, Capelozzi VL, Zin WA, Morales MM, Pelosi P, Rocco PR (2008) Recruitment maneuver in pulmonary and extrapulmonary experimental acute lung injury. Crit Care Med 36:1900–1908
Daly C, Pasnikowski E, Burova E, Wong V, Aldrich TH, Griffiths J, Ioffe E, Daly TJ, Fandl JP, Papadopoulos N, McDonald DM, Thurston G, Yancopoulos GD, Rudge JS (2006) Angiopoietin-2 functions as an autocrine protective factor in stressed endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:15491–15496
Mandriota SJ, Pepper MS (1998) Regulation of angiopoietin-2 mRNA levels in bovine microvascular endothelial cells by cytokines and hypoxia. Circ Res 83:852–859
Zhai R, Zhou W, Gong MN, Thompson BT, Su L, Yu C, Kraft P, Christiani DC (2007) Inhibitor kappaB-alpha haplotype GTC is associated with susceptibility to acute respiratory distress syndrome in Caucasians. Crit Care Med 35:893–898
Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet J, Falke K, Hudson L, Lamy M, LeGall JR, Morris A, Spragg R (1994) Report of the American–European consensus conference on ARDS: definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes and clinical trial coordination. The consensus committee. Intensive Care Med 20:225–232
Kraft P, Cox DG, Paynter RA, Hunter D, De Vivo I (2005) Accounting for haplotype uncertainty in matched association studies: a comparison of simple and flexible techniques. Genet Epidemiol 28:261–272
Benjamini Y, Yekutieli D (2005) Quantitative trait loci analysis using the false discovery rate. Genetics 171:783–790
Chapman JM, Cooper JD, Todd JA, Clayton DG (2003) Detecting disease associations due to linkage disequilibrium using haplotype tags: a class of tests and the determinants of statistical power. Hum Hered 56:18–31
Ganter MT, Cohen MJ, Brohi K, Chesebro BB, Staudenmayer KL, Rahn P, Christiaans SC, Bir ND, Pittet JF (2008) Angiopoietin-2, marker and mediator of endothelial activation with prognostic significance early after trauma? Ann Surg 247:320–326
van der Heijden M, van Nieuw Amerongen GP, Koolwijk P, van Hinsbergh VW, Groeneveld AJ (2008) Angiopoietin-2, permeability oedema, occurrence and severity of ALI/ARDS in septic and non-septic critically ill patients. Thorax 63:903–909
Gong MN, Zhou W, Williams PL, Thompson BT, Pothier L, Boyce P, Christiani DC (2005) -308GA and TNFB polymorphisms in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Eur Respir J 26:382–389
Pelosi P, D’Onofrio D, Chiumello D, Paolo S, Chiara G, Capelozzi VL, Barbas CS, Chiaranda M, Gattinoni L (2003) Pulmonary and extrapulmonary acute respiratory distress syndrome are different. Eur Respir J Suppl 42:48s–56s
Negri EM, Hoelz C, Barbas CS, Montes GS, Saldiva PH, Capelozzi VL (2002) Acute remodeling of parenchyma in pulmonary and extrapulmonary ARDS. An autopsy study of collagen-elastic system fibers. Pathol Res Pract 198:355–361
Santos FB, Nagato LK, Boechem NM, Negri EM, Guimaraes A, Capelozzi VL, Faffe DS, Zin WA, Rocco PR (2006) Time course of lung parenchyma remodeling in pulmonary and extrapulmonary acute lung injury. J Appl Physiol 100:98–106
dos Santos CC, Okutani D, Hu P, Han B, Crimi E, He X, Keshavjee S, Greenwood C, Slutsky AS, Zhang H, Liu M (2008) Differential gene profiling in acute lung injury identifies injury-specific gene expression. Crit Care Med 36:855–865
Ioannidis JP, Ntzani EE, Trikalinos TA, Contopoulos-Ioannidis DG (2001) Replication validity of genetic association studies. Nat Genet 29:306–309
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from National Institute of Health (HL60710, ES00002) and Flight Attendant Medical Research Institute (062459-YCSA). The authors would like to thank Weiling Zhang, Kelly McCoy, Thomas McCabe, Julia Shin, and Hanae Fujii-Rios for patient recruitment; Andrea Shafer and Starr Sumpter for research support; Maureen Convery for laboratory expertise; Janna Frelich for data management; and the patients and staff of ICUs at Massachusetts General Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
L. Su and R. Zhai contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, L., Zhai, R., Sheu, CC. et al. Genetic variants in the angiopoietin-2 gene are associated with increased risk of ARDS. Intensive Care Med 35, 1024–1030 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-009-1413-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-009-1413-8