Abstract
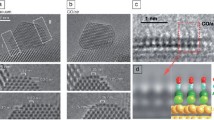
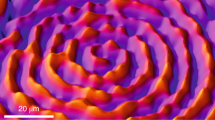
In situ scanning FTIR microscopy was built up for the first time in the present work, which consists of an FTIR apparatus, an IR microscope, an X-Y mapping stage, and the specially designed electrochemical IR cell and computer software. It has been demonstrated that this new space-resolvdin situ IR technique can be used to study vibration properties of micro-area, and to perform IR imaging of electrode surface. The chemical image obtained using this technique for CO adsorption on Pt electrode illustrated, at a space-resolution of 10-2 cm, the inhomogeneity and the distribu-tion of reactivity of micro-area of electrode surface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beden, B., Lamy, C., Bewick, A. et al., Electrosorption of methanol on a platinum electrode: IR spectroscopic evidence for adsorbed CO species.J. Electroarnal. Chem., 1981, 121: 343.
Beden, B., Lamy. C., Infrared reflection spectroscopy, Chap 5, inSpectroelectrochemistry-Theory- and Practice, New York and London: Plenum Press, 1988, 189–261.
Sun, S. G., Studying electrocatalytic oxidation of small organic molecules within-situ. infrared spectrosocpy, Chap. 6, inELectrocatalysis, New York: Willey-VCH Inc., 1998, 243–290.
Sun, S. G., Clavilier, J., Bewick, A., The mechanism of electrocatalytic oxidation of formic acid on Pt (100) and Pt (111) in sulphuric acid solution: an EMIRS study,J. Electroanal. Chem., 1988, 240: 147.
Daschbach, J., Heisler, D., Pous, S., Time-resolved infrared spectroscopy,Appl. Spectrosc., 1986, 40: 489.
Ross, P. N., Surface crystallography at the metal-solution interface, Chap. 2, inStructure of Electrified Interfaces, New York: VHC Publishers Inc., 1993, 35–63.
Stroscio, J. A.. Kaiser, W. J.,Scanning Tunning Microscopy, San Diego: Academic Press Inc., 1993.
Lahrech, A., Bachelot, R., Gleyzes, P. et al., Infrared-reflection-mode near-field microscopy using an apertureless probe with a resolution of λ/600,Optics Letters, 1996. 21: 1315.
Sun, S. G., Yang, D. F., Tian, Z. W.,In situ FTIR studies on the adsorption and oxidation of π-propanol and isopropanol at a platinum electrode,J. Electroanal. Chem., 1990, 289: 177.
Beden, B., Bewick, A., Kunimatsu, K. et al., Infrared study of adsorbed species on electrodes: adsorption of carbon monoxide on Pt, Rh and Au,J. Electroanal. Chem., 1982, 142: 345.
Banwell, C. N.,Fundamentals of Molecular Spectroscopy, 3rd ed., London: McGraw-Hill Book Company (UK) Limited, 1983, 2425.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 29525307).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, S., Hong, S., Chen, S. et al. In situ scanning FTIR microscopy and IR imaging of Pt electrode surface towards CO adsorption. Sc. China Ser. B-Chem. 42, 261–267 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02874241
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02874241