Abstract
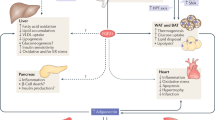
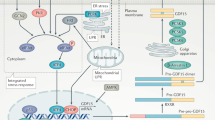
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) has been proposed as a novel putative therapeutic agent in type 2 diabetes. A large amount of data, predominantly obtained from murine models but also from non-human primates, suggest that FGF21 ameliorates obesity-associated hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia primarily via effects on adipose tissue and the pancreas. In addition, FGF21 has been reported to play a pivotal regulatory role in starvation and ketosis. However, while it is clear that FGF21 has potent effects in vivo in several animal models, the exact mechanisms remain elusive. Moreover, very recent results from different human cohort studies have shown a paradoxical regulation of plasma FGF21 in obesity and type 2 diabetes as well as other important qualitative differences in the effects and regulation of FGF21 between rodents and humans. This review focuses on the most recently published data on FGF21 with emphasis on results obtained in humans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Presta M, Dell’Era P, Mitola S, Moroni E, Ronca R, Rusnati M (2005) Fibroblast growth factor/fibroblast growth factor receptor system in angiogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16:159–178
Itoh N, Ornitz DM (2004) Evolution of the Fgf and Fgfr gene families. Trends Genet 20:563–569
Nishimura T, Nakatake Y, Konishi M, Itoh N (2000) Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 1492:203–206
ADHR Consortium (2000) Autosomal dominant hypophosphataemic rickets is associated with mutations in FGF23. Nat Genet 26:345–348
Shimada T, Mizutani S, Muto T, Yoneya T, Hino R, Takeda S, Takeuchi Y, Fujita T, Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2001) Cloning and characterization of FGF23 as a causative factor of tumor-induced osteomalacia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:6500–6505
Yamashita T, Yoshioka M, Itoh N (2000) Identification of a novel fibroblast growth factor, FGF-23, preferentially expressed in the ventrolateral thalamic nucleus of the brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 277:494–498
Nishimura T, Utsunomiya Y, Hoshikawa M, Ohuchi H, Itoh N (1999) Structure and expression of a novel human FGF, FGF-19, expressed in the fetal brain. Biochim Biophys Acta 1444:148–151
Inagaki T, Choi M, Moschetta A, Peng L, Cummins CL, McDonald JG, Luo G, Jones SA, Goodwin B, Richardson JA, Gerard RD, Repa JJ, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA (2005) Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an enterohepatic signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab 2:217–225
Lundasen T, Galman C, Angelin B, Rudling M (2006) Circulating intestinal fibroblast growth factor 19 has a pronounced diurnal variation and modulates hepatic bile acid synthesis in man. J Intern Med 260:530–536
Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2007) FGF23 is a hormone-regulating phosphate metabolism–unique biological characteristics of FGF23. Bone 40:1190–1195
Kharitonenkov A, Shiyanova TL, Koester A, Ford AM, Micanovic R, Galbreath EJ, Sandusky GE, Hammond LJ, Moyers JS, Owens RA, Gromada J, Brozinick JT, Hawkins ED, Wroblewski VJ, Li DS, Mehrbod F, Jaskunas SR, Shanafelt AB (2005) FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. J Clin Invest 115:1627–1635
Kharitonenkov A, Shanafelt AB (2008) Fibroblast growth factor-21 as a therapeutic agent for metabolic diseases. BioDrugs 22:37–44
Goetz R, Beenken A, Ibrahimi OA, Kalinina J, Olsen SK, Eliseenkova AV, Xu C, Neubert TA, Zhang F, Linhardt RJ, Yu X, White KE, Inagaki T, Kliewer SA, Yamamoto M, Kurosu H, Ogawa Y, Kuro-o M, Lanske B, Razzaque MS, Mohammadi M (2007) Molecular insights into the klotho-dependent, endocrine mode of action of fibroblast growth factor 19 subfamily members. Mol Cell Biol 27:3417–3428
