Abstract
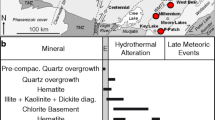
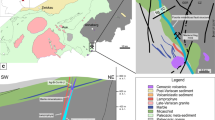
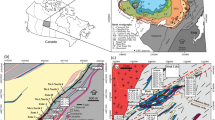
The Bou Jaber Ba-F-Pb-Zn deposit is located at the edge of the Bou Jaber Triassic salt diapir in the Tunisia Salt Diapir Province. The ores are unconformity and fault-controlled and occur as subvertical column-shaped bodies developed in dissolution-collapse breccias and in cavities within the Late Aptian platform carbonate rocks, which are covered unconformably by impermeable shales and marls of the Fahdene Formation (Late Albian–Cenomanian age). The host rock is hydrothermally altered to ankerite proximal to and within the ore bodies. Quartz, as fine-grained bipyramidal crystals, formed during hydrothermal alteration of the host rocks. The ore mineral assemblage is composed of barite, fluorite, sphalerite, and galena in decreasing abundance. The ore zones outline distinct depositional events: sphalerite-galena, barite-ankerite, and fluorite. Fluid inclusions, commonly oil-rich, have distinct fluid salinities and homogenization temperatures for each of these events: sphalerite-galena (17 to 24 wt% NaCl eq., and Th from 112 to 136 °C); ankerite-barite (11 to 17 wt% NaCl eq., and Th from 100 to 130 °C); fluorite (19 to 21 wt% NaCl eq., Th from 140 to 165 °C). The mean temperature of the ore fluids decreased from sphalerite (125 °C) to barite (115 °C) and increased during fluorite deposition (152 °C); then decreased to ∼110 °C during late calcite precipitation. Laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) analyses of fluid inclusions in fluorite are metal rich (hundreds to thousands ppm Pb, Zn, Cu, Fe) but the inclusions in barite are deficient in Pb, Zn, Cu, Fe. Inclusions in fluorite have Cl/Br and Na/Br ratios of several thousand, consistent with dissolution of halite while the inclusions analysed in barite have values lower than seawater which are indicative of a Br-enriched brine derived from evaporation plus a component of halite dissolution. The salinity of the barite-hosted fluid inclusions is less than obtained simply by the evaporation of seawater to halite saturation and requires a dilution of more than two times by meteoric water. The higher K/Na values in fluid inclusions from barite suggest that the brines interacted with K-rich rocks in the basement or siliciclastic sediments in the basin. Carbonate gangue minerals (ankerite and calcite) have δ13C and δ18O values that are close to the carbonate host rock and indicate fluid equilibrium between carbonate host rocks and hydrothermal brines. The δ34S values for sphalerite and galena fall within a narrow range (1 to 10 ‰) with a bulk value of 7.5 ‰, indicating a homogeneous source of sulfur. The δ34S values of barite are also relatively homogeneous (22 ‰), with 6 ‰ higher than the δ34S of local and regional Triassic evaporites (15 ‰). The latter are believed to be the source of sulfate. Temperature of deposition together with sulfur isotope data indicate that the reduced sulfur in sulfides was derived through thermochemical sulfate reduction of Triassic sulfate via hydrocarbons produced probably from Late Cretaceous source rocks. The 87Sr/86Sr ratio in the Bou Jaber barite (0.709821 to 0.711408) together with the lead isotope values of Bou Jaber galena (206Pb/204Pb = 18.699 to 18.737; 207Pb/204Pb = 15.635 to 15.708 and 208Pb/204Pb = 38.321 to 38.947) show that metals were extracted from homogeneous crustal source(s). The tectonic setting of the Bou Jaber ore deposit, the carbonate nature of the host rocks, the epigenetic style of the