Abstract.
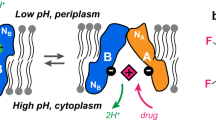
LmrP is an electrogenic H+/drug antiporter that extrudes a broad spectrum of antibiotics. Five carboxylic residues are implicated in drug binding (Asp142 and Glu327) and proton motive force-mediated restructuring (Asp68, Asp128 and Asp235). ATR-FTIR (Attenuated Total Reflection — Fourier Transform Infrared) and tryptophan quenching experiments revealed that phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) is required to generate the structural intermediates induced by ionization of carboxylic residues. Surprisingly, no ionization-induced conformational changes were detectable in the absence of PE, suggesting either that carboxylic acid residues do not ionize or that ionization does not lead to any conformational change. The mean pKa of carboxylic residues evaluated by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy was 6.5 for LmrP reconstituted in PE liposomes, whereas the pKa calculated in the absence of PE was 4.6. Considering that 16 of the 19 carboxylic residues are located in the extramembrane loops, the pKa values obtained in the absence and in the presence of PE suggest that the interaction of the loop acid residues with the membrane interface depends on the lipid composition.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 23 January 2007; received after revision 2 April 2007; accepted 20 April 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gbaguidi, B., Hakizimana, P., Vandenbussche, G. et al. Conformational changes in a bacterial multidrug transporter are phosphatidylethanolamine-dependent. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 64, 1571 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7031-0
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-007-7031-0