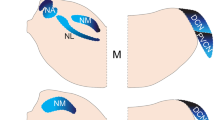
Abstract
Development and evolution of auditory hindbrain nuclei are two major unsolved issues in hearing research. Recent characterization of transgenic mice identified the rhombomeric origins of mammalian auditory nuclei and unraveled genes involved in their formation. Here, we provide an overview on these data by assembling them into rhombomere-specific gene regulatory networks (GRNs), as they underlie developmental and evolutionary processes. To explore evolutionary mechanisms, we compare the GRNs operating in the mammalian auditory hindbrain with data available from the inner ear and other vertebrate groups. Finally, we propose that the availability of genomic sequences from all major vertebrate taxa and novel genetic techniques for non-model organisms provide an unprecedented opportunity to investigate development and evolution of the auditory hindbrain by comparative molecular approaches. The dissection of the molecular mechanisms leading to auditory structures will also provide an important framework for auditory processing disorders, a clinical problem difficult to tackle so far. These data will, therefore, foster basic and clinical hearing research alike.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A–P:
-
Anterior–posterior
- AVCN:
-
Anterior ventral cochlear nucleus
- BMP:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein
- CNC:
-
Cochlear nucleus complex
- DCN:
-
Dorsal cochlear nucleus
- E:
-
Embryonic
- LSO:
-
Lateral superior olive
- MNTB:
-
Medial nucleus of the trapezoid body
- NA:
-
Nucleus angularis
- NL:
-
Nucleus laminaris
- NLL:
-
Nucleus of the lateral lemniscus
- NM:
-
Nucleus magnocellularis
- P:
-
Postnatal
- PVCN:
-
Posterior ventral cochlear nucleus
- r:
-
Rhombomere
- RA:
-
Retinoic acid
- SOC:
-
Superior olivary complex
- TF:
-
Transcription factor
References
Abouheif E (1997) Developmental genetics and homology: a hierarchical approach. Trends Ecol Evol 12:405–408
Abouheif E (1999) Establishing homology criteria for regulatory gene networks: prospects and challenges. Novartis Found Symp 222:207–221
Alasti F, Sadeghi A, Sanati MH, Farhadi M, Stollar E, Somers T, Van CG (2008) A mutation in HOXA2 is responsible for autosomal-recessive microtia in an Iranian family. Am J Hum Genet 82:982–991
Alexander T, Nolte C, Krumlauf R (2009) Hox genes and segmentation of the hindbrain and axial skeleton. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 25:431–456
Alonso A, Merchán P, Sandoval JE, Sánchez-Arrones L, Garcia-Cazorla A, Artuch R, Ferrán JL, Martínez-de-la-Torre M, Puelles L (2013) Development of the serotonergic cells in murine raphe nuclei and their relations with rhombomeric domains. Brain Struct Funct 218:1229–1277
Amores A, Force A, Yan YL, Joly L, Amemiya C, Fritz A, Ho RK, Langeland J, Prince V, Wang YL, Westerfield M, Ekker M, Postlethwait JH (1998) Zebrafish hox clusters and vertebrate genome evolution. Science 282:1711–1714
Appler JM, Lu CC, Druckenbrod NR, Yu W, Koundakjian EJ, Goodrich LV (2013) Gata3 is a critical regulator of cochlear wiring. J Neurosci 33:3679–3691
Aragon F, Pujades C (2009) FGF signaling controls caudal hindbrain specification through Ras-ERK1/2 pathway. BMC Dev Biol 9:61
Aragon F, Vazquez-Echeverria C, Ulloa E, Reber M, Cereghini S, Alsina B, Giraldez F, Pujades C (2005) vHnf1 regulates specification of caudal rhombomere identity in the chick hindbrain. Dev Dyn 234:567–576
Bami M, Episkopou V, Gavalas A, Gouti M (2011) Directed neural differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells is a sensitive system for the identification of novel Hox gene effectors. PLoS One 6:e20197
Barrow JR, Stadler HS, Capecchi MR (2000) Roles of Hoxa1 and Hoxa2 in patterning the early hindbrain of the mouse. Development 127:933–944
Bell D, Streit A, Gorospe I, Varela-Nieto I, Alsina B, Giraldez F (2008) Spatial and temporal segregation of auditory and vestibular neurons in the otic placode. Dev Biol 322:109–120
Bermingham NA, Hassan BA, Price SD, Vollrath MA, Ben Arie N, Eatock RA, Bellen HJ, Lysakowski A, Zoghbi HY (1999) Math1: an essential gene for the generation of inner ear hair cells. Science 284:1837–1841
Bermingham NA, Hassan BA, Wang VY, Fernandez M, Banfi S, Bellen HJ, Fritzsch B, Zoghbi HY (2001) Proprioceptor pathway development is dependent on Math1. Neuron 30:411–422
Birgbauer E, Fraser SE (1994) Violation of cell lineage restriction compartments in the chick hindbrain. Development 120:1347–1356
Boord RL, McCormick CA (1984) Central lateral line and auditory pathways: a phylogenetic perspective. Am Zool:765–774
Borst JGG, van Soria Hoeve (2012) The calyx of held synapse: from model synapse to auditory relay. Annu Rev Physiol 74:199–224
Bouchoucha YX, Reingruber J, Labalette C, Wassef MA, Thierion E, Desmarquet-Trin Dinh C, Holcman D, Gilardi-Hebenstreit P, Charnay P (2013) Dissection of a Krox20 positive feedback loop driving cell fate choices in hindbrain patterning. Mol Syst Biol 9:690
Brainard MS, Knudsen EI (1993) Experience-dependent plasticity in the inferior colliculus: a site for visual calibration of the neural representation of auditory space in the barn owl. J Neurosci 13:4589–4608
Bruce LL, Kingsley J, Nichols DH, Fritzsch B (1997) The development of vestibulocochlear efferents and cochlear afferents in mice. Int J Dev Neurosci 15:671–692