mineralization and the mineral associations, together with sulfur and oxygen isotope data and fluid inclusion data show that the Bou Jaber lead-zinc mineralization has the major characteristics of a salt diapir-related Mississippi Valley-type (MVT) deposit with superimposed events of fluorite and of barite deposition. Field relations are consistent with mineral deposition during the Eocene–Miocene Alpine orogeny from multiple hydrothermal events: (1) Zn-Pb sulfides formed by mixing of two fluids: one fluid metal-rich but reduced sulfur-poor and a second fluid reduced sulfur-rich; (2) barite precipitation involved the influx of a meteoric water component that mixed with a barium-rich fluid; and (3) fluorite precipitated from a highly saline fluid with higher temperatures.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akrour H, Aoudjehane M, Othmanine A, Thibieoz J, Touahri B (1991) Gites et indices de fluorine de l’Algérie du Nord : Inventaire et réflexion. Bull Off Natl Géol Alger 2(1):11–28
Allan MM, Yardley BWD, Forbes LJ, Shmulovich KI, Banks DA, Shepherd TJ (2005) Validation of LA-ICP-MS fluid inclusion analysis with synthetic fluid inclusions. Am Mineral 90:1767–1775
Amouri M (1989) Les minéralisations Pb-Zn-Ba-F liées aux faciès carbonatés aptiens dans l’Atlas Tunisien Central. Géol Méditerr Marseille XVI(2–3):85–199
Banks DA, Giuliani G, Yardley BWD, Cheilletz A (2000) Emerald mineralization in Colombia: fluid chemistry and the role of brine mixing. Miner Deposita 35:699–713
Béjaoui J, Bouhlel S, Cardellach E, Canals A, Perona J, Piqué A (2013) Mineralization and fluid inclusion studies of the Aptian carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn-Ba ore deposits at Jbel Hamra, Central Tunisia. J Geochem Explor 128:136–146
Ben Ayed N (1986) Évolution tectonique de l’avant-pays de la chaîne alpine de Tunisie du début du Mésozoïque à l’Actuel. Thesis. University Paris Sud, Paris
Ben Ferjani F, Burrolet PF, Mejri F (1990) Petrolium Geology of Tunisia. Entreprise Tunisienne des Activités Pétrolière xx 1990
Belayouni H (1992) Oil seeps and associated phenomena in northern Tunisia. Field Trip guidebook, IIIème Journées de Géologie Tunisienne Appliquées à la Recherche des hydrocarbures ETAP Tunis pp 18
Belayouni H, Brunelli D, Clocchiatti R, Di Staso A, El Hassani I, Guerrera F, Kassaa S, Laridhi-Ouazaa N, Martín M, Serrano F, Tramontana M (2010) La Galite Archipelago (Tunisia, North Africa): Stratigraphic and petrographic revision and insights for geodynamic evolution of the Maghrebian Chain. J Afri Earth Sci 56(1):15–28
Belayouni H, Guerrera F, Martín MM, Serrano F (2012) Stratigraphic update of the Cenozoic Sub-Numidian formations of the Tunisian Tell (North Africa): Tectonic/sedimentary evolution and correlations along the Maghrebian Chain. J Afr Earth Sci 64:48–64
Bellon H (1976) Séries magmatiques néogènes et quaternaires du pourtour de la Méditerranée occidentale, comparées dans leur cadre géochronologique; implications géodynamiques. Thèse Etat Orsay
Bodnar RJ (1993) Revised equation and table for determining the freezing-point depression of H2O-NaCl solutions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 57:683–684
Boltenhagen C (1985) Paléogéographie du crétacé moyen de la Tunisie centrale. 1er Congr Nat Sci Terre 1:97–114
Bolze J (1954) Ascension et percée de diapirs au Crétacé moyen dans les monts de Téborsouk. C R Somm Soc Géol Fr 7:139–141
Bolze J, Burollet PF, Castany G (1952) Le sillon tunisien, Monographies régionales, XIXe Congrès Géologique International, Alger, 2e série, n° 5, pp 112
