Abstract
Introduction
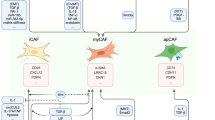
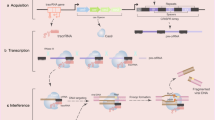
Chronic inflammation can affect the normal cell homeostasis and metabolism by rendering the cells susceptible to genomic instability that may lead to uncontrolled cellular growth and proliferation ensuing tumorigenesis. The causal agents for inflammation may be pathogenic infections like microbial agents ranging from viruses to bacteria. These infections lead to DNA damage or disruption of normal cell metabolism and alter the genome integrity.
Findings
In this review, we have highlighted the role of recurrent infections in tumor microenvironment can lead to recruitment of pro-inflammatory cells, cytokines and growth factors to the site of inflammation. This makes the environment rich in cytokines, chemokines, DNA-damaging agents (ROS, RNS) and growth factors which activate DNA damage response pathway and help in sustained proliferation of the tumor cells. In any inflammatory response, the production of cytokines and related signaling molecules is self-regulating and limiting. But in case of neoplastic risk, deregulation of these factors may lead to abnormalities and related pathogenesis.
Conclusion
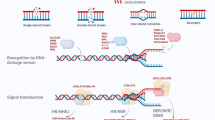
The scope of the present review is to explore the probable mechanistic link and factors responsible for chronic inflammation. The relation between chronic inflammation and DNA damage response was further elucidated to understand the mechanism by which it makes the cells susceptible to carcinogenesis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarkar D, Saha P, Gamre S, Bhattacharjee S, Hariharan C, Ganguly S, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of allylpyrocatechol in LPS-induced macrophages is mediated by suppression of iNOS and COX-2 via the NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2008;8:1264–71.
Vendramini-Costa DB, Carvalho JE. Molecular link mechanisms between inflammation and cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18:3831–52.
Wu Y, Antony S, Meitzler JL, Doroshow JH. Molecular mechanisms underlying chronic inflammation-associated cancers. Cancer Lett. 2014;345:164–73.
Kundu JK, Surh Y-J. Inflammation: gearing the journey to cancer. Mutat Res. 2008;659:15–30.
Clevers H. At the crossroads of inflammation and cancer. Cell. 2004;118:671–4.
Rakoff-Nahoum S. Why cancer and inflammation? Yale J Biol Med. 2006;79:123–30.
Roessner A, Kuester D, Malfertheiner P, Schneider-Stock R. Oxidative stress in ulcerative colitis-associated carcinogenesis. Pathol Res Pract. 2008;204:511–24.
Ghosal G, Chen J. DNA damage tolerance: a double-edged sword guarding the genome. Transl Cancer Res. 2013;2:107–29.
Rouse J, Jackson SP. Interfaces between the detection, signaling, and repair of DNA damage. Science. 2002;297:547–51.
Harper JW, Elledge SJ. The DNA damage response: ten years after. Mol Cell. 2007;28:739–45.
Jackson SP, Bartek J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature. 2009;461:1071–8.
Polo SE, Jackson SP. Dynamics of DNA damage response proteins at DNA breaks: a focus on protein modifications. Genes Dev. 2011;25:409–33.
O’Driscoll M, Jeggo PA. The role of double-strand break repair—insights from human genetics. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:45–54.
Khalil H, Tummala H, Chakarov S, Zhelev N, Lane D. Targeting ATM pathway for therapeutic intervention in cancer. Biodiscovery Dundee Science Press; 2012;1:3.
Kurz DJ, Decary S, Hong Y, Trivier E, Akhmedov A, Erusalimsky JD. Chronic oxidative stress compromises telomere integrity and accelerates the onset of senescence in human endothelial cells. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:2417–26.
Andreassen PR, Ho GPH, D’Andrea AD. DNA damage responses and their many interactions with the replication fork. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27:883–92.
Li W, Tian D, Guan X, Yun H, Wang H, Xiao Y, et al. Esophageal intraepithelial invasion of Helicobacter pylori correlates with atypical hyperplasia. Int J Cancer. 2014;134:2626–32.
