Abstract
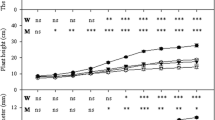
The effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activities on the drought-resistance of Hippophae rhamnoides under water stress have been studied using histochemical techniques. The result shows in the mycorrhizae that total hyphae and functional hyphae form the base for the active hyphae, and amounts follow the order total hyphae>functional hyphae>active hyphae. Active hyphae play an important role in the biomass accumulation of the hosts; the hyphae with phosphatase activity (ALP) have a positive and strong effect on H. rhamnoides growth and its drought-resistance, and the rise of ALP is related to an increase in the fresh weight of the host trees, and a reduction of wilting. The direct participation of ALP in the P nutrient exchange host trees can improve the nutrient and water conditions, and raise their drought-resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 17 August 1998 / Accepted: 18 March 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ming, T., Hui, C. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alkaline phosphatase activities on Hippophae rhamnoides drought-resistance under water stress conditions. Trees 14, 113–115 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009757
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00009757