Abstract
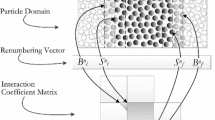
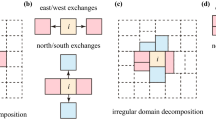
A parallel algorithm suitable for simulating multi-sized particle systems and multiphase fluid systems is proposed based on macro-scale pseudo-particle modeling (MaPPM). The algorithm employs space-decomposition of the computational load among the processing elements (PEs) and multi-level cell-subdivision technique for particle indexing. In this algorithm, a 2D gas-solid system is simulated with the temporal variations of drags on solids, inter-phase slip velocities and solids concentration elaborately monitored. Analysis of the results shows that the algorithm is of good parallel efficiency and scalability, demonstrating the unique advantage of MaPPM in simulating complex flows.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Monaghan, J. J., Smoothed particle hydrodynamics, Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys., 1992, 30: 543–574.
Liu, W. K., Hao, S., Multiple scale meshfree methods for damage fracture and localization, Computational Materials Science, 1999, 16: 197–205.
Cundall, P. A., Strack, O. D. L., A discrete numerical model for granular assemblies, Géotechnique, 1979, 29(1): 47–65.
Hoogerbrugge, P. J., Koelman, J. M. V. A., Simulating microscopic hydrodynamic phenomena with dissipative particle dynamics, Europhys. Lett., 1992,19(3): 155–160.
Boek, E. S., Coveney, P. V., Lekkerkerker, H. N. W., Computer simulation of rheological phenomena in dense colloidal suspensions with dissipative particle dynamics, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 1996, 8: 9509–9512.
Gibson, J. B., Chen, K., Chynoweth, S., Simulation of particle adsorption onto a polymer coated surface using the dissipative particle dynamics method, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1998, 206: 464–474.
Ge, W., Li, J., Pseudo-particle approach to hydrodynamics of gas/solid two-phase flow, Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Circulating Fluidized Bed, Beijing, China, Bijing: Science Press, 1996, 260–265.
Le, J., Wen, L., Ge, W. et al., Dissipative structure in concurrent-up-gas-solid flow, Chemical Engineering Science, 1998, 53(19): 3367–3379.
Ferrez, J. A., Dynamic triangulations for efficient 3D simulation of granular materials, Doctor Dissertation, Lausanne, EPFL, France, 2001, 9–31.
Ge, W., Li, J., Macro-scale pseudo-particle modeling for particle-fluid systems, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(18): 1503–1507.
Ge, W., Li, J., Macro-scale phenomena reproduced in microscopic systems—pseudo-particle modeling of fluidization, Chemical Engineering Science, 2003, 58: 1565–1585.
Ge, W., Multi-scale simulation of fluidization, Doctor Dissertation, Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 1998, 18–36.
Rapaport, D. C., The art of molecular dynamics simulation, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1995, 47–58, 332-334.
Plimpton, S., Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics, J. Comput. Phys., 1995, 117: 1–19.
Wang, X., Guo, L., Tang, D. et al., Parallel algorithm of two-phase Macro-scale pseudo-particle modeling, J. Chem. Indust. Eng., 2004, 55(5): 716–720.
Ge, W., Zhang, J., Li, T. et al., Pseudo-particle simulation of multi-scale heterogeneity in fluidization, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(7): 634–636.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, D., Ge, W., Wang, X. et al. Parallelizing of macro-scale pseudo-particle modeling for particle-fluid systems. Sc. China Ser. B-Chem. 47, 434–442 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990905
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990905