Abstract
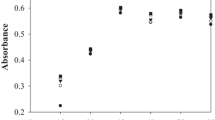
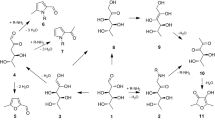
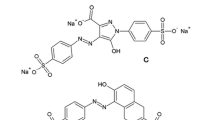
In the European Union, carminic acid and its ammonium, calcium, potassium or sodium salts and its aluminium lakes are approved as food additive E120. In beverages obtained from the German market 4-aminocarminic acid (“acid-stable carmine”) was detected by HPLC–PDA and LC–MS/MS. Isolation of the colorant from a liquid dye preparation used for the production of a beverage sample and subsequent NMR analysis confirmed the presence of 4-aminocarminic acid. Synthesis of 15N-4-aminocarminic acid clearly demonstrated that “acid-stable carmine” is not the ammonium salt of carminic acid, which is approved as food additive in the European Union. In fact, nitrogen in “acid-stable carmine” is covalently bound. The molecular structure of carminic acid is chemically modified and 4-aminocarminic acid does not comply with the specifications laid down for E120 in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012. 4-Aminocarminic acid was also detected in the red-colored glaze of a raspberry cake and in the liquid dye preparation used for coloring this glaze.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dapson RW (2005) A method for determining identity and relative purity of carmine, carminic acid and aminocarminic acid. Biotech Histochem 80:201–205
Dapson RW (2006) Erratum (A method for determining identity and relative purity of carmine, carminic acid and aminocarminic acid). Biotech Histochem 81:55
Dapson RW (2007) The history, chemistry and modes of action of carmine and related dyes. Biotech Histochem 82:173–187
Dapson RW, Frank M, Penney DP, Kiernan JA (2007) Revised procedures for the certification of carmine (C.I. 75470, Natural red 4) as a biological stain. Biotech Histochem 82:13–15
European Commission (2012) Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 of 9 March 2012 laying down specifications for food additives listed in Annexes II and III to Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council. Off J Eur Union L 83:1–295 22.3.2012
European Parliament and Council (2008) Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on food additives. Off J Eur Union L 354:16–33 31.12.2008
Gosetti F, Chiuminatto U, Mastroianni R, Mazzucco E, Manfredi M, Marengo E (2015) Retrospective analysis for the identification of 4-aminocarminic acid photo-degradation products in beverages. Food Addit Contam A 32:285–292
Kawasaki Y, Sugimoto N, Sato K, Yamazaki T, Ishiwata H, Maitani T (2002) Identification of acid-stable carmine in imported apple syrup product. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi (J Food Hyg Soc Jpn) 43:191–195
Sabatino L, Scordino M, Gargano M, Lazzaro F, Borzí MA, Traulo P, Gagliano G (2012) Aminocarminic acid in E120-labelled food additives and beverages. Food Addit Contam B 5:295–300
Schul J (1992) Colorant based on carminic acid, method of preparation, and method of coloring a foodstuff. US Patent Number 5(147):673
Schulze F, Titus J, Mettke P, Berger S, Siehl H-U, Zeller K-P, Sicker D (2013) Karminsäure—Das Rot aus Cochenilleläuse. Chem unserer Zeit 47:222–228
Stathopoulou K, Valianou L, Skaltsounis A-L, Karapanagiotis I, Magiatis P (2013) Structure elucidation and chromatographic identification of anthraquinone components of cochineal (Dactylopius coccus) detected in historical objects. Anal Chim Acta 804:264–272
Sugimoto N, Kawasaki Y, Sato K, Aoki H, Ichi T, Koda T, Yamazaki T, Maitani T (2002) Structure of acid-stable carmine. Shokuhin Eiseigaku Zasshi (J Food Hyg Soc Jpn) 43:18–23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, A., Lassek, E., Pfister, J. et al. Detection of 4-aminocarminic acid in beverages and cake glaze from the German market: a food additive not approved in the EU. J. Verbr. Lebensm. 11, 127–135 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-015-1012-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-015-1012-2