Abstract
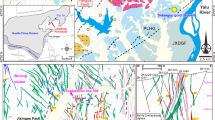
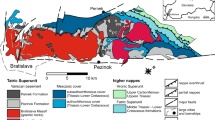
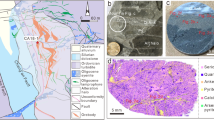
The dual geochemical character of paragenesis and fractionation between gold, arsenic and antimony in micro-disseminated gold deposits in southwestern Guizhou is discussed in terms of spatial distribution of independent deposits, lateral and vertical enrichment, mineralization stage and factor and correlation analyses. Thermodynamic calculations of solubility and speciation of gold and antimony minerals indicate that gold is transported in hydrothermal solution as Au(HS)- 2 and antimony is mainly as Sb (OH) 03 although HSb2S4 may be of increasing importance in acid environment at low temperatures during the late stage of mineralization. Changes in physicochemical conditions hold the key to the association and fractionation between gold and antimony. Gold and antimony response differently to physicochemical variations because they are distinct from each other in soluble speciation and mineral solubility, leading to precipitation at different times and localities during hydrothermal evolution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
He Lixian, The conditions of gold mineralization and the rule of gold occurrence in the mercury ore belt, Geology of Guizhou Province (in Chinese), 1990, 7(3): 188.
Liu Dongsheng (chief editor), Carlin-type (Fine Disseminated) Gold Deposits in China (in Chinese), Nanjing: Nanjing University Publishing House, 1994, 1–96.
Tan Yunjin, Geochemical types of micro-fine disseminated gold deposits in the Yunnan-Guizhou-Guangxi area, Mineral Deposits (in Chinese), 1994, (4): 308.
Qian Handong, Chen Wu, Hu Yong, The element association of As, Sb, Hg and Tl and mineral assemblage characteristics of micro-fine disseminated gold deposits in southwestern Guizhou and northwestern Guangxi, Journal of Geology for Universities (in Chinese), 1995, 1(2): 45.
Shenyang Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, Compiled Papers on the Regional Ore-forming Conditions of the Main Gold Ore Types in Southwestern Guizhou, China (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1989, 160–173.
Zhu Laimin, Hu Ruizhong, An analysis of metallogenesis of Au and As in the Zhimudang large-sized gold deposit, Acta Mineralogica Sinica (in Chinese), 1999, (1): 83.
Zhang Jingrong, Zhu Kaijun, Lu Jianjun et al., The strata-bound geochemistry of micro-fine disseminated gold deposits in southwestern Guizhou, Journal of Nanjing University (in Chinese) (Natural Science Edition), 1993, 29(2): 283.
Rytuba, J. J., Yao Zhongyou, Xiang Caize, Geochemistry of hydrothermal transport and deposition of gold and sulfide in the Carlin-type micro-fine disseminated gold deposits, Geology-Geochemistry (in Chinese), 1988, (10): 1.
Benedetti, M., Bouleque, J., Mechanism of gold transfer and deposition in a supergene environment, Geochimica et CosmochimicaActa, 1991, 55: 1539.
Benning, L. G., Seward, T. W., Hydrosulphide complex of Au(I) in hydrothermal solutions from 150-400°C and 500-1500 bar, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1996, 60(11): 1849.
Seward, T. W., Thiocomplexes of gold and the transport of gold in hydrothermal ore solutions, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1973, 37: 379.
Spycher, N. F., Reed, M. H., As(III) and Sb(III) sulfide complexes: An evaluation of stoichiomrtry and stability from existing experimental data, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53: 2185.
Tosse, J. A., The speciation of antimony in sulfidic solutions: A theoretical study, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58: 5093.
Spycher, N. F., Reed, M. H., Evolution of a broadlands-type epithermal ore fluid along alternative P-T paths: Implications for the transport and deposition of base, precious, and volatile metals, Economic Geology, 1989, 84: 328.
Williams-Jones, A. E., Normand, C., Controls of mineral parageneses in the system Fe-Sb-S-O, Economic Geology, 1997, 92: 308.
Reed, M. H., Spycher, N. F., SOLTHERM Data Base, Department of Geological Sciences, University of Oregon Eugene, Oregon, 1995, 1–4.
Zhu Laimin, He Mingyou, Fluid inclusion geochemistry of minerals in micro-fine disseminated gold deposits in southwestern Guizhou, Volcanic Geology and Mineral Resources (in Chinese), 1996, 17(1-2): 66.
Reed, M. H., Calculation of multicomopnent chemical equilibria and reaction processes in systems involving mineral, gases and aqueous phase, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1982, 46: 513.
Barnes, H. L., Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits, New York: Wiley Interscience, 1970, 380–425.
Tu Guangzhi (chief editor), Geochemistry of Strata-bound Ore Deposits in China (in Chinese), Vol. 3, Beijing: Science Press, 1988.
Chen Lu'an, The existing forms of Hg and thermodynamic analysis of heavy metal differentiation in the process of formation of Hg deposits in carbonate formations, Geology of Guizhou Province (in Chinese), 1989, 6(2): 175.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, L., Hu, R. Au-Sb association and fractionation in micro-disseminated gold deposits, southwestern Guizhou—geochemistry and thermodynamics. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 43, 208–216 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02878151
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02878151