Buecker C, Wysocka J (2012) Enhancers as information integration hubs in development: lessons from genomics. Trends Genet 28:276–284
Cambronero F, Puelles L (2000) Rostrocaudal nuclear relationships in the avian medulla oblongata: a fate map with quail chick chimeras. J Comp Neurol 427:522–545
Carr CE, Edds-Walton PL (2008) Vertebrate auditory pathways. In: Dallos P, Oertel D (eds) The senses: a comprehensive reference, vol 3. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 499–523
Carr CE, Soares D (2002) Evolutionary convergence and shared computational principles in the auditory system. Brain Behav Evol 59:294–311
Carr CE, Soares D, Parameshwaran S, Perney T (2001) Evolution and development of time coding systems. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:727–733
Casseday JH, Fremouw T, Covey E (2002) The Inferior colliculus: a hub for the central auditory system. In: Oertel D, Fay RR, Popper AA (eds) Springer handbook of auditory research: integrative functions in the mammalian auditory pathway. Springer, New York, pp 238–318
Chen J, Ruley HE (1998) An enhancer element in the EphA2 (Eck) gene sufficient for rhombomere-specific expression is activated by HOXA1 and HOXB1 homeobox proteins. J Biol Chem 273:24670–24675
Chermak GD, Musiek FE (1997) Central auditory processing disorders: new perspectives. Singular Publishing Group, San Diego
Chisaka O, Musci TS, Capecchi MR (1992) Developmental defects of the ear, cranial nerves and hindbrain resulting from targeted disruption of the mouse homeobox gene Hox-1.6. Nature 355:516–520
Chomette D, Frain M, Cereghini S, Charnay P, Ghislain J (2006) Krox20 hindbrain cis-regulatory landscape: interplay between multiple long-range initiation and autoregulatory elements. Development 133:1253–1262
Christensen-Dalsgaard J, Carr CE (2008) Evolution of a sensory novelty: tympanic ears and the associated neural processing. Brain Res Bull 75:365–370
Clack JA (1997) The Evolution of tetrapod ears and the fossil record. Brain Behav Evol 50(4):198–212
Clack JA (2002) Patterns and processes in the early evolution of the tetrapod ear. J Neurobiol 53(2):251–264. doi:10.1002/neu.10129
Clack JA, Allin E (2004) The evolution of single- and multiple ossicle ears in fishes and tetrapods. In: Manley GA, Popper AN, Fay RR (eds) Evolution of the vertebrate auditory system. Springer, New York, pp 128–163
Coffinier C, Thepot D, Babinet C, Yaniv M, Barra J (1999) Essential role for the homeoprotein vHNF1/HNF1beta in visceral endoderm differentiation. Development 126:4785–4794
Cordes SP, Barsh GS (1994) The mouse segmentation gene kr encodes a novel basic domain-leucine zipper transcription factor. Cell 79:1025–1034
Cramer KS, Fraser SE, Rubel EW (2000) Embryonic origins of auditory brain-stem nuclei in the chick hindbrain. Dev Biol 224:138–151
Davenne M, Maconochie MK, Neun R, Pattyn A, Chambon P, Krumlauf R, Rijli FM (1999) Hoxa2 and Hoxb2 control dorsoventral patterns of neuronal development in the rostral hindbrain. Neuron 22:677–691
Davidson EH (2006) The regulatory genome. Gene regulatory networks in development and evolution. Academic Press, Amsterdam
Davidson EH, Erwin DH (2006) Gene regulatory networks and the evolution of animal body plans. Science 311:796–800
Davis A, Scemama J, Stellwag EJ (2008) Japanese medaka Hox paralog group 2: insights into the evolution of Hox PG2 gene composition and expression in the Osteichthyes. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol 310:623–641
Dawes R, Dawson I, Falciani F, Tear G, Akam M (1994) Dax, a locust Hox gene related to fushi-tarazu but showing no pair-rule expression. Development 120:1561–1572
Dawid IB, Chitnis AB (2001) Lim homeobox genes and the CNS: a close relationship. Neuron 30:301–303
Deol MS (1964) The abnormalities of the inner ear in kreisler mice. J Embryol Exp Morphol 12:475–490
Derobert Y, Baratte B, Lepage M, Mazan S (2002) Pax6 expression patterns in Lampetra fluviatilis and Scyliorhinus canicula embryos suggest highly conserved roles in the early regionalization of the vertebrate brain. Brain Res Bull 57:277–280
Desmazieres A, Charnay P, Gilardi-Hebenstreit P (2009) Krox20 controls the transcription of its various targets in the developing hindbrain according to multiple modes. J Biol Chem 284:10831–10840
Di Bonito M, Narita Y, Avallone B, Sequino L, Mancuso M, Andolfi G, Franzè AM, Puelles L, Rijli FM, Studer M (2013) Assembly of the auditory circuitry by a Hox genetic network in the mouse brainstem. PLoS Genet 9:e1003249
Distel M, Wullimann MF, Koster RW (2009) Optimized Gal4 genetics for permanent gene expression mapping in zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:13365–13370
Dong D, Ruuska SE, Levinthal DJ, Noy N (1999) Distinct roles for cellular retinoic acid-binding proteins I and II in regulating signaling by retinoic acid. J Biol Chem 274:23695–23698
Duncan JS, Fritzsch B (2013) Continued expression of GATA3 is necessary for cochlear neurosensory development. PLoS One 8:e62046
Dupe V, Lumsden A (2001) Hindbrain patterning involves graded responses to retinoic acid signalling. Development 128:2199–2208
Ehmann H, Hartwich H, Salzig C, Hartmann N, Clément-Ziza M, Ushakov K, Avraham KB, Bininda-Emonds, Olaf RP, Hartmann AK, Lang P, Friauf E, Nothwang HG (2013) Time-dependent gene expression analysis of the developing superior olivary complex. J Biol Chem 288:25865–25879