Bouabdellah M, Brown AC, Sangster DF (1996) Mechanisms of formation of internal sediments at the Beddiane lead-zinc deposit, Toussit mining district, northeastern Morocco. Econ Geol Spec Publ 4:356–363
Bouabdellah M, Castorina F, Bodnar RJ, Banks D, Jébrak M, Prochaska W, Lowry D, Klügel A, Hoemle M (2013) Petroleum migration, fluid mixing, and halokinesis as the main ore-forming processes at the peridiapiric Jbel Tirremi fluorite-barite hydrothermal deposit, northeastern Morocco. Econ Geol 109:1223–1256
Bouaziz S, Barrier E, Soussi M, Turki MM, Zouari H (2002) Tectonic evolution of the northern African margin in Tunisia from paleostress data and sedimentary record. Tectonophysics 357:227–253
Bouhlel S (1982) Distribution du baryum et du strontium dans la province fluorée tunisienne; application aux gîtes de Hammam Jédidi et Hammam Zriba-Jebel Guebli. PhD Thesis, University of Toulouse III, France
Bouhlel S (1985) Composition chimique, fréquence des minéraux de la série barytine-célestite dans les gisements de fluorine de Hammam Jédidi et Hammam Zriba-Jebel Guebli (Tunisie Nord-Orientale). Bull Mineral 108:403–420
Bouhlel S (1987) Mineralized carbonates in fluorite and Pb-Zn ore deposits: Jurassic and Upper Cretaceous of northern Tunisia. In: Excursion Guidebook I.A.S. 8th Regional Meeting of Sedimentology, pp 1–44
Bouhlel S (1993) Gîtologie, minéralogie et essai modélisation des minéralisations à F-Ba-Sr-Pb-Zn-(S°) associées aux carbonates (jurassiques et crétacés) et aux diapirs triasiques : gisements de Stah-Kohol, Zriba, Guebli, Bou Jaber et Fedj el Adoum (Tunisie septentrionale). Thèse Doctorat d’Etat, University of Tunis El Manar, Tunisia
Bouhlel S (2005) Carbonate-hosted Mississippi Valley-type Pb-Zn deposits in Tunisia (eastern Atlassic Foreland belt). In: Zhao C and Guo B (eds) Mineral deposits research—Meeting the global challenge. Proceedings of the Eighth Biennial SGA Meeting (Beijing, China) 3:19–22
Bouhlel S, Fortuné JP, Guilhaumou N, Touray JC (1988) Les minéralisations stratiformes à F-Ba de Hammam Zriba, Jebel Guebli (Tunisie Nord Orientale): l’apport des études d’inclusions fluides à la modélisation génétique. Miner Deposita 23:166–173
Bouhlel S, Johnson CA, Leach DL (2007) The peridiapiric-type Pb-Zn deposit at Fedj el Adoum, Tunisia: geology, petrography, and stable isotopes. In: Andrew CJ et al. (eds) Proc Ninth Biennial SGA Meeting (Dublin, Ireland) 1:323–326
Bouhlel S, Leach DL, Johnson CA, Lehmann B (2009) Ore textures and isotope signatures of the peridiapiric carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit of Bou Grine, Tunisia. In Smart Science for Exploration and Mining P. J. Williams et al. (eds) Proceedings of the Tenth Biennial SGA Meeting (Townsville, Australia) 1:409–411
Bouhlel S, Garnit H, Béjaoui J, Skaggs S (2013) Lead isotopes signatures of the MVT lead-zinc (±F) deposits across Central-North Tunisia: evidence for the heterogeneity in uranium component of the underlying source rocks. In: Mineral deposit research for a high-tech world. Jonsson E et al. (eds) Proceedings of the 12th Biennial SGA Meeting (Uppsala, Sweden) 2:612–615
Bouzenoune A, Lécolle P (1997) Petrographic and geochemical arguments for hydrothermal formation of the Ouenza siderite deposit (NE Algeria). Miner Deposita 32:189–196
Braham A, Hatira N, Hammami M, Kadri A, Arfaoui M, Chihi L, Mansouri A, Souid R (2002) Le diapir de Bou Jaber (Tunisie Centre Ouest) Précisions biostratigraphiques et conséquences structurales. Serv Géol Tunisie 69:93–103
Burke WH, Denison RE, Hetherington EA, Keopnick RB, Nelson HF, Otto JB (1982) Variation of seawater 878r/86Sr throughout Phanerozoic time. Geology 10:516–519
