Abstract
Background
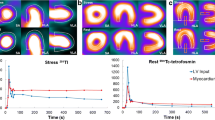
Technetium 99m tetrofosmin is a new ethylene diphosphine ligand for myocardial perfusion imaging and has unique properties. We have compared stress-rest single-photon emission computed tomographic (SPECT) imaging with99mTc tetrofosmin with same-day and separate-day rest imaging to detect myocardial perfusion defects.
Methods and Results
Myocardial SPECT imaging was performed in 22 patients with coronary artery disease who had undergone planar thallium 201 imaging and coronary angiography. Single-day (stress-rest) and separate-day rest99mTc tetrofosmin SPECT protocols were compared in the same patient. Images were assessed by a blinded panel to identify myocardial infarction, ischemia, or normal scans. Overall sensitivity for identification of patients with coronary artery disease was 86% (19/22) by both same-day stress-rest and separate-day rest protocols with99mTc tetrofosmin (p=NS). Of a total of 396 segments studied, 107 abnormal segments were identified at exercise and 76 and 81 at the same-day and separate-day rest tests, respectively (p=NS). Same-day stress-rest and separate-day rest99mTc tetrofosmin SPECT protocols were also useful for detecting individual coronary stenosis with a greater than 50% lesion: 80% of the left anterior descending, 93% of the right coronary, and 75% of the left circumflex coronary arteries were detected.
Conclusion
Excellent images were obtained with99mTc tetrofosmin during both stress and rest.99mTc tetrofosmin imaging with the same-day stress-rest and separate-day rest imaging protocols have similar diagnostic sensitivities for detection of coronary heart disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pohost GM, Zir LM, Moore RM, Guiney TE, Beller GAA. Differentiation of transiently ischemic from infarcted myocardium by serial imaging after a single dose of thallium-201. Circulation 1979;55:294–302.
Okada RG, Boucher CA, Strauss HW, Pohost GM. Exercise radionuclide imaging approaches to coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 1980;46:1188–204.
Brown KA, Boucher CA, Okada RD, et al. Prognostic value of exercise thallium-201 imaging in patients presenting for evaluation of chest pain. J Am Coll Cardiol 1983;4:994–1001.
Gibson RS, Watson DD, Craddock GB, et al. Prediction of cardiac events after uncomplicated myocardial infarction: a prospective study comparing predischarge exercise thallium-201 scintigraphy and coronary angiography. Circulation 1983;68:321–36.
Strauss H, Pitt B. Thallium-201 as a myocardial perfusion imaging agent. Semin Nucl Med 1977;7:3–7.
Deutsch E, Glavan KA, Sodd VJ, Nishiyama H, Ferguson DL, Lukes SJ. Cationic Tc-99m complexes as potential myocardial imaging agents. J Nucl Med 1981;22:897–907.
Holman LB, Jones AG, Lister-James J, et al. A new Tc-99m-labelled myocardial imaging agent, hexakis(t-butyliso-nitrile) technetium(I) [Tc-99m TBI]: initial experience in the human. J Nucl Med 1984;25:1350–5.
Johnson LL, Seldin DW. Clinical experience with Technetium-99m-teboroxime, a neutral, lipophilic myocardial perfusion imaging agent. Am J Cardiol 1990;66:63E-7E.
Lahiri A, Higley B, Smith T, et al. Myocardial perfusion imaging in man using new Tc-99m-labelled diphosphine complexes [Abstract]. Nucl Med Commun 1989; 10:245.
Wackers FJ, Berman DS, Maddahi J, et al. Technetium 99m hexakis 2-methoxyisobutyl isonotrile: human bio-distribution, dosimetry, safety and preliminary comparison to thallium-201 for myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Med 1989;30:301–11.
Iskandrian A, Heo J, Nguyen T, Mercuro J. Myocardial imaging with Tc-99m teboroxime: technique and initial results. Am Heart J 1991;121:889–94.
Berman DS, Kiat H, Maddahi M. The new Tc-99m myocardial perfusion imaging agents: Tc-99m-sesta-mibi and Tc-99m-teboroxime. Circulation 1991;84 (suppl): I-7–I-21.
Okada RD, Glover D, Gaffeny T, Williams S. Myocardial kinetics of technetium-99m-hexakis-2-methoxy-2-methoxypropyl isonotrile. Circulation 1988;77:491–8.
Kelly JD, Higley B, Archer CM, et al. New functionalized diphosphine complexes of Tc-99m for myocardial perfusion imaging [Abstract]. J Nucl Med 1989;30:773.
Kelly JD, Higley B, Archer CM, et al. Technetium-99m complexes of functionalized diphosphines for myocardial imaging. In: Nicolini M, Bandoli G, Mazzi U, eds. Technetium and rhenium in chemistry and nuclear medicine 3. New York: Raven Press, 1990:405–12.
Kelly JD, Foster AM, Higley B, et al. Tc-99m tetrofosmin as a new radiopharmaceutical for myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Med 1993;34:222–7.
Higley B, Lahiri A, Kelly JD. Technetium-99m complexes of functionalised diphosphines for myocardial perfusion imaging in man. In: Van Der Wall EE, Sochor H, Righetti A, Niemeyer MG, eds. What’s new in cardiac imaging. Dorchecht: Kluver Academic Publisher, 1992:93–109.
Higley B, Smith FW, Smith T, et al. Technetium-99m phosphino-ether complexes: technetium-99m tetrofosmin as a new radiopharmaceutical for myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Med 1993;34:30–8.
Taillefer R, Primeau M, Costi P, Labert R, Leveille J, Latour Y. Tc-99m-sestamibi myocardial perfusion imaging in detection of coronary artery disease: comparison between initial (1 hour) and delayed (3 hour) post exercise images. J Nucl Med 1991;32:1961–5.
Sridhara BS, Braat S, Itti R, Rigo P, Cload P, Lahiri A. Early and late myocardial imaging with a new technetium-99m diphosphine (PPN1011) in coronary artery disease [Abstract]. J Am Coll Cardiol 1992;19:202A.
Sridhara BS, Braat S, Rigo P, Itti R, Cload P, Lahiri A. Comparison of myocardial perfusion imaging with99mTc tetrofosmin versus201Tl in coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol 1993;72:1015–9.
Kiat H, Maddahi J, Roy LT, et al. Comparison of technetium 99m methoxy isobutyl isonitrile and thallium-201 for evaluation of coronary artery disease by planar and tomographic methods. Am Heart J 1989; 117:1–11.
Van Train K, Berman DS, Garcia EV, et al. Quantitative analysis of stress thallium-201 myocardial scintigrams: a multicenter trial. J Nucl Med 1986;27:17–25.
Prigent F, Maddahi J, Garcia E, et al. Non-invasive quantification of the extent of jeopardized myocardium in patients with single-vessel disease by stress thallium-201 single photon emission computerized rotational tomography. Am Heart J 1986;111:578–86.
Rigo P, Braat S, Itti R, et al. Myocardial imaging with technetium-99m P53: comparison with thallium in suspected coronary artery disease [Abstract]. J Am Coll Cardiol 1992;19:202A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sridhara, B., Sochor, H., Rigo, P. et al. Myocardial single-photon emission computed tomographic imaging with technetium 99m tetrofosmin: Stress-rest imaging with same-day and separate-day rest imaging. J Nucl Cardiol 1, 138–143 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02984085
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02984085