Abstract
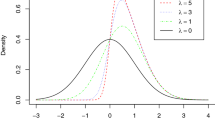
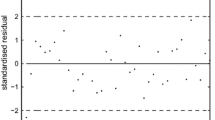
The local influence method plays an important role in regression diagnostics and sensitivity analysis. To implement it, we need the Delta matrix for the underlying scheme of perturbations, in addition to the observed information matrix under the postulated model. Galea, Paula and Bolfarine (1997) has recently given the observed information matrix and the Delta matrix for a scheme of scale perturbations and has assessed of local influence for elliptical linear regression models. In the present paper, we consider the same elliptical linear regression models. We study the schemes of scale, predictor and response perturbations, and obtain their corresponding Delta matrices, respectively. To illustrate the methodology for assessment of local influence for these schemes and the implementation of the obtained results, we give an example.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiktson, A.C. (1985)Plots, Transformations, and Regression, Clarendon, Oxford.
Chatterjee, S. and Hadi, A. S. (1988)Sensitivity Analysis in Linear Regression, Wiley, New York.
Cook, R.D. (1986) Assessment of local influence (with discussion),J. R. Statist. Soc. B, 48, 133–169.
Cook, R.D. (1997) Local influence, inEncyclopedia of Statist. Sciences, Kotz, S., Read, C.B. and Banks, D.L. eds., Wiley, New York, Update Vol. 1, 380–385.
Davison, A.C. and Tsai, C.-L. (1992) Regression model diagnostics,Int. Statist. Rev., 60, 337–353.
Fang, K.T. and Anderson, T.W. (1990)Statistical Inferences in Elliptical Contoured and Related Distributions, Allerton, New York.
Fang, K.T. and Zhang, Y. (1990)Generalized Multivariate Analysis, Science Press, Beijing/Springer, Berlin.
Farebrother, R.W. (1992) Relative local influence and the condition number,Commun. Statist.-Simulation. Comput., 21, 707–710.
Farebrother, R.W. (1999)Fitting Linear Relationships: A History of the Calculus of Observations 1750–1900, Springer, New York.
Galea, M., Paula, G.A. and Bolfarine, H. (1997) Local influence in elliptical linear regression models,The Statistician, 46(1), 71–79.
Jung, K.M., Kim, M.G. and Kim, B.C. (1997) Second order local influence in linear discriminant analysis,J. Japan. Soc. Comp. Statist., 10(1), 1–11.
Kollo, T. and Neudecker, H. (1993) Asymptotics of eigenvalues and unit-length eigenvectors of sample variance and correlation matrices,J. Multivar. Anal., 47, 283–300. Corrigendum, 51, 210.
Kollo, T. and Neudecker, H. (1997) Asymptotics of Pearson-Hotelling principalcomponent vectors of sample variance and correlation matrices.Behaviormetrika, 24(1), 51–69.
Magnus, J.R. and Neudecker, H. (1999)Matrix Differential Calculus with Applications in Statistics and Econometrics, second edition, Wiley, Chichester.
Peña, D. (1997) Combining information in statistical modeling,The Am. Statistician, 51(4), 326–332.
Ruppert, D. and Carroll, R.J. (1980) Trimmed least squares estimation in the linear model,J. Am. Statist. Ass., 75, 828–838.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S. On local influence for elliptical linear models. Statistical Papers 41, 211–224 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02926104
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02926104
Keywords
- Likelihood displacement
- observed information matrix
- Delta matrix
- regression diagnostics
- matrix differential