Burollet PF (1956) Contribution à l’étude stratigraphique de la Tunisie centrale. Ann Min Géol (Tunis) No.18
Calvez JY, Orgeval JJ, Marcoux E (1986) Étude isotopique du plomb du gisement de Bou Grine (Zone des dômes, Tunisie) et comparaison avec quelques données de la province tunisienne. BRGM Sci Tech 121–123
CastanyG (1952) Paléogéographie, tectonique et orogenèse de la Tunisie. XIXth international Geological Congress, "Monographies Régionales", 2 (1) pp 63
Chaari (2002) Geochemical study of Late Albian and Cenomanian-Turonian source rocks: a key to assess the geodynamic evolution of petroleum system of Jebel Goraa area, Salt dome zone, Northern Tunisia. Master thesis, University Tunis el manar, Faculty of Sciences of Tunis
Charef A, Sheppard SMF (1987) Pb-Zn mineralization associated with diapirism: fluid inclusion and stable isotope (H, C, O) evidence for the origin and evolution of the fluids at Fedj-el-Adoum, Tunisia. Chem Geol 61:113–134
Chihi L (1995) Les fossés néogènes à quaternaires de la Tunisie et de la mer pélagienne: leur étude structurale et leur signification dans le cadre géodynamique de la méditerranée centrale, Thesis. University of Tunis El Manar, Tunisia
Claypool GE, Molsen WT, Kaplan IR, Sakai M, Zak I (1980) The age of curves of sulfur and oxygen isotopes in marine sulfate and their mutual interpretation. Chem Geol 28:199–260
Cooke DR, Bull SW, Large RR, McGoldrick PJ (2000) The importance of oxidized brines for the formation of Australian Proterozoic stratiform sediment-hosted Pb-Zn (Sedex) deposits. Econ Geol 95:1–18
Decrée S (2008) Caractérisation géochimique et isotopique dans un système d’altération complexe du protolithe magmatique à la minéralisation fer-plomb-zinc : le cas de la mine de Sidi Driss. Thesis, Université Libre de Bruxelles
Decrée S, Marignac C, De Putter T, Deloule E, Liégeois JP, Demaiffe D (2008) Pb-Zn mineralization in a Miocene regional extensional context: the case of the Sidi Driss and the Douahria ore deposits (Nefza mining district, northern Tunisia). Ore Geol Rev 34:285–303
Dewey JF, Helman ML, Turco E, Hutton, Knott SD (1989) Kinematics of the western Mediterranean. In : Alpine Tectonics, Coward MP, DietrichD and Parker G (eds), Geological Society Special Publication 45:265–283
Dubourdieu G (1956) Étude géologique de la région de l’Ouenza (confins algéro-tunisiens). Serv Carte Géol Algérie Alger No. 10
Evan DG, Nunn JA, Hanor JS (1991) Mechanisms of driving groundwater flow near salt domes. Geophysical Reasearch 94:927–930
Erraoui L (1994) Environnements sédimentaires et géochimie des séries de l’Eocène du Nord-Est de la Tunisie. Thèse de Doctorat de Spécialité. University of Tunis El Manar, Tunisia
Frank MH, Lohmann KC (1986) Textural and chemical alteration of dolomite: Interaction of mineralizing fluids and host rock in a Mississippi Valley-type deposit, Bonneterre Formation, Viburnum Trend. In: Hagni RD (eds) Process mineralogy VI: Warrendale PA Metallurgical Society 103–116
Fuchs Y (1973) Sur les relations entre émersion et concentration métallifére (quelques exemples tunisiens). In: Livre Jubilaire Solignac. Ann Mines Géol Tunis 26:479–509
Garnit H, Bouhlel S, Barca D, Craig AJ, Chtara C (2012) Phosphorite-hosted zinc and lead mineralization in the Sekarna deposit (Central Tunisia). Miner Deposita 47:546–562
Giesemann A, Jager HJ, Norman AL, Krouse HR, Brand WA (1994) On-line sulfur determination using an elemental analyser coupled to a mass spectrometer. Anal Chem 66:2816–2819