Englitz B, Tolnai S, Typlt M, Jost J, Rubsamen R (2009) Reliability of synaptic transmission at the synapses of Held in vivo under acoustic stimulation. PLoS One 4:e7014
Ettensohn CA (2013) Encoding anatomy: developmental gene regulatory networks and morphogenesis. Genesis 51:383–409
Farago AF, Awatramani RB, Dymecki SM (2006) Assembly of the brainstem cochlear nuclear complex is revealed by intersectional and subtractive genetic fate maps. Neuron 50:205–218
Frasch M, Chen X, Lufkin T (1995) Evolutionary-conserved enhancers direct region-specific expression of the murine Hoxa-1 and Hoxa-2 loci in both mice and Drosophila. Development 121:957–974
Fraser S, Keynes R, Lumsden A (1990) Segmentation in the chick embryo hindbrain is defined by cell lineage restrictions. Nature 344:431–435
Fritzsch B (1988) The amphibian octavo-lateralis system and its regressive and progressive evolution. Acta Biol Hung 39:305–322
Fritzsch B, Beisel KW, Pauley S, Soukup G (2007) Molecular evolution of the vertebrate mechanosensory cell and ear. Int J Dev Biol 51:663–678
Fritzsch B, Pauley S, Feng F, Matei V, Nichols DH (2006) The molecular and developmental basis of the evolution of the vertebrate auditory system. Int J Comp Psychol 19:1–25
Fu Y, Tvrdik P, Makki N, Paxinos G, Watson C (2011) Precerebellar cell groups in the hindbrain of the mouse defined by retrograde tracing and correlated with cumulative Wnt1-cre genetic labeling. Cerebellum 10:570–584
Gaj T, Gersbach CA, Barbas (2013) ZFN, TALEN, and CRISPR/Cas-based methods for genome engineering. Trends Biotechnol 31:397–405
Garcia-Gutierrez P, Juarez-Vicente F, Gallardo-Chamizo F, Charnay P, Garcia-Dominguez M (2011) The transcription factor Krox20 is an E3 ligase that sumoylates its Nab coregulators. EMBO Rep 12:1018–1023
Gaufo GO, Thomas KR, Capecchi MR (2003) Hox3 genes coordinate mechanisms of genetic suppression and activation in the generation of branchial and somatic motoneurons. Development 130:5191–5201
Gavalas A (2002) ArRAnging the hindbrain. Trends Neurosci 25:61–64
Gavalas A, Davenne M, Lumsden A, Chambon P, Rijli FM (1997) Role of Hoxa-2 in axon pathfinding and rostral hindbrain patterning. Development 124(19):3693–3702
Gavalas A, Ruhrberg C, Livet J, Henderson CE, Krumlauf R (2003) Neuronal defects in the hindbrain of Hoxa1, Hoxb1 and Hoxb2 mutants reflect regulatory interactions among these Hox genes. Development 130:5663–5679
Geiger JRP, Melcher T, Koh DS, Sakmann B, Seeburg PH, Jonas P, Monyer H (1995) Relative abundance of subunit mRNAs determines gating and Ca2+ permeability of AMPA receptors in principal neurons and interneurons in rat CNS. Neuron 15:193–204
von Gersdorff H, Borst JGG (2002) Short-term plasticity at the calyx of Held. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:53–64
Glover JC, Renaud J, Rijli FM (2006) Retinoic acid and hindbrain patterning. J Neurobiol 66:705–725
Goddard JM, Rossel M, Manley NR, Capecchi MR (1996) Mice with targeted disruption of Hoxb-1 fail to form the motor nucleus of the VIIth nerve. Development 122:3217–3228
Golding NL (2012) Neuronal Response Properties and Voltage-Gated Ion Channels in the Auditory System. In: Trussell LO, Popper AN, Fay AN (eds) Synaptic Mechanisms in the Auditory System. Springer, New York, pp 7–41
Gould A, Itasaki N, Krumlauf R (1998) Initiation of rhombomeric Hoxb4 expression requires induction by somites and a retinoid pathway. Neuron 21:39–51
Grothe B (2000) The evolution of temporal processing in the medial superior olive, an auditory brainstem structure. Prog Neurobiol 61:581–610
Grothe B, Carr CE, Casseday JH, Fritzsch B, Köppl C (2004) The Evolution of Central Pathways and Their Neural Processing Patterns. In: Manley GA, Popper AN, Fay RR (eds) Springer handbook of auditory research: evolution of the vertebrate system. Springer, New York, pp 289–359
Grothe B, Pecka M, Mcalpine D (2010) Mechanisms of sound localization in mammals. Physiol Rev 90:983–1012
Gruters KG, Groh JM (2012) Sounds and beyond: multisensory and other non-auditory signals in the inferior colliculus. Front Neural Circuits 6:96
Hatch EP, Noyes CA, Wang X, Wright TJ, Mansour SL (2007) Fgf3 is required for dorsal patterning and morphogenesis of the inner ear epithelium. Development 134:3615–3625
Held H (1893) Die centrale Gehörleitung. Arch Anat Physiol Anat Arch Anat Physiol, Anat Abt (Archiv für Anatomie und Physiologie, Anatomische Abteilung) 17:201–248
Hernandez RE, Rikhof HA, Bachmann R, Moens CB (2004) vhnf1 integrates global RA patterning and local FGF signals to direct posterior hindbrain development in zebrafish. Development 131:4511–4520
Hirtz JJ, Boesen M, Braun N, Deitmer JW, Kramer F, Lohr C, Muller B, Nothwang HG, Striessnig J, Lohrke S, Friauf E (2011) Cav1.3 calcium channels are required for normal development of the auditory brainstem. J Neurosci 31:8280–8294
Hirtz JJ, Braun N, Griesemer D, Hannes C, Janz K, Lohrke S, Muller B, Friauf E (2012) Synaptic refinement of an inhibitory topographic map in the auditory brainstem requires functional CaV1.3 calcium channels. J Neurosci 32:14602–14616
Hobert O, Carrera I, Stefanakis N (2010) The molecular and gene regulatory signature of a neuron. Trends Neurosci 33:435–445
Houle M, Prinos P, Iulianella A, Bouchard N, Lohnes D (2000) Retinoic acid regulation of Cdx1: an indirect mechanism for retinoids and vertebral specification. Mol Cell Biol 20:6579–6586
Howard ML, Davidson EH (2004) cis-Regulatory control circuits in development. Dev Biol 271:109–118