Harmer NJ, Pellegrini L, Chirgadze D, Fernandez-Recio J, Blundell TL (2004) The crystal structure of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 19 reveals novel features of the FGF family and offers a structural basis for its unusual receptor affinity. Biochemistry 43:629–640
Kurosu H, Ogawa Y, Miyoshi M, Yamamoto M, Nandi A, Rosenblatt KP, Baum MG, Schiavi S, Hu MC, Moe OW, Kuro-o M (2006) Regulation of fibroblast growth factor-23 signaling by klotho. J Biol Chem 281:6120–6123
Urakawa I, Yamazaki Y, Shimada T, Iijima K, Hasegawa H, Okawa K, Fujita T, Fukumoto S, Yamashita T (2006) Klotho converts canonical FGF receptor into a specific receptor for FGF23. Nature 444:770–774
Kurosu H, Choi M, Ogawa Y, Dickson AS, Goetz R, Eliseenkova AV, Mohammadi M, Rosenblatt KP, Kliewer SA, Kuro-o M (2007) Tissue-specific expression of beta-Klotho and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor isoforms determines metabolic activity of FGF19 and FGF21. J Biol Chem 282:26687–26695
Ogawa Y, Kurosu H, Yamamoto M, Nandi A, Rosenblatt KP, Goetz R, Eliseenkova AV, Mohammadi M, Kuro-o M (2007) BetaKlotho is required for metabolic activity of fibroblast growth factor 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:7432–7437
Kharitonenkov A, Dunbar JD, Bina HA, Bright S, Moyers JS, Zhang C, Ding L, Micanovic R, Mehrbod SF, Knierman MD, Hale JE, Coskun T, Shanafelt AB (2008) FGF-21/FGF-21 receptor interaction and activation is determined by betaKlotho. J Cell Physiol 215:1–7
Suzuki M, Uehara Y, Motomura-Matsuzaka K, Oki J, Koyama Y, Kimura M, Asada M, Komi-Kuramochi A, Oka S, Imamura T (2008) betaKlotho is required for fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 21 signaling through FGF receptor (FGFR) 1c and FGFR3c. Mol Endocrinol 22:1006–1014
Ito S, Kinoshita S, Shiraishi N, Nakagawa S, Sekine S, Fujimori T, Nabeshima YI (2000) Molecular cloning and expression analyses of mouse betaklotho, which encodes a novel Klotho family protein. Mech Dev 98:115–119
Micanovic R, Raches DW, Dunbar JD, Driver DA, Bina HA, Dickinson CD, Kharitonenkov A (2008) Different roles of N- and C-termini in the functional activity of FGF21. J Cell Physiol 219:227–234
Yie J, Hecht R, Patel J, Stevens J, Wang W, Hawkins N, Steavenson S, Smith S, Winters D, Fisher S, Cai L, Belouski E, Chen C, Michaels ML, Li YS, Lindberg R, Wang M, Veniant M, Xu J (2009) FGF21 N- and C-termini play different roles in receptor interaction and activation. FEBS Lett 583:19–24
Coskun T, Bina HA, Schneider MA, Dunbar JD, Hu CC, Chen Y, Moller DE, Kharitonenkov A (2008) Fibroblast growth factor 21 corrects obesity in mice. Endocrinology 149:6018–6027
Xu J, Lloyd DJ, Hale C, Stanislaus S, Chen M, Sivits G, Vonderfecht S, Hecht R, Li YS, Lindberg RA, Chen JL, Jung DY, Zhang Z, Ko HJ, Kim JK, Veniant MM (2009) Fibroblast growth factor 21 reverses hepatic steatosis, increases energy expenditure, and improves insulin sensitivity in diet-induced obese mice. Diabetes 58:250–259
Kharitonenkov A, Wroblewski VJ, Koester A, Chen YF, Clutinger CK, Tigno XT, Hansen BC, Shanafelt AB, Etgen GJ (2007) The metabolic state of diabetic monkeys is regulated by fibroblast growth factor-21. Endocrinology 148:774–781
Wente W, Efanov AM, Brenner M, Kharitonenkov A, Koster A, Sandusky GE, Sewing S, Treinies I, Zitzer H, Gromada J (2006) Fibroblast growth factor-21 improves pancreatic beta-cell function and survival by activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase ½ and Akt signaling pathways. Diabetes 55:2470–2478
Badman MK, Pissios P, Kennedy AR, Koukos G, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E (2007) Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARalpha and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab 5:426–437
Inagaki T, Dutchak P, Zhao G, Ding X, Gautron L, Parameswara V, Li Y, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Esser V, Elmquist JK, Gerard RD, Burgess SC, Hammer RE, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA (2007) Endocrine regulation of the fasting response by PPARalpha-mediated induction of fibroblast growth factor 21. Cell Metab 5:415–425