Goldstein RH, Reynolds TJ (1994) Systematics of fluid inclusions in diagenetic minerals. SEPM Short Course 31:1–199
Grandia F, Canals À, Cardellach E, Banks DA, Perona J (2003) Origin of ore-forming brines in sediment-hosted Zn-Pb deposits of the Basque-Cantabrian basin, northern Spain. Econ Geol 98:1397–1411
Guilhaumou N, Szydlowski N, Pradier B (1990) Characterization of hydrocarbon fluid inclusions by infra-red and fluorescence microspectrometry. Min Mag 54:311–324
Guillong M, Meir DL, Allan MM, Heinrich CA, Yardley BWD (2008) SILLS: A Matlab based program for the reduction of Laser Ablation ICP-MS data of homogeneous materials and inclusions. Miner Assoc Can Short Course 40:328–333
Guirand R, Maurin JC (1991) Le rifting en Afrique au Crétacé inférieur: synthèse structurale, mise en évidence de deux étapes dans la génèse des bassins, relation avec les ouvertures océaniques peri-africaines. Bull Soc Geol Fr 162(5):811–823
Hanna MA, Wolf A (1934) Texas and Louisiana salt dome cap rock minerals. Bull Am Assoc Petr Geol 3:212–225
Jrad L, Perthuisot V (1995) Diapirisme, orogenèse et mineralisation Pb-Zn en Afrique du Nord: exemple des gisements du J. Ajred et du J. Hamra en Tunisie centrale. C R Acad Sci Paris 321:721–728
Juteau M, Michard A, Albared F (1986) The Pb-Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry of some recent circum-Mediterranean granites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 92:331–340
Kampschulte A, Strauss H (2004) The sulfur isotopic evolution of Phanerozoic seawater based on the analysis of structurally substituted sulfate in carbonates. Chem Geol 204:255–286
Kendrick MA, Burgess R, Leach D, Patrick RAD (2002) Hydrothermal fluid origins in Mississippi Valley-type ore deposits: combined noble gas (He, Ar, Kr) and halogen (Cl, Br, I) analysis of fluid inclusions from the Illinois-Kentucky fluorspar district, Viburnum trend, and the Tri-State districts, Midcontinent United States. Econ Geol 97:453–469
Koepenick RB, Burke WH, Denison RE, Hetherington EA, Nelson HF, Otto JB, Waite LE (1985) Construction of the seawater 87Sr/86Sr curve for the Cenozoic and Cretaceous: supporting data. Chem Geol 58(1–2):55–81
Kyle JR, Posey HH (1991) Halokinesis, cap rock development and salt dome mineral resources. In: Melvin JL (eds) Evaporites Petroleum and Mineral Resources: Developments in Sedimentology 50:413–474
Kyle JR, Price PK (1986) Metallic sulphide mineralization in salt-dome cap rocks, Gulf Coast, U.S.A. Trans Inst Min Metall Sect B 95:B6–B16
Land LS (1980) The isotopic chemistry and trace element geochemistry of dolomite: the state of the art. SEPM 28:87–110
Lange S, Chaudhuri S, Clauer N (1983) Strontium isotopic evidence for the origin of barites and sulfides from the Mississippi Valley-type ore deposits in southeast Missouri. Econ Geol 78(6):1255–1261
Laridhi-Ouazaa N (1994) Étude minéralogique et géochimique des episodes magmatiques mesozoiques et miocènes de la Tunisie, Thesis. University of Tunis El Manar, Tunisia
Leach DL, Sangster DF (1993) Mississippi Valley-type lead-zinc deposits. In: Kirkham RV, Sinclair WD, Thorp RI, Duke JM (eds) Mineral Deposit Modelling Geol Ass Canada Spec Paper 40: 289–314
Leach DL, Sangster DF, Kelly KD, Large RR, Carven G, Allen CR, Gutzmen J, Walters S (2005) Sediment- hosted lead-zinc deposits: a global perspective. In: Hedenquist JW, Thompson JFH, Goldfarb RJ, Richards JP (eds) Econ Geol 100th Anniv Vol, pp 561–607
Leach DL, Taylor RD, Fey DL, Diehl SF, Saltus RW (2010) A deposit model for Mississippi Valley-type lead-zinc ores. In: Mineral deposit models for resource assessment. http://www.usgs.gov/ pubprod.