Howell DM, Morgan WJ, Jarjour AA, Spirou GA, Berrebi AS, Kennedy TE, Mathers PH (2007) Molecular guidance cues necessary for axon pathfinding from the ventral cochlear nucleus. J Comp Neurol 504:533–549
Hunt P, Gulisano M, Cook M, Sham MH, Faiella A, Wilkinson D, Boncinelli E, Krumlauf R (1991) A distinct Hox code for the branchial region of the vertebrate head. Nature 353(6347):861–864. doi:10.1038/353861a0
Jacoby J, Rubinson K (1983) The acoustic and lateral line nuclei are distinct in the premetamorphic frog, Rana catesbeiana. J Comp Neurol 216:152–161
Jahan I, Pan N, Kersigo J, Fritzsch B (2010) Neurod1 suppresses hair cell differentiation in ear ganglia and regulates hair cell subtype development in the cochlea. PLoS One 5:e11661
Jalabi W, Kopp-Scheinpflug C, Allen PD, Schiavon E, DiGiacomo RR, Forsythe ID, Maricich SM (2013) Sound Localization Ability and Glycinergic Innervation of the Superior Olivary Complex Persist after Genetic Deletion of the Medial Nucleus of the Trapezoid Body. J Neurosci 33:15044–15049
Jaramillo MA, Kramer EM (2007) The role of developmental genetics in understanding homology and morphological evolution in plants. Int J Plant Sci 168:61–72
Johnston J, Forsythe ID, Kopp-Scheinpflug C (2010) Going native: voltage-gated potassium channels controlling neuronal excitability. J Physiol 588:3187–3200
Kadner A, Kulesza RJ, Berrebi AS (2006) Neurons in the medial nucleus of the trapezoid body and superior paraolivary nucleus of the rat may play a role in sound duration coding. J Neurophysiol 95:1499–1508
Kapatos G, Hirayama K, Shimoji M, Milstien S (1999) GTP cyclohydrolase I feedback regulatory protein is expressed in serotonin neurons and regulates tetrahydrobiopterin biosynthesis. J Neurochem 72:669–675
Karis A, Pata I, van Doorninck JH, Grosveld F, Zeeuw CI de, de CD, Fritzsch B (2001) Transcription factor GATA-3 alters pathway selection of olivocochlear neurons and affects morphogenesis of the ear. J Comp Neurol 429:615–630
Katsanis SH, Katsanis N (2013) Molecular genetic testing and the future of clinical genomics. Nat Rev Genet 14(6):415–426. doi:10.1038/nrg3493
Kayam G, Kohl A, Magen Z, Peretz Y, Weisinger K, Bar A, Novikov O, Brodski C, Sela-Donenfeld D (2013) A novel role for Pax6 in the segmental organization of the hindbrain. Development 140:2190–2202
Khan MAF, Soto-Jimenez LM, Howe T, Streit A, Sosinsky A, Stern CD (2013) Computational tools and resources for prediction and analysis of gene regulatory regions in the chick genome. Genesis:1–14
Kim EJ, Hori K, Wyckoff A, Dickel LK, Koundakjian EJ, Goodrich LV, Johnson JE (2011) Spatiotemporal fate map of neurogenin1 (Neurog1) lineages in the mouse central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 519:1355–1370
Kim FA, Sing LA, Kaneko T, Bieman M, Stallwood N, Sadl VS, Cordes SP (2005) The vHNF1 homeodomain protein establishes early rhombomere identity by direct regulation of Kreisler expression. Mech Dev 122:1300–1309
Kim WY, Fritzsch B, Serls A, Bakel LA, Huang EJ, Reichardt LF, Barth DS, Lee JE (2001) NeuroD-null mice are deaf due to a severe loss of the inner ear sensory neurons during development. Development 128:417–426
Krumlauf R, Marshall H, Studer M, Nonchev S, Sham MH, Lumsden A (1993) Hox homeobox genes and regionalisation of the nervous system. J Neurobiol 24:1328–1340
Kwak S, Phillips BT, Heck R, Riley BB (2002) An expanded domain of fgf3 expression in the hindbrain of zebrafish valentino mutants results in mis-patterning of the otic vesicle. Development 129:5279–5287
Landsberg RL, Awatramani RB, Hunter NL, Farago AF, DiPietrantonio HJ, Rodriguez CI, Dymecki SM (2005) Hindbrain rhombic lip is comprised of discrete progenitor cell populations allocated by Pax6. Neuron 48:933–947
Larsell O (1934) The differentiation or the peripheral and central acoustic apparatus im the frog. J Comp Neurol:473–527
Lecaudey V, Anselme I, Rosa F, Schneider-Maunoury S (2004) The zebrafish Iroquois gene iro7 positions the r4/r5 boundary and controls neurogenesis in the rostral hindbrain. Development 131:3121–3131
Li W, Kaczmarek LK, Perney TM (2001) Localization of two high-threshold potassium channel subunits in the rat central auditory system. J Comp Neurol 437:196–218
Liu M, Pereira FA, Price SD, Chu MJ, Shope C, Himes D, Eatock RA, Brownell WE, Lysakowski A, Tsai MJ (2000) Essential role of BETA2/NeuroD1 in development of the vestibular and auditory systems. Genes Dev 14:2839–2854
Liu S, Li W, Chen Y, Lin Q, Wang Z, Li H (2011) Mouse auditory organ development required bone morphogenetic protein signaling. Neuro Report 22:396–401
Lorente-Cánovas B, Marín F, Corral-San-Miguel R, Hidalgo-Sánchez M, Ferrán JL, Puelles L, Aroca P (2012) Multiple origins, migratory paths and molecular profiles of cells populating the avian interpeduncular nucleus. Dev Biol 361:12–26
Louvi A, Yoshida M, Grove EA (2007) The derivatives of the Wnt3a lineage in the central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 504:550–569
Ma Q, Chen Z, del, Barco Barrantes I, de la Pompa JL, Anderson DJ (1998) Neurogenin1 is essential for the determination of neuronal precursors for proximal cranial sensory ganglia. Neuron 20:469–482
Machold R, Fishell G (2005) Math1 is expressed in temporally discrete pools of cerebellar rhombic-lip neural progenitors. Neuron 48:17–24
Macleod KM, Carr CE (2012) Synaptic Mechanisms of Coincidence Detection. In: Trussell LO, Popper AN, Fay AN (eds) Synaptic mechanisms in the auditory system. Springer, New York, pp 135–164
