Abstract
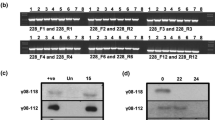
Rpg1 is a stem rust resistance gene that has protected barley from severe losses for over 60 years in the US and Canada. It confers resistance to many, but not all, pathotypes of the stem rust fungus Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici. A fast neutron induced deletion mutant, showing susceptibility to stem rust pathotype Pgt-MCC, was identified in barley cv. Morex, which carries Rpg1. Genetic and Rpg1 mRNA and protein expression level analyses showed that the mutation was a suppressor of Rpg1 and was designated Rpr1 (Required for P. graminis resistance). Genome-wide expression profiling, using the Affymetrix Barley1 GeneChip containing ∼22,840 probe sets, was conducted with Morex and the rpr1 mutant. Of the genes represented on the Barley1 microarray, 20 were up-regulated and 33 were down-regulated by greater than twofold in the mutant, while the Rpg1 mRNA level remained constant. Among the highly down-regulated genes (greater than fourfold), genomic PCR, RT-PCR and Southern analyses identified that three genes (Contig4901_s_at, HU03D17U_s_at, and Contig7061_s_at), were deleted in the rpr1 mutant. These three genes mapped to chromosome 4(4H) bin 5 and co-segregated with the rpr1-mediated susceptible phenotype. The loss of resistance was presumed to be due to a mutation in one or more of these genes. However, the possibility exists that there are other genes within the deletions, which are not represented on the Barley1 GeneChip. The Rpr1 gene was not required for Rpg5- and rpg4-mediated stem rust resistance, indicating that it shows specificity to the Rpg1-mediated resistance pathway.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts MG, te Lintel Hekkert B, Holub EB, Beynon JL, Stiekema WJ, Pereira A (1998) Identification of R-gene homologous DNA fragments genetically linked to disease resistance loci in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 11:251–258
Bittner-Eddy PD, Beynon JL (2001) The Arabidopsis downy mildew resistance gene, RPP13-Nd, functions independently of NDR1 and EDS1 and does not require the accumulation of salicylic acid. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 14:416–421
Brueggeman R, Rostoks N, Kudrna D, Kilian A, Han F, Chen J, Druka A, Steffenson B, Kleinhofs A (2002) The barley stem rust-resistance gene Rpg1 is a novel disease-resistance gene with homology to receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9328–9333
Century KS, Holub EB, Staskawicz BJ (1995) NDR1, a locus of Arabidopsis thaliana that is required for disease resistance to both a bacterial and a fungal pathogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6597–6601
Close TJ, Wanamaker SI, Caldo RA, Turner SM, Ashlock DA, Dickerson JA, Wing RA, Muehlbauer GJ, Kleinhofs A, Wise RP (2004) A new resource for cereal genomics: 22K Barley1 GeneChip comes of age. Plant Physiol 134:960–968
Collins NC, Lahaye T, Peterhansel C, Freialdenhoven A, Corbitt M, Schulze-Lefert P (2001) Sequence haplotypes revealed by sequence-tagged site fine mapping of the Ror1 gene in the centromeric region of barley chromosome 1H. Plant Physiol 125:1236–1247
Collins NC, Thordal-Christensen H, Lipka V, Bau S, Kombrink E, Qiu JL, Huckelhoven R, Stein M, Freialdenhoven A, Somerville SC, Schulze-Lefert P (2003) SNARE-protein-mediated disease resistance at the plant cell wall. Nature 425:973–977
Dixon MS, Golstein C, Thomas CM, van Der Biezen EA, Jones JD (2000) Genetic complexity of pathogen perception by plants: the example of Rcr3, a tomato gene required specifically by Cf-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:8807–8814
Feys BJ, Moisan LJ, Newman MA, Parker JE (2001) Direct interaction between the Arabidopsis disease resistance signaling proteins, EDS1 and PAD4. Embo J 20:5400–5411
Freialdenhoven A, Peterhansel C, Kurth J, Kreuzaler F, Schulze-Lefert P (1996) Identification of genes required for the function of non-race-specific mlo resistance to powdery mildew in barley. Plant Cell 8:5–14
Gadjieva R, Axelsson E, Olsson U, Vallon-Christersson J, Hansson M (2004) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in barley mutants allows the cloning of mutated genes by a microarray approach. Plant Physiol Biochem 42:681–685
Horvath H, Rostoks N, Brueggeman R, Steffenson B, von Wettstein D, Kleinhofs A (2003) Genetically engineered stem rust resistance in barley using the Rpg1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:364–369
Jorgensen JH (1988) Genetic analysis of barley mutants with modifications of powdery mildew resistance gene Mla12. Genome 30:129–132
Jorgensen JH (1996) Effect of three suppressors on the expression of powdery mildew resistance gene in barley. Genome 39:492–498