Reitman ML (2007) FGF21: a missing link in the biology of fasting. Cell Metab 5:405–407
Lundasen T, Hunt MC, Nilsson LM, Sanyal S, Angelin B, Alexson SE, Rudling M (2007) PPARalpha is a key regulator of hepatic FGF21. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 360:437–440
Muise ES, Azzolina B, Kuo DW, El-Sherbeini M, Tan Y, Yuan X, Mu J, Thompson JR, Berger JP, Wong KK (2008) Adipose fibroblast growth factor 21 is up-regulated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and altered metabolic states. Mol Pharmacol 74:403–412
Wang H, Qiang L, Farmer SR (2008) Identification of a domain within peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma regulating expression of a group of genes containing fibroblast growth factor 21 that are selectively repressed by SIRT1 in adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol 28:188–200
Izumiya Y, Bina HA, Ouchi N, Akasaki Y, Kharitonenkov A, Walsh K (2008) FGF21 is an Akt-regulated myokine. FEBS Lett 582:3805–3810
Stevenson EJ, Koncarevic A, Giresi PG, Jackman RW, Kandarian SC (2005) Transcriptional profile of a myotube starvation model of atrophy. J Appl Physiol 98:1396–1406
Moyers JS, Shiyanova TL, Mehrbod F, Dunbar JD, Noblitt TW, Otto KA, Reifel-Miller A, Kharitonenkov A (2007) Molecular determinants of FGF-21 activity-synergy and cross-talk with PPARgamma signaling. J Cell Physiol 210:1–6
Zhang X, Yeung DC, Karpisek M, Stejskal D, Zhou ZG, Liu F, Wong RL, Chow WS, Tso AW, Lam KS, Xu A (2008) Serum FGF21 levels are increased in obesity and are independently associated with the metabolic syndrome in humans. Diabetes 57:1246–1253
Arner P, Pettersson A, Mitchell PJ, Dunbar JD, Kharitonenkov A, Ryden M (2008) FGF21 attenuates lipolysis in human adipocytes–a possible link to improved insulin sensitivity. FEBS Lett 582:1725–1730
Arner P (2002) Insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes: role of fatty acids. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 18[Suppl 2]:S5–S9
Galman C, Lundasen T, Kharitonenkov A, Bina HA, Eriksson M, Hafstrom I, Dahlin M, Amark P, Angelin B, Rudling M (2008) The circulating metabolic regulator FGF21 is induced by prolonged fasting and PPARalpha activation in man. Cell Metab 8:169–174
Dostalova I, Kavalkova P, Haluzikova D, Lacinova Z, Mraz M, Papezova H, Haluzik M (2008) Plasma concentrations of fibroblast growth factors 19 and 21 in patients with anorexia nervosa. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:3627–3632
Li L, Yang G, Ning H, Yang M, Liu H, Chen W (2008) Plasma FGF-21 levels in type 2 diabetic patients with ketosis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 82:209–213
Stein S, Bachmann A, Lossner U, Kratzsch J, Bluher M, Stumvoll M, Fasshauer M (2009) Serum levels of the adipokine FGF21 depend on renal function. Diabetes Care 32:126–128
Lonnqvist F, Arner P, Nordfors L, Schalling M (1995) Overexpression of the obese (ob) gene in adipose tissue of human obese subjects. Nat Med 1:950–953
O’Rahilly S (2001) Leptin: pathophysiology and implications for therapy. Eat Weight Disord 6:21
Farooqi IS, Jebb SA, Langmack G, Lawrence E, Cheetham CH, Prentice AM, Hughes IA, McCamish MA, O’Rahilly S (1999) Effects of recombinant leptin therapy in a child with congenital leptin deficiency. N Engl J Med 341:879–884
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank Prof Mats Rudling, Prof Bo Angelin and Niklas Mejhert for valuable discussions during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rydén, M. Fibroblast growth factor 21: an overview from a clinical perspective. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 2067–2073 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0003-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0003-9