Summary
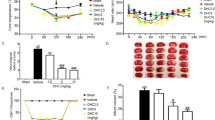
The effect of dilazep dihydrochloride (dilazep) against ischemia and reperfusion-induced disruption of blood-brain barrier (BBB) was quantitatively investigated in Slc:Wistar strain rats using Evans blue dye as a BBB destruction indicator. The forebrain of sham-operated animal had a small amount of the dye. A treatment of 3.5-h ischemia plus 2-h reflow extravasated the dye into the brain and markedly increased the dye content as compared with that of sham group (P < 0.01 vs. sham group). Continuous infusion (i.v.) of dilazep during cerebral ischemia dose-dependently reduced the increase of the dye content, and a significant reduction was found at 3 mg/kg/h (P < 0.05 vs. control group). Evans blue dye extravasation after ischemia was also greatly reduced in saline-perfused brains by the treatment with dilazep. Dilazep has been reported to inhibit edema formation in cerebral ischemia model of spontaneously hypertensive rats. These results suggest that dilazep prevents the ischemic damage of BBB, which may contribute to reduction of the brain edema.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auer L (1977) Brain edema in acute arterial hypertension I. Macroscopical findings. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 38:67–72
Bhakoo KK, Crockard HA, Lascelles PC, Avery SF (1984) Prostaglandin synthesis and oedema formation during reperfusion following experimental brain ischemia in the gerbil. Stroke 15:891–895
Buynski JP, Losada M, Bierwagen ME, Gardier RW (1972) Cerebral and coronary vascular effects of a symmetrical N,N′-disubstituted hexahydrodiazepine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 181:522–528
Hattori M, Ogawa K, Satake T, Sugiyama S, Ozawa T (1985) Depletion of membrane phospholipid and mitochondrial dysfunction associated with coronary reperfusion. Basic Res Cardiol 80: 241–250
Iannotti F, Hoff J (1983) Ischemic brain edema with and without reperfusion: An experimental study in gerbils. Stroke 14:562–567
Ito M, Go KG, Walker Jr T, Spatz JM, Klatzo I (1976) Experimental cerebral ischemia in mongolian gerbils III. Behavior of the blood-brain barrier. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 34:1–6
Ito U, Ohno N, Nakamura R, Suganuma F, Inaba Y (1979) Brain edema during ischemia and after restoration of blood flow measurement of water, sodium, potassium content and plasma protein permeability. Stroke 10:542–547
Ito U, Ohno K, Yamaguchi T, Takei H, Tomita H, Inaba Y (1980) Effect of hypertension of blood-brain barrier change after restoration of blood flow in post-ischemic gerbil brains. An electron-microscopic study. Stroke 11:606–611
Itoh T, Kawakami M, Yamauchi Y, Shimizu S, Nakamura M (1986) Effect of allopurinol on ischemia and reperfusion-induced cerebral injury in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Stroke 17:1284–1287
Katayama S, Shionoya H, Ohtake S (1978) A new method for extraction of extravasated dye in the skin and the influence of fasting stress on passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in guinea pigs and rats. Microbiol Immunol 22:89–101
Katzman R, Clasen CR, Klatzo I, Meyer JS, Pappius HM, Waltz AG (1977) Brain edema in stroke. Stroke 8:512–540
Klatzo I (1967) Neuropathological aspects of brain edema. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 26:1–14
Kogure K, Busto R, Scheinberg P (1981) The role of hydrostatic pressure in ischemic brain edema. Ann Neurol 9:273–282
Kuroiwa T, Ting P, Martinez H, Klatzo I (1985) The biphasic opening of the blood-brain barrier to proteins following temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 68:122–129
Persson LI, Rosengren LE, Johansson BB (1980) Albumin extravasation in bicuculline-induced blood-brain barrier dysfunction. Acta Neurol Scand 62:259–262
Rawson R (1943) The binding of T-1824 and structurally related diazo dyes by the plasma proteins. Am J Physiol 138:708–717
Sadoshima S, Fujishima M, Ogata J, Ibayashi S, Shiokawa O, Omae T (1983) Distribution of blood-brain barrier following bilateral carotid artery occlusion in spontaneously hypertensive rats. A quantitative study. Stroke 14:876–882
Sano N (1974) Enhancement of coronary vasodilating action of adenosine by dilazep and dipyridamole in the dog. Jpn J Pharmacol 24:471–478
Sano N, Katsuki S, Kawada M (1972) Enhancement of coronary vasodilator action of adenosine by 1,4-bis-[3-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl-oxy)-propyl]-perhydro-1,4-diazepine (dilazep I.N.N.). Arzneim-Forsch (Drug Res) 22:1655–1658
Schubert P, Dux E (1990) Selective neuronal death in cerebral ischemia and protective mechanisms. In: Schurr A, Rigor BM (eds) Cerebral ischemia and resuscitation. CRC Press, Boston, pp 259–269
Seida M, Wagner HG, Vass K, Klatzo I (1988) Effect of aminophylline on postischemic edema and brain damage in cats. Stroke 19:1275–1282
Steinwall O, Klatzo I (1966) Selective vulnerability of the blood-brain barrier in chemically induced lesions. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 25: 542–559
Sztriha L, Joo F, Szerdahelyi P, Eck E, Koltai M (1986) Effects of dexamethasone on brain edema induced by kainic acid seizures. Neuroscience 17:107–114
Ueura T, Tamura A, Kirino T, Mizuno S, Karasawa S, Kanemitsu H, Sano K (1985) Bilateral common carotid arteries occlusion model in wistar rats. Abstr 26th Soc Jpn Neurol pp 30
Uyama O, Okamura N, Yanase M, Narita M, Kawabata K, Sugita M (1988) Quantitative evaluation of vascular permeability in the gerbil brain after transient ischemia using evans blue fluorescence. J Cerebr Blood Flow Metab 8:282–284
Yamauchi Y, Ikuta J, Shimizu S, Nakamura M (1990) Effect of dilazep dihydrochloride on ischemia and reperfusion-induced cerebral injury in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Folia Pharmacol Jpn 95:239–246
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send of fprint requests to J. Kawagoe at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawagoe, Ji., Abe, K., Ikuta, J. et al. Effect of dilazep dihydrochloride against ischemia and reperfusion-induced disruption of blood-brain barrier in rats: a quantitative study. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 345, 485–488 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00176629
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00176629