Maconochie MK, Nonchev S, Studer M, Chan SK, Pöpperl H, Sham MH, Mann RS, Krumlauf R (1997) Cross-regulation in the mouse HoxB complex: the expression of Hoxb2 in rhombomere 4 is regulated by Hoxb1. Genes Dev 11(14):1885–1895
Maden M (2002) Retinoid signalling in the development of the central nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:843–853
Manis PB, Xie R, Wang Y, Marrs GS, Spirou GA (2012) The Endbulbs of Held. In: Trussell LO, Popper AN, Fay AN (eds) Synaptic mechanisms in the auditory system. Springer, New York, pp 61–93
Mann RS, Carroll SB (2002) Molecular mechanisms of selector gene function and evolution. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12:592–600
Manzanares M, Cordes S, Kwan CT, Sham MH, Barsh GS, Krumlauf R (1997) Segmental regulation of hoxb-3 by kreisler. Nature 387:191–195
Manzanares M, Nardelli J, Gilardi-Hebenstreit P, Marshall H, Giudicelli F, Martinez-Pastor MT, Krumlauf R, Charnay P (2002) Krox20 and kreisler co-operate in the transcriptional control of segmental expression of Hoxb3 in the developing hindbrain. EMBO J 21:365–376
Manzanares M, Trainor PA, Nonchev S, Ariza-McNaughton L, Brodie J, Gould A, Marshall H, Morrison A, Kwan CT, Sham MH, Wilkinson DG, Krumlauf R (1999) The role of kreisler in segmentation during hindbrain development. Dev Biol 211:220–237
Maricich SM, Xia A, Mathes EL, Wang VY, Oghalai JS, Fritzsch B, Zoghbi HY (2009) Atoh1-lineal neurons are required for hearing and for the survival of neurons in the spiral ganglion and brainstem accessory auditory nuclei. J Neurosci 29:11123–11133
Marin F, Charnay P (2000) Hindbrain patterning: FGFs regulate Krox20 and mafB/kr expression in the otic/preotic region. Development 127:4925–4935
Marin F, Puelles L (1995) Morphological fate of rhombomeres in quail/chick chimeras: a segmental analysis of hindbrain nuclei. Eur J Neurosci 7:1714–1738
Marín F, Aroca P, Puelles L (2008) Hox gene colinear expression in the avian medulla oblongata is correlated with pseudorhombomeric domains. Dev Biol 323:230–247
Mark M, Ghyselinck NB, Chambon P (2009) Function of retinoic acid receptors during embryonic development. Nucl Recept Signal 7:e002
Marrs GS, Morgan WJ, Howell DM, Spirou GA, Mathers PH (2013) Embryonic origins of the mouse superior olivary complex. Dev Neurobiol:384–398
Martínez S (2001) The isthmic organizer and brain regionalization. Int J Dev Biol 45:367–371
Matei V, Pauley S, Kaing S, Rowitch D, Beisel KW, Morris K, Feng F, Jones K, Lee J, Fritzsch B (2005) Smaller inner ear sensory epithelia in Neurog 1 null mice are related to earlier hair cell cycle exit. Dev Dyn 234:633–650
Maves L, Jackman W, Kimmel CB (2002) FGF3 and FGF8 mediate a rhombomere 4 signaling activity in the zebrafish hindbrain. Development 129:3825–3837
McCormick CA (1999) Anatomy of the central auditory pathways of fish and amphibian. In: Fay RR, Popper AN (eds) Comparative hearing: fish and amphibians. Springer, New York, pp 155–217
McGettigan PA (2013) Transcriptomics in the RNA-seq era. Curr Opin Chem Biol 17:4–11
McKay IJ, Lewis J, Lumsden A (1996) The role of FGF-3 in early inner ear development: an analysis in normal and kreisler mutant mice. Dev Biol 174:370–378
McKay IJ, Muchamore I, Krumlauf R, Maden M, Lumsden A, Lewis J (1994) The kreisler mouse: a hindbrain segmentation mutant that lacks two rhombomeres. Development 120:2199–2211
Mechta-Grigoriou F, Garel S, Charnay P (2000) Nab proteins mediate a negative feedback loop controlling Krox-20 activity in the developing hindbrain. Development 127:119–128
Mic FA, Molotkov A, Benbrook DM, Duester G (2003) Retinoid activation of retinoic acid receptor but not retinoid X receptor is sufficient to rescue lethal defect in retinoic acid synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(12):7135–7140. doi:10.1073/pnas.1231422100
Michna M, Knirsch M, Hoda JC, Muenkner S, Langer P, Platzer J, Striessnig J, Engel J (2003) Cav1.3 (alpha1D) Ca2+ currents in neonatal outer hair cells of mice. J Physiol 553:747–758
Moreno-Bravo JA, Perez-Balaguer A, Martinez-Lopez JE, Aroca P, Puelles L, Martinez S, Puelles E (2014) Role of Shh in the development of molecularly characterized tegmental nuclei in mouse rhombomere 1. Brain Struct Funct 219:777–792
Murphy P, Davidson DR, Hill RE (1989) Segment-specific expression of a homoeobox-containing gene in the mouse hindbrain. Nature 341:156–159
Murphy P, Hill RE (1991) Expression of the mouse labial-like homeobox-containing genes, Hox 2.9 and Hox 1.6, during segmentation of the hindbrain. Development 111:61–74
Neves J, Uchikawa M, Bigas A, Giraldez F (2012) The prosensory function of Sox2 in the chicken inner ear relies on the direct regulation of Atoh1. PLoS One 7:e30871
Nichols DH, Bruce LL (2006) Migratory routes and fates of cells transcribing the Wnt-1 gene in the murine hindbrain. Dev Dyn 235:285–300
Niederreither K, Vermot J, Schuhbaur B, Chambon P, Dollé P (2000) Retinoic acid synthesis and hindbrain patterning in the mouse embryo. Development 127:75–85
Nolte C, Amores A, Nagy Kovacs E, Postlethwait J, Featherstone M (2003) The role of a retinoic acid response element in establishing the anterior neural expression border of Hoxd4 transgenes. Mech Dev 120:325–335