Kleinhofs A, Graner A (2001) An integrated map of the barley genome. In: Phillips RL, Vasil IK (eds) DNA-based markers in plants, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 187–199
Kleinhofs A, Kilian A, Saghai Maroof MA, Biyashev RM, Hayes P, Chen FQ, Lapitan N, Fenwick A, Blake TK, Kanazin V, Ananiev E, Dahleen L, Kudrna D, Bollinger J, Knapp SJ, Liu B, Sorrells M, Heun M, Franckowiak JD, Hoffman D, Skadsen R, Steffenson B (1993) A molecular, isozyme and morphological map of the barley (Hordeum vulgare) genome. Theor Appl Genet 86:705–712
Kleinhofs A, Owais WM, Nilan RA (1978) Azide. Mutat Res 55:165–195
Li X, Zhang Y (2002) Reverse genetics by fast neutron mutagenesis in higher plants. Funct Integr Genomics 2:254–258
Li X, Zhang Y (2005) Novel reverse genetics tools in plant functional genomics. In: Leister D (eds) Plant functional genomics. Food Products Press, pp 37–53
Li X, Song Y, Century K, Straight S, Ronald P, Dong X, Lassner M, Zhang Y (2001a) A fast neutron deletion mutagenesis-based reverse genetics system for plants. Plant J 27:235–242
Li Z, Jayasankar S, Gray DJ (2001b) An improved enzyme linked immunosorbent assay protocol for the detection of small lytic peptides in transgenic grapevines (Vitis vinifera). Plant Mol Biol Rep 19:341–351
McDowell JM, Cuzick A, Can C, Beynon J, Dangl JL, Holub EB (2000) Downy mildew (Peronospora parasitica) resistance genes in Arabidopsis vary in functional requirements for NDR1, EDS1, NPR1 and salicylic acid accumulation. Plant J 22:523–529
Mitra RM, Gleason CA, Edwards A, Hadfield J, Downie JA, Oldroyd GE, Long SR (2004) A Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase required for symbiotic nodule development: gene identification by transcript-based cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:4701–4705
Muskett PR, Kahn K, Austin MJ, Moisan LJ, Sadanandom A, Shirasu K, Jones JD, Parker JE (2002) Arabidopsis RAR1 exerts rate-limiting control of R gene-mediated defenses against multiple pathogens. Plant Cell 14:979–992
Nirmala J, Brueggeman R, Maier C, Clay C, Rostoks N, Kannangara CG, von Wettstein D, Steffenson B, Kleinhofs A (2006) Sub-cellular localization and functions of the barley stem rust resistance receptor-like serine/threonine-specific protein kinase Rpg1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:7518–7523
Rostoks N, Steffenson BJ, Kleinhofs A (2004) Structure and expression of the barley stem rust resistance gene Rpg1 messenger RNA. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 64:91–101
Shen QH, Zhou F, Bieri S, Haizel T, Shirasu K, Schulze-Lefert P (2003) Recognition specificity and RAR1/SGT1 dependence in barley Mla disease resistance genes to the powdery mildew fungus. Plant Cell 15:732–744
Shirasu K, Lahaye T, Tan MW, Zhou F, Azevedo C, Schulze-Lefert P (1999) A novel class of eukaryotic zinc-binding proteins is required for disease resistance signaling in barley and development in C. elegans. Cell 99:355–366
Steffenson BJ (1992) Analysis of durable resistance to stem rust in barley. Euphytica 63:153–167
Steffenson BJ, Miller JD, Jin Y (1993) Detection of the stem rust resistance gene Rpg1 in barley seedlings. Plant Dis 77:626–629
Sun Y, Steffenson BJ (2005) Reaction of barley seedlings with different stem rust resistance genes to Puccinia graminis f. sp. tritici and P. g. f. sp. secalis. Can J Plant Pathol 27:80–89
Tornero P, Merritt P, Sadanandom A, Shirasu K, Innes RW, Dangl JL (2002) RAR1 and NDR1 contribute quantitatively to disease resistance in Arabidopsis, and their relative contributions are dependent on the R gene assayed. Plant Cell 14:1005–1015
Torp J, Jorgensen JH (1986) Modification of powdery mildew resistance gene Ml-a12 by induced mutation. Can J Genet Cytol 28:725–731
Yu Y, Tomkins R, Waugh R, Frisch DA, Kudrna D, Kleinhofs A, Brueggeman R, Muehlbauer GJ, Wise RP, Wing RA (2000) A bacterial artificial chromosome library for barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) and the identification of clones containing putative resistance genes. Theor Appl Genet 101:1093–1099
Zakhrabekova S, Kannangara CG, von Wettstein D, Hansson M (2002) A microarray approach for identifying mutated genes. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:189–197
Acknowledgments
This is Scientific Paper No. 0301-06 from the College of Agricultural, Human, and Natural Sciences Research Center, Washington State University, Pullman, WA 99164, Project 0196. Research was supported by USDA-NRI grant No. 2004-35301-14635 and the US Barley Genome Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Kilian
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Fetch, T., Nirmala, J. et al. Rpr1, a gene required for Rpg1-dependent resistance to stem rust in barley. Theor Appl Genet 113, 847–855 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0342-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0342-y