Leach DL, Song YC, Hou ZQ, Yang TA, Xue CD (2013)The giant Jinding Zn-Pb deposit: Ore formation in an evaporitedome, Lanping Basin, Yunan, China. In: Mineral deposit research for a high-tech world. Jonsson E et al. (eds) Proceedings of the 12th Biennial SGA Meeting (Uppsala, Sweden) 3:1424–1427
Light MPR, Posey HH, Kyle JR, Price PE (1987) Model for the origins of geopressured brines, hydrocarbons, cap rocks and metallic mineral deposits: Gulf Coast, U.S.A. In: Lerche L, O’Brien J (eds) Dynamical Geology of Salt and Related Structures, Academic Press, pp. 497–542
M’Rabet A (1987) Stratigraphie, sédimentation et diagenèse carbonatée des séries du Crétacé inférieur de la Tunisie centrale. Ann Mines Géol Tunis 30:412
Maameri K, Daadouch Imed (1986) Etude des indices de pétrole en surface dans la Tunisie des avant nappes. Mémoire de Fin d’Etude Ingénieur, Faculté des Sciences de Tunis, Université Tunis el Manar
Machel HG, Krouse HR, Sassen R (1995) Products and distinguishing criteria of bacterial and thermochemical sulfate reduction. Appl Geochem 10:373–389
Macquar JC, Rouvier H, Thibiéroz J (1990) Les minéralisations Zn, Pb, Fe, Ba, F péri-cévenoles: cadre structuro-sédimentaire et distribution spatio-temporelle. Doc BRGM Orléans 183:143–158
Marie J, Trouve P, Desforges G, Dufaure P (1984) Nouveaux éléments de paléogéographie du Crétacé de Tunisie. Notes Mém TOTAL-CFP Paris 19:37
Martinez C, Truillet R (1987) Evolution structurale et paléogeographie de la Tunisie. Mem Soc Geol It 38:35–45
Masse JP, Chikhi-Aouimer F (1982) La plate-forme carbonatée de l’Ouenza (Sud canstantinois-Algerie) Organisation et dynamique Durant l’Aptian supérieur. Géol Mediterr IX(3):259–267
Matlock JF, Misra KC (1993) Sphalerite-bearing detrital ‘sand’ bodies in Mississippi Valley-type zinc deposits, Mascot-Jefferson City district, Tennessee Implications for the age of mineralization. Mineral Deposita 28:344–353
Mc Limans RK (1975) Systematic fluid inclusion and sulfide isotope studies of the Upper Mississippi Valley Pb-Zn deposits. Econ Geol 70(7):1324, Abstract
Mc Limans RK (1977) Geological, fluid inclusion, and stable isotope studies of the Upper Mississippi Valley zinc-lead district, southwest Wisconsin: Ph.D. thesis, Pennsylvania State University
McCrea JM (1950) On the isotopic chemistry of carbonates and a paleotemperature scale. J Chem Phys 18:849–857
Mejri F, Burollet PF, Ben Ferjani A (2006) Petroleum Geology of Tunisia, A Renewed Synthesis.Entreprise Tunisienne des Activités Pétrolières, Tunis. Memoir No. 22pp 233
Nesbitt BE, Muehlenbachs K (1994) Paleohydrogeology of the Canadian Rockies and origins of basinal brines, Pb-Zn deposits and dolomitization in the Western Canada sedimentary basin. Geology 22:243–246
Orgeval JJ (1994) Peridiapiric metal concentrations: example of the Bou Grine deposit (Tunisian Atlas). In: Fontboté L, Boni M (eds) Sediment-hosted Zn-Pb ores. Society for Geology Applied to Mineral Deposits Spec Publ 10:354–389
Paytan A, Kastner M, Campbell D, Thiemens MH (1998) Sulfur isotopic composition of Cenozoic seawater sulfate. Science 282:1459–1462
Perthuisot V (1978) Dynamique et pétrogenèse des extrusions triasiques en Tunisie septentrionale. Thesis, École Normale Sup Paris
Perthuisot V (1981) Diapirism in northern Tunisia. J Struct Geol 3:231–235
Perthuisot V, Rouvier H (1992) Les diapirs d’Algerie et de Tunisie : des appareils varies, resultats d’une evolution structurale et petrogenetique complexe. Bull Soc Géol Fr 163(6):751–760
Perthuisot V, Rouvier H, Smati A (1998) Style et importance des déformations anté-vraconiennes dans le Maghreb oriental: exemple du diapir du Jebel Slata. Bull Soc Géol Fr 8:389–398
Philip H, Andrieux J, Dlala M, Chihi L, Ben Ayed N (1986) Evolution tectonique mio-plio-quaternaire du Fossé de Kasserine (Tunisie centrale); implications sur l’évolution géodynamique récente de la Tunisie. Bull Soc Géol Fr 2(8):559–568, No.5-6