Nonchev S, Maconochie M, Vesque C, Aparicio S, riza-McNaughton L, Manzanares M, Maruthainar K, Kuroiwa A, Brenner S, Charnay P, Krumlauf R (1996) The conserved role of Krox-20 in directing Hox gene expression during vertebrate hindbrain segmentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:9339–9345
Oertel D (1997) Encoding of timing in the brain stem auditory nuclei of vertebrates. Neuron 19:959–962
Oertel D (2009) A team of potassium channels tunes up auditory neurons. J Physiol 587:2417–2418
Ohyama T, Basch ML, Mishina Y, Lyons KM, Segil N, Groves AK (2010) BMP signaling is necessary for patterning the sensory and nonsensory regions of the developing mammalian cochlea. J Neurosci 30:15044–15051
Ørvlg T (1971) Comments on the lateral line system of some brachythoracid and ptyctodontid arthrodires. Zool Scripta 1:5–35
Oury F, Murakami Y, Renaud JS, Pasqualetti M, Charnay P, Ren SY, Rijli FM (2006) Hoxa2- and rhombomere-dependent development of the mouse facial somatosensory map. Science 313:1408–1413
Palfery TD, Duff D (2007) Central auditory processing disorders: review and case study. Axone 28:20–23
Pan N, Jahan I, Kersigo J, Duncan JS, Kopecky B, Fritzsch B (2012) A novel Atoh1 “self-terminating” mouse model reveals the necessity of proper Atoh1 level and duration for hair cell differentiation and viability. PLoS One 7:e30358
Pan N, Jahan I, Kersigo J, Kopecky B, Santi P, Johnson S, Schmitz H, Fritzsch B (2011) Conditional deletion of Atoh1 using Pax2-Cre results in viable mice without differentiated cochlear hair cells that have lost most of the organ of Corti. Hear Res 275:66–80
Parameshwaran S, Carr CE, Perney TM (2001) Expression of the Kv3.1 potassium channel in the avian auditory brainstem. J Neurosci 21:485–494
Parks TN (1981) Morphology of axosomatic endings in an avian cochlear nucleus: nucleus magnocellularis of the chicken. J Comp Neurol 203:425–440
Pata I, Studer M, van Doorninck JH, Briscoe J, Kuuse S, Engel JD, Grosveld F, Karis A (1999) The transcription factor GATA3 is a downstream effector of Hoxb1 specification in rhombomere 4. Development 126:5523–5531
Patel NH, Ball EE, Goodman CS (1992) Changing role of even-skipped during the evolution of insect pattern formation. Nature 357:339–342
Pattyn A, Vallstedt A, Dias JM, Samad OA, Krumlauf R, Rijli FM, Brunet J, Ericson J (2003) Coordinated temporal and spatial control of motor neuron and serotonergic neuron generation from a common pool of CNS progenitors. Genes Dev 17:729–737
Pecka M, Zahn TP, Saunier-Rebori B, Siveke I, Felmy F, Wiegrebe L, Klug A, Pollak GD, Grothe B (2007) Inhibiting the inhibition: a neuronal network for sound localization in reverberant environments. J Neurosci 27:1782–1790
Platzer J, Engel J, Schrott-Fischer A, Stephan K, Bova S, Chen H, Zheng H, Striessnig J (2000) Congenital deafness and sinoatrial node dysfunction in mice lacking class D L-type Ca2 + channels. Cell 102:89–97
Pouilhe M, Gilardi-Hebenstreit P, Desmarquet-Trin Dinh C, Charnay P (2007) Direct regulation of vHnf1 by retinoic acid signaling and MAF-related factors in the neural tube. Dev Biol 309:344–357
Prince V, Lumsden A (1994) Hoxa-2 expression in normal and transposed rhombomeres: independent regulation in the neural tube and neural crest. Development 120:911–923
Prinos P, Joseph S, Oh K, Meyer BI, Gruss P, Lohnes D (2001) Multiple pathways governing Cdx1 expression during murine development. Dev Biol 239:257–269
Pujades C, Kamaid A, Alsina B, Giraldez F (2006) BMP-signaling regulates the generation of hair-cells. Dev Biol 292:55–67
Qiu R, Liu Y, Wu JY, Liu K, Mo W, He R (2009) Misexpression of miR-196a induces eye anomaly in Xenopus laevis. Brain Res Bull 79:26–31
Raft S, Koundakjian EJ, Quinones H, Jayasena CS, Goodrich LV, Johnson JE, Segil N, Groves AK (2007) Cross-regulation of Ngn1 and Math1 coordinates the production of neurons and sensory hair cells during inner ear development. Development 134:4405–4415
Raman IM, Zhang S, Trussell LO (1994) Pathway-specific variants of AMPA receptors and their contribution to neuronal signaling. J Neurosci 14:4998–5010
Ren S, Angrand P, Rijli FM (2002) Targeted insertion results in a rhombomere 2-specific Hoxa2 knockdown and ectopic activation of Hoxa1 expression. Dev Dyn 225:305–315
Rose MF, Ahmad KA, Thaller C, Zoghbi HY (2009) Excitatory neurons of the proprioceptive, interoceptive, and arousal hindbrain networks share a developmental requirement for Math1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:22462–22467
Rosengauer E, Hartwich H, Hartmann AM, Rudnicki A, Satheesh SV, Avraham KB, Nothwang HG (2012) Egr2:Cre mediated conditional ablation of dicer disrupts histogenesis of Mammalian Central Auditory Nuclei. PLoS One 7:e49503
Rossant J, Zirngibl R, Cado D, Shago M, Giguere V (1991) Expression of a retinoic acid response element-hsplacZ transgene defines specific domains of transcriptional activity during mouse embryogenesis. Genes Dev 5:1333–1344
Rossel M, Capecchi MR (1999) Mice mutant for both Hoxa1 and Hoxb1 show extensive remodeling of the hindbrain and defects in craniofacial development. Development 126:5027–5040
Rubel EW, Smith D, Miller LC (1976) Organization and development of brain stem auditory nuclei of the chicken: ontogeny of N. magnocellularis and N. laminaris. J Comp Neurol 166:469–490
Russo MW, Sevetson BR, Milbrandt J (1995) Identification of NAB1, a repressor of NGFI-A- and Krox20-mediated transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:6873–6877