Blanco D, Vicent S, Fraga MF, Fernandez-Garcia I, Freire J, Lujambio A, et al. Molecular analysis of a multistep lung cancer model induced by chronic inflammation reveals epigenetic regulation of p16 and activation of the DNA damage response pathway. Neoplasia. 2007;9:840–52.
Gerić M, Gajski G, Garaj-Vrhovac V. γ-H2AX as a biomarker for DNA double-strand breaks in ecotoxicology. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2014;105:13–21.
He H, Wang C, Shen Z, Fang Y, Wang X, Chen W, et al. Upregulated expression of C–X–C chemokine receptor 4 is an independent prognostic predictor for patients with gastric cancer. PLoS One. 2013;8:e71864.
Guo F, Li J, Du W, Zhang S, O’Connor M, Thomas G, et al. mTOR regulates DNA damage response through NF-κB-mediated FANCD2 pathway in hematopoietic cells. Leukemia. 2013;27:2040–6.
Sobolewski C, Cerella C, Dicato M, Ghibelli L, Diederich M. The role of cyclooxygenase-2 in cell proliferation and cell death in human malignancies. Int J Cell Biol. 2010;2010:215158.
Medzhitov R, Janeway C. Innate immunity. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:338–44.
Takahashi H, Ogata H, Nishigaki R, Broide DH, Karin M. Tobacco smoke promotes lung tumorigenesis by triggering IKKbeta- and JNK1-dependent inflammation. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:89–97.
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 2010;140:883–99.
Itzkowitz SH, Yio X. Inflammation and cancer IV. Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: the role of inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;287:G7–17.
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108.
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008;454:436–44.
Meira LB, Bugni JM, Green SL, Lee C-W, Pang B, Borenshtein D, et al. DNA damage induced by chronic inflammation contributes to colon carcinogenesis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:2516–25.
Padhi S, Saha A, Kar M, Ghosh C, Adhya A, Baisakh M, et al. Clinico-pathological correlation of β-catenin and telomere dysfunction in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. J Cancer. 2015;6:192–202.
Lu H, Ouyang W, Huang C. Inflammation, a key event in cancer development. Mol Cancer Res. 2006;4:221–33.
Lin W-W, Karin M. A cytokine-mediated link between innate immunity, inflammation, and cancer. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:1175–83.
Santibañez JF, Quintanilla M, Bernabeu C. TGF-β/TGF-β receptor system and its role in physiological and pathological conditions. Clin Sci (Lond). 2011;121:233–51.
Smyth MJ, Cretney E, Kershaw MH, Hayakawa Y. Cytokines in cancer immunity and immunotherapy. Immunol Rev. 2004;202:275–93.
Szlosarek P, Charles KA, Balkwill FR. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha as a tumour promoter. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42:745–50.
Charles KA, Kulbe H, Soper R, Escorcio-Correia M, Lawrence T, Schultheis A, et al. The tumor-promoting actions of TNF-alpha involve TNFR1 and IL-17 in ovarian cancer in mice and humans. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:3011–23.
Tang Q, Li J, Zhu H, Li P, Zou Z, Xiao Y. Hmgb1-IL-23-IL-17-IL-6-Stat3 axis promotes tumor growth in murine models of melanoma. Mediat Inflamm. 2013;2013:713859.
Hodge DR, Hurt EM, Farrar WL. The role of IL-6 and STAT3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41:2502–12.
Schottelius AJ, Mayo MW, Sartor RB, Baldwin AS. Interleukin-10 signaling blocks inhibitor of kappaB kinase activity and nuclear factor kappaB DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:31868–74.
Coussens LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 2002;420:860–7.
Kujawski M, Kortylewski M, Lee H, Herrmann A, Kay H, Yu H. Stat3 mediates myeloid cell-dependent tumor angiogenesis in mice. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:3367–77.
Yang L, Huang J, Ren X, Gorska AE, Chytil A, Aakre M, et al. Abrogation of TGF beta signaling in mammary carcinomas recruits Gr-1+ CD11b+ myeloid cells that promote metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2008;13:23–35.
Federico A, Morgillo F, Tuccillo C, Ciardiello F, Loguercio C. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress in human carcinogenesis. Int J Cancer. 2007;121:2381–6.