Plumlee GS, Leach DL, Hofstra AH, Landis GP, Rowan EL, Viets JG (1994) Chemical reaction path modeling of ore deposition in Mississippi Valley-type Pb-Zn deposits of the Ozark region, US Midcontinent. Econ Geol 89:1361–1383
Posey HH, Kyle JR (1988) Fluid-rock interactions in the salt dome environment: an introduction and review. Chem Geol 74:1–24
Posey HH, Kyle JR, Agee WN (1994) Relations between diapiric salt structures and metal concentrations, Gulf Coast sedimentary basin, Southern North America. In: Fontboté L, Boni M (eds) Sediment hosted Zn-Pb ores. Society for Geology Applied to Mineral Deposits Spec Publ 10:140–164
Price PE, Kyle JR (1983) Metallic sulphide deposits in Gulf Coast salt-dome caprocks. Gulf Coast Assoc Geol Soc Trans 33:189–193
Roedder E (1963) Studies of fluid inclusions, II: freezing data and their interpretation. Econ Geol 58:167–211
Roedder E (1984) Fluid inclusions. Rev Mineral Am Mineral Soc 12:646
Rouvier H (1977) Géologie de l’Extrême-Nord tunisien: tectonique et paléogéographie superposées à l’extrémité de la chaîne nord-maghrébine. Ann Mines Géol Tunis 29:427
Rouvier R, Perthuisot V, Mansouri A (1985) Pb-Zn deposits and salt bearing diapirs in southern Europe and North Africa. Econ Geol 80:666–687
Saïdi M, Belayouni H (1994)Étude géologique et géochimique des roches mères albo-vraconienne dans le domaine de la Tunisie centro-septentrional. Proceeding of the 4th Petroleum Exploration Conference 7:91–116, Tunis
Sainfeld P (1956) The lead-zinc-bearing deposits of Tunisia. Econ Geol 51:150–177
Salmi-Laouar S (2004) Contribution à l’étude géologique et géochimie des isotopes stables (S,0, C) des minéralisation polymétallique (Zn, Pb, F, Ba, Fe) de la zone des diapirs du nord de Tébessa, NE Algerien) Thèse de Doctorat d’Etat. Université de Annaba, Algerie
Salmi-Laouar S, Laouar R, Boyce AJ, Boutaleb A, Zerdazi A, Arouch YE (2004) Rapports istotopiques du soufre, de l’oxygène et du carbone dans le massif de Bou Jaber, NE algerien: Origine des minéralisations à Pb-Zn-Ba et sources des fluides. Serv Géol Algérie 15:3–25
Salmi-Laouar S, Laouar R, Boyce AJ, Boutaleb A, Lamouroux C (2007) Premières données isotopiques sur la mer triasique dans l’Atlas Saharien Oriental (Algérie). Serv Géol Algérie 18:315–323
Sass-Gustkiewics M (1996) Internal sediments as a key to understanding the hydrothermal karst origin of the Upper Silesia Zn-Pb ore deposits. Econ Geol Spec Publ 4:171–181
Schmidt SC (1999) Re-activation of the Bougrine Mine, Tunisia. 101st Ann Gen Meeting, Can Inst Min Metal Petro, Techn Progr CD-ROM : Major Canadian Overseas Project Paper 1:1–9
Sheppard SMF, Charef A, Bouhlel S (1996) Diapirs and Zn-Pb mineralizations: a general model based on Tunisian (N. Africa) and Gulf Coast (U.S.A.) deposits. Econ Geol Spec Publ 4:230–243
Skaggs S, Norman N, Garrison E, Coleman D, Bouhlel S (2012) Local mining or lead importation in the Roman province of Africa Proconsularis? Lead isotope analysis of curse tablets from Roman Carthage, Tunisia. J Archaeol Sci 39(4):970–983
Soua M (2009) Structural context of the paleogeography of the Cenomanian-Turonian anoxic event in the eastern Atlas basins of the Maghreb. CR Geosci 341(12):1029–1037
Spangenberg J, Fontboté L, Sharp ZD, Hunziker J (1996) Carbon and oxygen isotope study of hydrothermal carbonates in the zinc-lead deposits of the San Vicente district, central Peru. Chem Geol 133:289–315
Tlig S, Erraioui L, Ben Aissa L, Aluoani R, Tagorti MA (1991) Tectogenèses alpine et atlasique : deux événements distincts dans l’histoire géologique de la Tunisie. Corrélation avec les événements clés en Méditerranée. Comptes Rendus de l’Académ de Sci Paris 312(Série II):295–301