Sadl VS, Sing A, Mar L, Jin F, Cordes SP (2003) Analysis of hindbrain patterning defects caused by the kreisler(enu) mutation reveals multiple roles of Kreisler in hindbrain segmentation. Dev Dyn 227:134–142
Sakai Y, Meno C, Fujii H, Nishino J, Shiratori H, Saijoh Y, Rossant J, Hamada H (2001) The retinoic acid-inactivating enzyme CYP26 is essential for establishing an uneven distribution of retinoic acid along the anterio-posterior axis within the mouse embryo. Genes Dev 15:213–225
Samad OA, Geisen MJ, Caronia G, Varlet I, Zappavigna V, Ericson J, Goridis C, Rijli FM (2004) Integration of anteroposterior and dorsoventral regulation of Phox2b transcription in cranial motoneuron progenitors by homeodomain proteins. Development 131:4071–4083
Satheesh SV, Kunert K, Ruttiger L, Zuccotti A, Schonig K, Friauf E, Knipper M, Bartsch D, Nothwang HG (2012) Retrocochlear function of the peripheral deafness gene Cacna1d. Hum Mol Genet 21:3896–3909
Schneider BF, Norton S (1979) Equivalent ages in rat, mouse and chick embryos. Teratology 19:273–278
Schneider-Maunoury S, Seitanidou T, Charnay P, Lumsden A (1997) Segmental and neuronal architecture of the hindbrain of Krox-20 mouse mutants. Development 124:1215–1226
Seitanidou T, Schneider-Maunoury S, Desmarquet C, Wilkinson DG, Charnay P (1997) Krox-20 is a key regulator of rhombomere-specific gene expression in the developing hindbrain. Mech Dev 65:31–42
Sham MH, Vesque C, Nonchev S, Marshall H, Frain M, Gupta RD, Whiting J, Wilkinson D, Charnay P, Krumlauf R (1993) The zinc finger gene Krox20 regulates HoxB2 (Hox2.8) during hindbrain segmentation. Cell 72:183–196
Shubin N, Tabin C, Carroll S (1997) Fossils, genes and the evolution of animal limbs. Nature 388:639–648
Shubin N, Tabin C, Carroll S (2009) Deep homology and the origins of evolutionary novelty. Nature 457:818–823
Sirbu IO, Gresh L, Barra J, Duester G (2005) Shifting boundaries of retinoic acid activity control hindbrain segmental gene expression. Development 132:2611–2622
Smith DJ, Rubel EW (1979) Organization and development of brain stem auditory nuclei of the chicken: dendritic gradients in nucleus laminaris. J Comp Neurol 186:213–239
Smith PH, Spirou GA (2002) From the Cochlea to the Cortex and Back. In: Oertel D, Fay RR, Popper AN (eds) Integrative functions in the mammalian auditory pathway. Springer, New York, pp 6–71
Stotler WA (1953) An experimental study of the cells and connections of the superior olivary complex of the cat. J Comp Neurol. 98:401–431
Studer M, Gavalas A, Marshall H, Ariza-McNaughton L, Rijli FM, Chambon P, Krumlauf R (1998) Genetic interactions between Hoxa1 and Hoxb1 reveal new roles in regulation of early hindbrain patterning. Development 125:1025–1036
Studer M, Lumsden A, Ariza-McNaughton L, Bradley A, Krumlauf R (1996) Altered segmental identity and abnormal migration of motor neurons in mice lacking Hoxb-1. Nature 384:630–634
Sturgeon K, Kaneko T, Biemann M, Gauthier A, Chawengsaksophak K, Cordes SP (2011) Cdx1 refines positional identity of the vertebrate hindbrain by directly repressing Mafb expression. Development 138:65–74
Sun Z, Hopkins N (2001) vhnf1, the MODY5 and familial GCKD-associated gene, regulates regional specification of the zebrafish gut, pronephros, and hindbrain. Genes Dev 15:3217–3229
Sundin OH, Eichele G (1990) A homeo domain protein reveals the metameric nature of the developing chick hindbrain. Genes Dev 4:1267–1276
Svaren J, Sevetson BR, Apel ED, Zimonjic DB, Popescu NC, Milbrandt J (1996) NAB2, a corepressor of NGFI-A (Egr-1) and Krox20, is induced by proliferative and differentiative stimuli. Mol Cell Biol 16:3545–3553
Szeto I, Leung K, Sham M, Cheah K (2009) Utility of HoxB2 enhancer-mediated Cre activity for functional studies in the developing inner ear. Genesis 47:361–365
Takahashi M, Osumi N (2011) Pax6 regulates boundary-cell specification in the rat hindbrain. Mech Dev 128:289–302
Taneja R, Thisse B, Rijli FM, Thisse C, Bouillet P, Dolle P, Chambon P (1996) The expression pattern of the mouse receptor tyrosine kinase gene MDK1 is conserved through evolution and requires Hoxa-2 for rhombomere-specific expression in mouse embryos. Dev Biol 177:397–412
Taschenberger H, von Gersdorff H (2000) Fine-tuning an auditory synapse for speed and fidelity: developmental changes in presynaptic waveform, EPSC kinetics, and synaptic plasticity. J Neurosci 20:9162–9173
Theil T, Ariza-McNaughton L, Manzanares M, Brodie J, Krumlauf R, Wilkinson DG (2002) Requirement for downregulation of kreisler during late patterning of the hindbrain. Development 129:1477–1485
Theil T, Frain M, Gilardi-Hebenstreit P, Flenniken A, Charnay P, Wilkinson DG (1998) Segmental expression of the EphA4 (Sek-1) receptor tyrosine kinase in the hindbrain is under direct transcriptional control of Krox-20. Development 125:443–452
Trussell LO (1999) Synaptic mechanisms for coding timing in auditory neurons. Annu Rev Physiol 61:477–496
Tsuchitani C (1997) Input from the medial nucleus of trapezoid body to an interaural level detector. Hear Res 105:211–224
Tümpel S, Cambronero F, Ferretti E, Blasi F, Wiedemann LM, Krumlauf R (2007) Expression of Hoxa2 in rhombomere 4 is regulated by a conserved cross-regulatory mechanism dependent upon Hoxb1. Dev Biol 302:646–660
Tümpel S, Cambronero F, Sims C, Krumlauf R, Wiedemann LM (2008) A regulatory module embedded in the coding region of Hoxa2 controls expression in rhombomere 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:20077–20082
