Abstract
The dynamical framework of the nine-level version of the IAP AGCM is presented in this paper. The emphasis of the model's description is put on the following two aspects.
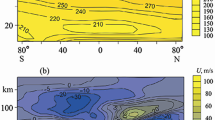
(1) A model's standard atmosphere, which is a satisfactory approximation to the observed troposphere and lower stratosphere standard atmosphere, is introduced into the equations of the model to permit a more accurate calculation of the vertical transport terms, especially near the tropopause; (2) The vertical levels of the model are carefully se lected to guarantee a smooth dependence of layer thickness upon pressure in order to reduce the truncation error involved in the unequal interval vertical finite-differencing. For testing the model, two kinds of linear baroclinic Rossby-Haurwitz waves, one of which has a dynamically stable vertical structure and the other has a relatively unstable one, are constructed to provide initial conditions for numerical experiments. The two waves have been integrated for more than 300 days and 100 days respectively by using the model and both of them are propagating westward with almost identical phase-speed during the time period of the integrations. No obvious change of the wave patterns is found at the levels in the model's troposphere. The amplitudes of both two waves at the uppermost level, however, exhibit rather significant oscillation with time, of which the periods are exactly 20 days and 25 days respectively. The explanation of this interesting phenomena is still under investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arakawa, A. and V. R. Lamb, (1977), Computational design of the basic dynamical processes of the UCLA general circulation model,Methods in Computational Physics,17: 173–265.
DeBoor, C. and J. R. Rice, (1968), Cubic Spline approximation II-variable knots, Computer Sciences Department. TR21, Purdue Univ., April, 1968.
Liang, X.-Z., (1986), The Design of IAP GCM and the Simulation of Climate and Its Interseasonal Variability, Ph.D. Thesis, 200pp.
Lu, L. and Q.-C. Zeng, (1987), The impact of the diurnal variation of solar radiation on the climate modeling,SCupcientia ATMOSPHERICA SINICA,11: 351–358.
U.S. STANDARD ATMOSPHERE (1976), National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, National Aeronautic and Space Administration, United States Air Force.
Reinsch, C. H., (1967), Smoothing by Spline functions, Numerical Mathematik,10(3), 177–183.
Wang, W.-Q., (1987), A numerical simulation of the impact of ground temperature anomaly on the general circulation (to be published)
Yuan, C.-G., (1987), A simulation of East Asia monsoon by using IAP 2-L GCM,IAP LASG Annual Report, 1987, 232–265.
Zeng, Q.-C., (1979),Physical-Mathematical Basis of Numerical Weather Predition, Vol. 1, (in Chinese), Beijing, Science Press, 543pp.
Zeng, Q.-C., (1983), Some numerical ocean-atmosphere coupling models,Proceedings of the First International Symposium of Integrated Global Ocean Modeling, Tullins, SSR, Oct. 2–10, 1983.
—, Z.-Z. Ji and C.-G. Yuan, (1982), Design of difference schemes for the primitive equations, SCIENTIA SINICA, Series B,XXV(2), 183–199.
Zeng, Q.-C., C.-G. Yuan, X.-H. Zhang, X.-Z. Liang and N. Bao, (1986), A global gridpoint general circulation model, in Collection of Papers Presented at WMO/IUGG NWP Symposium, Tokyo, 4–8, August, 1986, 421–430.
—, and X.-H. Zhang, (1987), Available energy conservative finite-difference schemes for primitive equations on spherical baroclinic atmosphere,Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences,11, 121–142.
Zhang, X.-H., N. Bao, C.-G. Yuan and Q.-C. Zeng, (1987), Studies on the sensitivity of dynamical frame of a general circulation model to initial conditions, SCIENTIA SINICA. Series B, Vol. XXX, No. 7, 739–750.
—, and X.-Z. Liang, (1989), Comparison and examination of dynamic frameworks of IAP and OSU AGCM,Advances in Atmospheric Sciences 6: 265–274.
Zhang, X.-H., and X.-Z. Liang, (1988), A description of IAP two-level atmospheric general circulation model, in Proceedings from the Second Science Team Meeting of USA DOE and PRC AS Joint Research Program on CO2- Induced Climate Change, West Verginia, August 26–29, 1987, 1–26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xuehong, Z. Dynamical framework of IAP nine-level atmospheric general circulation model. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 7, 67–77 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919169
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02919169