Weyemi U, Lagente-Chevallier O, Boufraqech M, Prenois F, Courtin F, Caillou B, et al. ROS-generating NADPH oxidase NOX4 is a critical mediator in oncogenic H-Ras-induced DNA damage and subsequent senescence. Oncogene. 2012;31:1117–29.
Roque AT, Gambeloni RZ, Felitti S, Ribeiro ML, Santos JC. Inflammation-induced oxidative stress in breast cancer patients. Med Oncol. 2015;32:263.
Gorgoulis VG, Halazonetis TD. Oncogene-induced senescence: the bright and dark side of the response. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010;22:816–27.
Moore RJ, Owens DM, Stamp G, Arnott C, Burke F, East N, et al. Mice deficient in tumor necrosis factor-alpha are resistant to skin carcinogenesis. Nat Med. 1999;5:828–31.
Woo CH, Eom YW, Yoo MH, You HJ, Han HJ, Song WK, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha generates reactive oxygen species via a cytosolic phospholipase A2-linked cascade. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:32357–62.
Hussain SP, Hofseth LJ, Harris CC. Radical causes of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:276–85.
Coward J, Kulbe H, Chakravarty P, Leader D, Vassileva V, Leinster DA, et al. Interleukin-6 as a therapeutic target in human ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:6083–96.
Song L, Rawal B, Nemeth JA, Haura EB. JAK1 activates STAT3 activity in non-small-cell lung cancer cells and IL-6 neutralizing antibodies can suppress JAK1-STAT3 signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10:481–94.
Dorff TB, Goldman B, Pinski JK, Mack PC, Lara PN, Van Veldhuizen PJ, et al. Clinical and correlative results of SWOG S0354: a phase II trial of CNTO328 (siltuximab), a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-6, in chemotherapy-pretreated patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:3028–34.
Yu H, Pardoll D, Jove R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:798–809.
Jakowlew SB. Transforming growth factor-beta in cancer and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006;25:435–57.
Bierie B, Moses HL. TGF-beta and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2006;17:29–40.
Galizia G, Orditura M, Romano C, Lieto E, Castellano P, Pelosio L, et al. Prognostic significance of circulating IL-10 and IL-6 serum levels in colon cancer patients undergoing surgery. Clin Immunol. 2002;102:169–78.
Schottenfeld D, Beebe-Dimmer J. Chronic inflammation: a common and important factor in the pathogenesis of neoplasia. CA Cancer J Clin. 2006;56:69–83.
Roy S, Chakraborty A, Ghosh C, Banerjee B. Systematic analysis of integrated gene functional network of four chronic stress-related lifestyle disorders. Genome Integr. 2015;6:1.
Bao Z, Xiong J, Li W, Chen Z, Shen H, Ying S. Genomic instability in chronic airway inflammatory diseases. Biomed J. 2015;38:117–24.
Trachootham D, Lu W, Ogasawara MA, Nilsa R-DV, P Huang. Redox regulation of cell survival. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008;10:1343–74.
Poonepalli A, Banerjee B, Ramnarayanan K, Palanisamy N, Putti TC, Hande MP. Telomere-mediated genomic instability and the clinico-pathological parameters in breast cancer. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2008;47:1098–109.
Bhattacharjee RN, Banerjee B, Akira S, Hande MP. Telomere-mediated chromosomal instability triggers TLR4 induced inflammation and death in mice. PLoS One. 2010;5:e11873.
Wiseman H, Kaur H, Halliwell B. DNA damage and cancer: measurement and mechanism. Cancer Lett. 1995;93:113–20.
Gates KS. An overview of chemical processes that damage cellular DNA: spontaneous hydrolysis, alkylation, and reactions with radicals. Chem Res Toxicol. 2009;22:1747–60.
Cooke MS, Evans MD, Dizdaroglu M, Lunec J. Oxidative DNA damage: mechanisms, mutation, and disease. FASEB J. 2003;17:1195–214.
Huang Y, Li L. DNA crosslinking damage and cancer—a tale of friend and foe. Transl Cancer Res. 2013;2:144–54.
Kryston TB, Georgiev AB, Pissis P, Georgakilas AG. Role of oxidative stress and DNA damage in human carcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 2011;711:193–201.
