Abstract
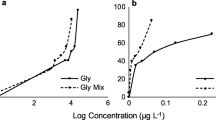
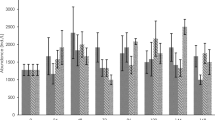
The individual and combined effects of pesticides (chlorpyrifos, triadimefon and butachlor) on the zooplankton assemblages of microcosms were investigated. Laboratory microcosms were constructed with water and sediment to simulate aquatic conditions in China’s rice paddy fields. Results from principal response curves analysis showed that butachlor and triadimefon had no significant impact individually on the population level in zooplankton assemblages. The deleterious effects of pesticide mixtures on the zooplankton were mainly caused by chlorpyrifos. In fact, assemblage succession only occurred in the treatments containing chlorpyrifos. There was no synergy effect on the microcosm from combinations of pesticides on the assemblages. The zooplankton assemblages affected by chlorpyrifos did not recover at the termination of the experiment, i.e., after 56 days.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali JM, Farhat YA, Kolok AS (2016) Biological impacts in Fathead minnow larvae following a 7-day exposure to agricultural runoff: a microcosm study. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96(4):432–437. doi:10.1007/s00128-016-1762-2
Bjergager MA, Hanson ML, Lissemore L, Henriquez N, Solomon KR, Cedergreen N (2011) Synergy in microcosms with environmentally realistic concentrations of prochloraz and esfenvalerate. Aquat Toxicol 101(2):412–422. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2010.11.004
Campbell P (1998) Higher-tier aquatic risk assessment for pesticides. In guidance document from the SETAC-Europe/OECD/EC workshop, held at Lacanau Océan, France, 19–22 April 1998
Cedergreen N (2014) Quantifying synergy: a systematic review of mixture toxicity studies within environmental toxicology. PLoS ONE, 9(5):1–12. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0096580
Choung CB, Hyne RV, Stevens MM, Hose GC (2013) The ecological effects of a herbicide-insecticide mixture on an experimental freshwater ecosystem. Environ Pollut 172:264–274. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2012.09.002
Daam MA, Rodrigues AMF, Van den Brink PJ, Nogueira AJA (2009) Ecological effects of the herbicide linuron in tropical freshwater microcosms. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 72(2):410–423. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.07.009
Daam MA, Satapornvanit K, Van den Brink PJ, Nogueira AJA (2010). Direct and indirect effects of the fungicide Carbendazim in tropical freshwater microcosms. Arch Environ Conntam Toxicol, 58(2):315–324. doi:10.1007/s00244-009-9367-y
Dong K, Dong Y, Wang HL, Chen B, Zhang LM, Zan QA, Li ZY (2014) A characterization of rice multiple-pest injuries and quantification of yield losses. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 34(21):6124–6136. Retrieved from http://lib.cqvip.com/qk/90772X/201421/662937987.html
Fairchild JF, Point TW, Schwartz TR (1994) Effects of an herbicide and insecticide mixture in aquatic mesocosms. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 27(4):527–533. doi:10.1007/BF00214845
Fleeger JW, Carman KR, Nisbet RM (2003) Indirect effects of contaminants in aquatic ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 317(1–3):207–233. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(03)00141-4
Grippo RS, McNeely VM, Farris JL (2016) Unexpected increases in fecundity of Ceriodaphnia dubia exposed to reused rice irrigation water. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96(6):720–724. doi:10.1007/s00128-016-1818-3
Hassold E, Backhaus T (2014) The predictability of mixture toxicity of demethylase inhibiting fungicides to Daphnia magna depends on life-cycle parameters. Aquat Toxicol 152C:205–214. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.04.009
He H, Li H, Yu J, He J, Chen G, Li W (2012) Acute toxicity of butachlor and atrazine to freshwater green alga Scenedesmus obliquus and cladoceran Daphnia carinata. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2012.02.009
Inao K, Watanabe H, Karpouzas DG, Capri E (2008) Simulation models of pesticide fate and transport in paddy environment for ecological risk assessment and management. JARQ 42(1):13–21. Retrieved from https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jarq/42/1/42_13/_article
Kittusamy G, Kandaswamy C, Kandan N, Subramanian M (2014) Pesticide residues in two frog species in a paddy agroecosystem in Palakkad District, Kerala, India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 93(6):728–734. doi:10.1007/s00128-014-1351-1
Koesukwiwat U, Sanguankaew K, Leepipatpiboon N (2014) Evaluation of a modified QuEChERS method for analysis of mycotoxins in rice. Food Chem 153:44–51. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.12.029
Le TTY, Peijnenburg WJGM (2013) Modeling toxicity of mixtures of per fl uorooctanoic acid and triazoles (triadimefon and paclobutrazol) to the benthic cladoceran Chydorus sphaericus. Am Chem Soc 47:6621–6629
OECD (2002) Test No. 308: Aerobic and Anaerobic Transformation in Aquatic Sediment System. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, (April), 19. doi:10.1787/9789264070523-en
Pavlaki MD, Ferreira ALG, Soares AMVM, Loureiro S (2014) Changes of chemical chronic toxicity to Daphnia magna under different food regimes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 109:48–55. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.07.039
Phyu YL, Palmer CG, Warne MSJ, Hose GC, Chapman JC, Lim RP (2011) A comparison of mixture toxicity assessment: examining the chronic toxicity of atrazine, permethrin and chlorothalonil in mixtures to Ceriodaphnia cf. dubia. Chemosphere 85(10):1568–1573. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.07.061
Relyea RA (2009) A cocktail of contaminants: how mixtures of pesticides at low concentrations affect aquatic communities. Oecologia 159(2):363–376. doi:10.1007/s00442-008-1213-9
Rohr JR, Crumrine PW (2014) Effects of an herbicide and an insecticide on pond community structure and processes. Ecol Appl 15(4):1135–1147
Shurin JB, Clasen JL, Greig HS, Kratina P, Thompson PL (2012) Warming shifts top-down and bottom-up control of pond food web structure and function. Philos Trans R Soc London B 367(1605):3008–3017. doi:10.1098/rstb.2012.0243
ter Braak CJF, Šmilauer P (2012) Canoco reference manual and user’s guide: software for ordination, version 5.0. Ithaca, USA: Microcomputer Power. Retrieved from http://www.canoco5.com/
Van Wijngaarden RPA, Brock TCM, Douglas MT (2005) Effects of chlorpyrifos in freshwater model ecosystems: the influence of experimental conditions on ecotoxicological thresholds. Pest Manag Sci 61(10):923–935. doi:10.1002/ps.1084
van den Brink PJ, ter Braak CJF (1999) Principal response curves: analysis of time-dependent multivariate responses of a biological community to stress. Toxicol Chem 18:138–148
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Key research and development project of Zhejiang Province (No. 2015C02G2010084) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31101458). We thank LetPub (http://www.letpub.com) for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, P., Liu, F., Liu, Y. et al. Effects of Pesticide Mixtures on Zooplankton Assemblages in Aquatic Microcosms Simulating Rice Paddy Fields. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 99, 27–32 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2105-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-017-2105-7