Tlig S, Sahli H, Er-Raioui L, Alouani R, Mzoughi M (2010) Depositional environment controls on petroleum potential of the Eocene in the North of Tunisia. J Pet Sci Eng 71(3–4):91–105
Turchyn AV, Schrag DP (2004) Oxygen isotope constraints on the sulfur cycle over the past 10 million years. Science 303:2004–2007
Turki MM, Delteil J, Truillet R, Yaich C (1988) Les inversions tectoniques de la Tunisie centro-septentrionale. Bull Soc Géol France (8) IV 3:399–406
Ulrich MR, Bodnar RJ (1988) Systematic stretching of fluid inclusions. II. Barite at 1 atmosphere confining pressure. Econ Geol 83:1037–1046
Veizer J, Compston W (1974) 87Sr/86Sr composition of seawater during Phanerozoic. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 38:1461–1484
Veizer J, Hoefs J (1976) The nature of O-18 /O-16 and C-13 /C-12 secular trends in sedimentary carbonate rocks. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 40(11):1387–1395
Vially R, Letouzey J, Bernard F, Haddadi N, Deforges G, Askri H, Boudjema A (1994) Basin inversion along the North African margin: the Sahara Atlas (Algeria). In: Roure F (ed) PeriTethyan platforms. Technip, Paris, pp 79–118
Vila JM, Charrière A (1993) Découverte d’Albien calcaire et de Trias resédimenté au Djebel Bou Jaber (partie ouest, Algérie); corrélations avec les forages et conséquences sur l’organisation du Crétacé inférieur des confins algéro-tunisiens. C R Acad Sci 316(2):243–249
Vila J-M, Ben Youssef M, Bouhlel S, Ghanmi M, Kassaâ S, Miaadi F (1998) Tectonique en radeaux au toit d’un glacier de sel sous-marin albien de Tunisie du Nord-Ouest : exemple du secteur minier de Gueurn Halfaya. C R Acad Sci Paris 327:563–570
Vila JM, Kassaâ S, Bouhlel S, Ben Youssef M, Dali T, Ghanmi M (1999) Inversion tectonique de structures halocinétiques et localisation des minéralisations (Zn, Sr): émergence au Jebel Bou Khil (Nord-Ouest tunisien) d’un chevauchement entre un domaine nord à « glaciers de sel » sous-marins et un domaine sud à « diapirs typiques ». Bull Soc Géol Fr 170(2):161–172
Xue C, Zeng R, Liu S, Chi G, Qing H, Chen Y, Yang J, Wang D (2007) Geologic, fluid inclusion and isotopic characteristics of the Jinding Zn–Pb deposit, western Yunnan, South China: a review. Ore Geol Rev 31:337–359
Yardley BWD (2005) 100th Anniversary Special Paper: metal concentrations in crustal fluids and their relationship to ore formation. Econ Geol 100:613–632
Zartman RE, Doe BR (1981) Plumbotectonics—the model. Tectonophysics 75:135–162
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Fethi M’Barek, director of the Bou Jaber mine, for his assistance to allow underground sampling. We wish also to thank Cyndi Kester, for assistance during the C, O, and S isotope analysis. The authors thank the following individuals for helpful discussions on the geology and halokinesis of the Tunisian Salt Diapir Province: Habib Belayouni, Saïd Tlig; Ali Zaier from the University of Tunis El Manar; Ahmed Braham from the Office National des Mines Tunisia and S.M.F. Sheppard from CRPG Nancy and ENS Lyon. Discussions with Pr. Habib Belayouni on the organic matter and mineralization relationships were very helpful. Karen Kelley from the USGS Denver and Bernd Lehman from Technical University of Clausthal are thanked for their constructive discussion and comments on the initial manuscript. Financial aid was provided to Salah Bouhlel by a research grant from the CIES/USA, Fulbright program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial handling: B. Lehmann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouhlel, S., Leach, D.L., Johnson, C.A. et al. A salt diapir-related Mississippi Valley-type deposit: the Bou Jaber Pb-Zn-Ba-F deposit, Tunisia: fluid inclusion and isotope study. Miner Deposita 51, 749–780 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-015-0634-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-015-0634-8