Tominaga H, Kodama S, Matsuda N, Suzuki K, Watanabe M. Involvement of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the induction of genetic instability by radiation. J Radiat Res. 2004;45:181–8.
Shen Z. Genomic instability and cancer: an introduction. J Mol Cell Biol. 2011;3:1–3.
Aguilera A, García-Muse T. Causes of genome instability. Annu Rev Genet. 2013;47:1–32.
Hakem R. DNA-damage repair; the good, the bad, and the ugly. EMBO J. 2008;27:589–605.
Ogrunc M, Di Micco R, Liontos M, Bombardelli L, Mione M, Fumagalli M, et al. Oncogene-induced reactive oxygen species fuel hyperproliferation and DNA damage response activation. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21:998–1012.
Roth S, Rottach A, Lotz-Havla AS, Laux V, Muschaweckh A, Gersting SW, et al. Rad50-CARD9 interactions link cytosolic DNA sensing to IL-1β production. Nat Immunol. 2014;15:538–45.
Kondo T, Kobayashi J, Saitoh T, Maruyama K, Ishii KJ, Barber GN, et al. DNA damage sensor MRE11 recognizes cytosolic double-stranded DNA and induces type I interferon by regulating STING trafficking. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:2969–74.
Muralidharan S, Mandrekar P. Cellular stress response and innate immune signaling: integrating pathways in host defense and inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. 2013;94:1167–84.
Ferguson BJ, Mansur DS, Peters NE, Ren H, Smith GL. DNA-PK is a DNA sensor for IRF-3-dependent innate immunity. Elife. 2012;1:e00047.
Gasser S, Orsulic S, Brown EJ, Raulet DH. The DNA damage pathway regulates innate immune system ligands of the NKG2D receptor. Nature. 2005;436:1186–90.
Miyamoto S. Nuclear initiated NF-κB signaling: NEMO and ATM take center stage. Cell Res. 2011;21:116–30.
Lim JW, Kim H, Kim KH. Expression of Ku70 and Ku80 mediated by NF-kappa B and cyclooxygenase-2 is related to proliferation of human gastric cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:46093–100.
Fang L, Choudhary S, Zhao Y, Edeh CB, Yang C, Boldogh I, et al. ATM regulates NF-κB-dependent immediate-early genes via RelA Ser 276 phosphorylation coupled to CDK9 promoter recruitment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:8416–32.
Xue W, Zender L, Miething C, Dickins RA, Hernando E, Krizhanovsky V, et al. Senescence and tumour clearance is triggered by p53 restoration in murine liver carcinomas. Nature. 2007;445:656–60.
Takaoka A, Hayakawa S, Yanai H, Stoiber D, Negishi H, Kikuchi H, et al. Integration of interferon-α/β signalling to p53 responses in tumour suppression and antiviral defence. Nature. 2003;424:516–23.
Moiseeva O, Mallette FA, Mukhopadhyay UK, Moores A, Ferbeyre G. DNA damage signaling and p53-dependent senescence after prolonged beta-interferon stimulation. Mol Biol Cell. 2006;17:1583–92.
Niida H, Murata K, Shimada M, Ogawa K, Ohta K, Suzuki K, et al. Cooperative functions of Chk1 and Chk2 reduce tumour susceptibility in vivo. EMBO J. 2010;29:3558–70.
Xu M, Yu Q, Subrahmanyam R, Difilippantonio MJ, Ried T, Sen JM. Beta-catenin expression results in p53-independent DNA damage and oncogene-induced senescence in prelymphomagenic thymocytes in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 2008;28:1713–23.
Cordon-Cardo C. At the crossroad of tumorigenesis: drivers and hitchhikers. Hum Pathol. 1999;30:1001–3.
Lawrence T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2009;1:a001651.
Dvorak HF. Rous-Whipple Award Lecture. How tumors make bad blood vessels and stroma. Am J Pathol. 2003;162:1747–57.
Bubici C, Papa S, Pham CG, Zazzeroni F, Franzoso G. The NF-kB-mediated control of ROS and JNK signaling. Histol Histopathol. 2006;21:69–80.
