Abstract
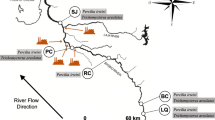
Mullet (Mugil liza) were sampled in five different areas along the Guanabara Bay, southeastern Brazil, classified as non-contaminated, moderately contaminated and contaminated. Morphometric (Fulton condition factor, relative condition factor and weight to length scaling coefficient) and organosomatic (hepatosomatic index) indices of environmental stress were analysed. Fish from the differentially contaminated areas show statistically different Fulton and relative condition factors and hepatosomatic indices, but not the weight to length scaling coefficient. The Kn and the FCF followed the same trend, with fish from São Gonçalo (1.07 ± 0.04 and 0.89 ± 0.03), Itaipu (0.84 ± 0.01 and 0.86 ± 0.01) and the Rodrigo de Freitas Lagoon (1.03 ± 0.01 and 0.87 ± 0.20) showing higher FCFs than fish from Magé (0.96 ± 0.01 and 0.81 ± 0.01). Fish from Itaipu showed significantly higher HSI values than the other sampling sites (1.68 ± 0.07), with fish from Olaria and Ipiranga showing the lowest (1.56 ± 0.12 and 1.60 ± 0.07, respectively).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams SM, Brown AM, Goede RW (1993) A Quantitative Health Assessment Index for rapid evaluation of fish condition in the field. Trans Am Fish Soc 122:63–73
Couture P and Rajotte JW (2003) Morphometric and metabolic indicators of metal stress in wild yellow perch (Perca flavescens) from Sudbury, Ontario: a review. J Environ Monitor 5:216-221
Eastwood S, Couture P (2002) Seasonal variations in condition and liver metal concentrations of yellow perch (Perca flavescens) from a metal-contaminated environment. Aquat Toxicol 58:43–56
Espino GL (2000) In: P. y. V. Editores (ed) Organismo indicadores de la calidad del agua y de la contaminación (bioindicadores). México City pp 17–42
Francioni E, Wagener A, Scofield AL, Cavalier B (2005) Biomonitoring of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon in Perna perna from Guanabara Bay. Brazil Environ Forensics 6:361–370
Halpern BS, Walbridge S, Selkoe KA, Kappel CV, Micheli F, D’Agrosa C, Bruno JF, Casey KS, Ebert C, Fox HE, Fujita R, Heinemann D, Lenihan HS, Madin EMP, Perry MT, Selig ER, Spalding M, Steneck R, Watson R (2008) A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 319:948–952
INEA (2009) A Lagoa Rodrigo de Freitas. www.inea.rj.gov.br/
Jenkins JA (2004) Fish bioindicators of ecosystem condition at the calcasieu estuary, Louisiana. In: National Wetlands Research Center, USGS, U.S. Department of the Interior Lafayette. pp 1–47
Laflamme JS, Couillard Y, Campbell PGC, Hontela A (2000) Interrenal metallothionein and cortisol secretion in relation to Cd, Cu, and Zn exposure in yellow perch, Perca flavescens, from Abitibi lakes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 57:1692–1700
Le Cren ED (1951) The length-weight relationship and seasonal cycle in the gonad weight and condition in the perch (Perca fluviatilis). J Anim Ecol 20:201–219
Loureiro DD, Fernandez MA, Herms F, Lacerda LD (2009) Heavy metal inputs evolution to an urban hypertrophic coastal lagoon. Rodrigo De Freitas Lagoon, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil. Environ Monit Assess 159:577–588
Maddock DM, Burton MPM (1998) Gross and histological observations of ovarian development and related condition changes in American plaice. J Fish Biol 53:928–944
Mansour SA, Sidky MM (2002) Ecotoxicological studies. 3. Heavy metals contaminating water and fish from Fayoum Governorate.Egypt. Food Chem 78:15–22
Miranda AL, Roche H, Randi MAF, Menezes ML, Ribeiro CAO (2008) Bioaccumulation of chlorinated pesticides and PCBs in the tropical freshwater fish Hoplias malabaricus: histopathological, physiological, and immunological findings. Environ Int 34:939–949
Neves RLS, Oliveira TF and Ziolli RL (2007) Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in fish bile (Mugil liza) as biomarkers for environmental monitoring in oil contaminated areas. Mar Pollute Bull 54:1818-1824
Nikolsky GV (1963) The ecology of fishes. Academic Press, London
Norris DO, Camp JM, Maldonado TA, Woodling JD (2000) Some aspects of hepatic function in feral brown trout, Salmo trutta, living in metal contaminated water. Comp Biochem Physiol C 127:71–78
Querol MVM, Querol E, Gomes NNA (2002) Fator de Condição gonadal, índice hepatossomático e recrutamento como indicadores do período de reprodução de Loricariichthys platymetopon (Osteichthyes, Loricariidae), bacia do rio Uruguai Médio, sul do Brasil. Sér Zool 92:79–84
Silva CA, Oliveira Ribeiro CA, Katsumiti A, Araújo MLP, Zandoná EM, Costa Silva GP, Maschio J, Roche H , Silva de Assis HC (2009) Evaluation of waterborne exposure to oil spill 5 years after an accident in Southern Brazil Ecotox Environ Safe 72:400–409
Soares-Gomes A, Neves RL, Aucelio R, Van der Ven PH, Pitombo FB, Mendes CLT, Ziolli RL (2010) Changes and variations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon concentrations in fish, barnacles and crabs following an oil spill in a mangrove of Guanabara Bay. Southeast Brazil. Mar Pollute Bull 60:1359–1363
Sutton SG, Bult TP, Haedrich RL (2000) Relationships among fat weight, body weight, water weight, and condition factors in wild Atlantic salmon parr. Trans Am Fish Soc 129:527–538
van der Oost R, Beyer J, Vermeulen NPE (2003) Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: a review. Environ Toxicol Pharm 13:57–149
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank INCTBio and CNPq for financial support and FINEP/Convênio FNDCT n. 0106005901. Many thanks go to Natália Quinete for her invaluable help in the fish analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hauser-Davis, R.A., Lavandier, R.C., Bastos, F.F. et al. Alterations in Morphometric and Organosomatic Indices and Histopathological Analyses Indicative of Environmental Contamination in Mullet, Mugil liza, from Southeastern Brazil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89, 1154–1160 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0846-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0846-x