Tümpel S, Maconochie M, Wiedemann LM, Krumlauf R (2002) Conservation and diversity in the cis-regulatory networks that integrate information controlling expression of Hoxa2 in hindbrain and cranial neural crest cells in vertebrates. Dev Biol 246:45–56
Tümpel S, Wiedemann LM, Krumlauf R (2009) Hox genes and segmentation of the vertebrate hindbrain. Curr Top Dev Biol 88:103–137
Vesque C, Maconochie M, Nonchev S, Ariza-McNaughton L, Kuroiwa A, Charnay P, Krumlauf R (1996) Hoxb-2 transcriptional activation in rhombomeres 3 and 5 requires an evolutionarily conserved cis-acting element in addition to the Krox-20 binding site. EMBO J 15:5383–5396
Vieira C, Pombero A, García-Lopez R, Gimeno L, Echevarria D, Martínez S (2010) Molecular mechanisms controlling brain development: an overview of neuroepithelial secondary organizers. Int J Dev Biol 54:7–20
Wagner GP (2007) The developmental genetics of homology. Nat Rev Genet 8:473–479
Walshe J, Maroon H, McGonnell IM, Dickson C, Mason I (2002) Establishment of hindbrain segmental identity requires signaling by FGF3 and FGF8. Curr Biol 12:1117–1123
Wang VY, Rose MF, Zoghbi HY (2005) Math1 expression redefines the rhombic lip derivatives and reveals novel lineages within the brainstem and cerebellum. Neuron 48:31–43
Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M (2009) RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet 10:57–63
Webster DB (1992) An overview of mammalian auditory pathways with an emphasis on humans. In: Webster DB, Popper AN, Fay RR (eds) The mammalian auditory pathway: neuroanatomy. Springer, New York, pp 1–22
Weisinger K, Kayam G, Missulawin-Drillman T, Sela-Donenfeld D (2010) Analysis of expression and function of FGF-MAPK signaling components in the hindbrain reveals a central role for FGF3 in the regulation of Krox20, mediated by Pea3. Dev Biol 344:881–895
Wendling O, Ghyselinck NB, Chambon P, Mark M (2001) Roles of retinoic acid receptors in early embryonic morphogenesis and hindbrain patterning. Development 128:2031–2038
Wiellette EL, Sive H (2004) Early requirement for fgf8 function during hindbrain pattern formation in zebrafish. Dev Dyn 229:393–399
Wilkinson DG, Bhatt S, Chavrier P, Bravo R, Charnay P (1989) Segment-specific expression of a zinc-finger gene in the developing nervous system of the mouse. Nature 337:461–464
Will U, Luhede G, Görner P (1985) The area octavo-lateralis in Xenopus laevis. Cell Tissue Res 239:163–175
Willaredt MA, Ebbers L, Nothwang HG (2014) Central auditory function of deafness genes. Hear Res 312C:9–20
Wong EY, Wang XA, Mak SS, Sae-Pang JJ, KW L, Fritzsch B, Sham MH (2011) Hoxb3 negatively regulates Hoxb1 expression in mouse hindbrain patterning. Dev Biol 352:382–392
Wright TJ, Mansour SL (2003) Fgf3 and Fgf10 are required for mouse otic placode induction. Development 130:3379–3390
Wu SH, Kelly JB (1993) Response of neurons in the lateral superior olive and medial nucleus of the trapezoid body to repetitive stimulation: intracellular and extracellular recordings from mouse brain slice. Hear Res 68:189–201
Wullimann MF, Mueller T, Distel M, Babaryka A, Grothe B, Köster RW (2011) The long adventurous journey of rhombic lip cells in jawed vertebrates: a comparative developmental analysis. Front Neuroanat 5:1–27
Wurst W, Bally-Cuif L (2001) Neural plate patterning: upstream and downstream of the isthmic organizer. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:99–108
Xiao L, Michalski N, Kronander E, Gjoni E, Genoud C, Knott G, Schneggenburger R (2013) BMP signaling specifies the development of a large and fast CNS synapse. Nat Neurosci 16:856–864
Yan D, Tekin M, Blanton SH, Liu XZ (2013) Next-generation sequencing in genetic hearing loss. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 17:581–587
Yin TCT (2002) Neural mechanisms of encoding binaural localization cues in the auditory brainstem. In: Oertel D, Fay RR, Popper AA (eds) Springer handbook of auditory research: integrative functions in the mammalian auditory pathway. Springer, New York, pp 99–159
Yu W, Appler JM, Kim Y, Nishitani AM, Holt JR, Goodrich LV (2013) A Gata3-Mafb transcriptional network directs post-synaptic differentiation in synapses specialized for hearing. Elife 2:e01341
Zervas M, Millet S, Ahn S, Joyner AL (2004) Cell behaviors and genetic lineages of the mesencephalon and rhombomere 1. Neuron 43:345–357
Zhang M, Kim HJ, Marshall H, Gendron-Maguire M, Lucas DA, Baron A, Gudas LJ, Gridley T, Krumlauf R, Grippo JF (1994) Ectopic Hoxa-1 induces rhombomere transformation in mouse hindbrain. Development 120:2431–2442
Zittlau KE, Claas B, Münz H (1986) Directional sensitivity of lateral line units in the clawed toadXenopus laevis Daudin. J Comp Physiol 158:469–477
Acknowledgments
We thank Geoff Manley for helpful discussions and input to this paper. We also acknowledge insightful comments from two anonymous reviewers. M.A. Willaredt is financed by the Cluster of Excellence Hearing4all, and T. Schlüter by the Research Training Group Molecular Basis of Sensory Biology GRK 1885/1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Willaredt, M.A., Schlüter, T. & Nothwang, H.G. The gene regulatory networks underlying formation of the auditory hindbrain. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 72, 519–535 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1759-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1759-0