Herrero R, Castellsagué X, Pawlita M, Lissowska J, Kee F, Balaram P, et al. Human papillomavirus and oral cancer: the International Agency for Research on Cancer multicenter study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2003;95:1772–83.
Yu H, Lee H, Herrmann A, Buettner R, Jove R. Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: new and unexpected biological functions. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14:736–46.
Kim Y-H, Woo KJ, Lim JH, Kim S, Lee TJ, Jung EM, et al. 8-Hydroxyquinoline inhibits iNOS expression and nitric oxide production by down-regulating LPS-induced activity of NF-κB and C/EBPβ in Raw 264.7 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;329:591–7.
Tatemichi M, Sawa T, Gilibert I, Tazawa H, Katoh T, Ohshima H. Increased risk of intestinal type of gastric adenocarcinoma in Japanese women associated with long forms of CCTTT pentanucleotide repeat in the inducible nitric oxide synthase promoter. Cancer Lett. 2005;217:197–202.
Li Q, Verma IM. NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:725–34.
Ricciotti E, FitzGerald GA. Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31:986–1000.
Polakis P. Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes Dev. 2000;14:1837–51.
Angelova M, Zwezdaryk K, Ferris M, Shan B, Morris CA, Sullivan DE. Human cytomegalovirus infection dysregulates the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. PLoS Pathog (Public Library of Science). 2012;8:e1002959.
Atherton JC. The pathogenesis of helicobacter pylori-induced gastro-duodenal diseases. Annu Rev Pathol. 2006;1:63–96.
Gold JS, Bayar S, Salem RR. Association of Streptococcus bovis bacteremia with colonic neoplasia and extracolonic malignancy. Arch Surg. 2004;139:760–5.
Marnett LJ. Oxyradicals and DNA damage. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:361–70.
Yu MC, Yuan J-M. Environmental factors and risk for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S72–8.
Masarone M, Persico M. Antiviral therapy: why does it fail in HCV-related chronic hepatitis? Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2011;9:535–43.
Levrero M. Viral hepatitis and liver cancer: the case of hepatitis C. Oncogene. 2006;25:3834–47.
Laurent-Puig P, Zucman-Rossi J. Genetics of hepatocellular tumors. Oncogene. 2006;25:3778–86.
Bosch FX, de Sanjosé S. Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer–burden and assessment of causality. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 2003;31:3–13.
Tartour E, Gey A, Sastre-Garau X, Pannetier C, Mosseri V, Kourilsky P, et al. Analysis of interleukin 6 gene expression in cervical neoplasia using a quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay: evidence for enhanced interleukin 6 gene expression in invasive carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1994;54:6243–8.
Castrilli G, Tatone D, Diodoro MG, Rosini S, Piantelli M, Musiani P. Interleukin 1alpha and interleukin 6 promote the in vitro growth of both normal and neoplastic human cervical epithelial cells. Br J Cancer. 1997;75:855–9.
Nasca MR, Innocenzi D, Micali G. Penile cancer among patients with genital lichen sclerosus. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;41:911–4.
Aituov B, Duisembekova A, Bulenova A, Alibek K. Pathogen-driven gastrointestinal cancers: time for a change in treatment paradigm? Infect Agent Cancer. 2012;7:18.
Shibata D, Weiss LM. Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric adenocarcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1992;140:769–74.
Del Valle L, White MK, Khalili K. Potential mechanisms of the human polyomavirus JC in neural oncogenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008;67:729–40.
Abenavoli L, Masarone M, Peta V, Milic N, Kobyliak N, Rouabhia S, et al. Insulin resistance and liver steatosis in chronic hepatitis C infection genotype 3. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:15233–40.
Marnett LJ. Inflammation and cancer: chemical approaches to mechanisms, imaging, and treatment. J Org Chem. 2012;77:5224–38.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the rant from Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Govt. of India, and Grant Number: MED/2013/93 (BT/519/NE/TBP/2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The manuscript complies with ethical standards.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anuja, K., Roy, S., Ghosh, C. et al. Prolonged inflammatory microenvironment is crucial for pro-neoplastic growth and genome instability: a detailed review. Inflamm. Res. 66, 119–128 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-016-0985-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-016-0985-3