Summary
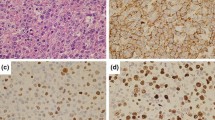
A B-cell line was established from the liver of an 11-yr-old boy with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD). The cells were morphologically heterogenous, CD10 (CALLA) negative, and expressed several B-cell antigens, including CD23, in a manner reminiscent of lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs) reported in the literature. However, the cells also showed expression of the CD77 antigen, carried a 14q32+ chromosomal anomaly, and showed IgM-kappa immunoglobulin isotype restriction immediately after their outgrowth in culture. These latter properties are typically associated with Burkitt’s lymphoma cell lines rather than LCLs. Aberrant expression of the L60 antigen on these B-cells was found as additional evidence of altered growth regulation in these cells. EBV infection was demonstrated by the abundant expression of EBNA-2 and LMP viral antigens in culture. The cell line described should be useful in planning in vitro experiments designed to understand the factors that modulate the growth of PTLD in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allday, M. J.; Crawford, D. H.; Griffin, B. E. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression during the initiation of B cell immortalization. J. Gen. Virol. 70:1755–1764; 1989.
Avila-Carino, J.; Torsteinsdottir, S.; Ehlin-Henriksson, B., et al. Search for the critical characteristics of phenotypically different B cell lines, Burkitt lymphoma cells and lymphoblastoid cell lines, which determine differences in their functional interaction with allogeneic lymphocytes. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 34:128–132; 1991.
Bechet, J. M.; Fialkow, P. J.; Nilsson, K., et al. Immunoglobulin synthesis and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase as cell markers in human lymphoblastoid cell lines. Exp. Cell. Res. 89:275–282; 1974.
Blazar, B. A.; Murphy, A. M. Induction of B cell responsiveness to growth factors by Epstein-Barr virus conversion: comparison of endogenous factors and interleukin-1. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 80:62–68; 1990.
Buck, J.; Hammerling, U.; Hoffmann, M. K., et al. Purification and biochemical characterization of a human autocrine growth factor produced by Epstein-Barr virus-transformed B cells. J. Immunol. 138:2923–2928; 1987.
Cannon, M. J.; Pisa, P.; Fox, R. I. et al., Epstein-Barr virus induces aggressive lymphoproliferative disorders of human B cell origin in SCID/hu chimeric mice. J. Clin. Invest. 85:1333–1337; 1990.
Cleary, M. L.; Nalesnik, M. A.; Shearer, W. T., et al. Clonal analysis of transplant-associated lymphoproliferations based on the structure of the genomic termini of the Epstein-Barr virus. Blood 72:349–352; 1988.
Cleary, M. L.; Sklar, J. Lymphoproliferative disorders in cardiac transplant recipients are multiclonal lymphomas. Lancet 1:489–493; 1984.
Cohen, J. H. M.; Revillard, J. P.; Magaud, J. P., et al. B-cell maturation stages of Burkitt’s lymphoma cell lines according to Epstein-Barr virus status and type of chromosome translocation. JNCI 78:235–242; 1987.
Deeg, J. H.; Sanders, J.; Martin, P., et al. Secondary malignancies after marrow transplantation. Exp. Hematol. 12:660–666; 1984.
Elias, J. A.; Lentz, V. IL-1 and tumor necrosis factor synergistically stimulate fibroblast IL-6 production and stabilize IL-6 messenger RNA. J. Immunol. 145:161–166; 1990.
Favrot, M. C.; Maritaz, O.; Suzuki, T., et al. EBV-negative and positive Burkitt cell lines variably express receptors for B-cell activation and differentiation. Int. J. Cancer 38:901–906; 1986.
Frizzera, G.; Hanto, D. W.; Gajl-Peczalska, K. J., et al. Polymorphic diffuse B-cell hyperplasia and lymphomas in renal transplant recipients. Cancer Res. 41:4262–4279; 1981.
Gerrard, T. L.; Volkman, D. J. IL 1-like activity in antigen-presenting human B cell lines. J. Immunol. 135:3217–3223; 1985.
Giovanella, B.; Nilson, K.; Zech, L., et al. Growth of diploid, Epstein-Barr virus-carrying human lymphoblastoid cell lines heterotransplanted into nude mice under immunologically privileged conditions. Int. J. Cancer 24:103–113; 1979.
Gordon, J.; Ley, S. C.; Melamed, M. D., et al. Soluble factor requirements for the autostimulatory growth of B lymphoblasts immortalized by Epstein-Barr virus. J. Exp. Med. 159:1554–1559; 1984.
Hanto, D. W.; Birkenbach, M.; Frizzera, G., et al. Confirmation of the heterogeneity of posttransplant Epstein-Barr virus-associated B cell proliferations by immunoglobulin gene rearrangement analyses. Transplantation 47:458–464; 1989.
Hanto, D. W.; Sakamoto, K.; Purtilo, D. T., et al. The Epstein-Barr virus in the pathogenesis of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Surgery 90:204–213; 1981.
Heslop, H. E.; Bianchi, A. C. M.; Cordingley, F. T., et al. Effects of interferon on autocrine growth factor loops in B lymphoproliferative disorders. J. Exp. Med. 172:1729–1734; 1990.
Hopkins, K. A. Basic microlymphocytotoxicity test. In: Zachary, A. A.; Teresi, G. A., eds. American Society for Histocompatibility and Immunogenetics Laboratory Manual. Chicago, IL: ASCP Press; 1990:195–201.
Jarvis, J. E.; Ball, G.; Rickinson, A. B., et al. Cytogenetic studies on human lymphoblastoid cell lines from Burkitt’s lymphomas and other sources. Int. J. Cancer 14:716–721; 1974.
Katz, B.; Saini, U. Presence of the diffuse early antigen of Epstein-Barr virus in lymphomas and lymphoproliferative disorders. Am. J. Pathol. 140:1247–1254; 1992.
Kimura, A.; Sasazuki, T. Eleveth international histocompatibility workshop reference protocol for the HLA DNA typing technique. In: Tsuji, K.; Aizawa, M.; Sasazuki, T., eds. Proceedings of the eleventh international histocompatibility workshop, vol. I. England: Oxford University Press; 1992:397–419.
Khyatti, M.; Stefanescu, I.; Menezes, J. Evidence for interleukin-2 mediated control of EBV infected/transformed cells: effect exerted through effector cells with dual CD8+ /CD16+ phenotype. In: Tursz, J. S.; Pagano, J. S.; Ablashi, G.; Lenoir, G.; Pearson, G. R., eds. The Epstein Barr virus and associated diseases. Paris: Colloque INSERM/John Libbey Eurotext Ltd.; 1993:325–331.
Krause, J. R.; Penchansky, L.; Contis, L., et al. Flow cytometry in the diagnosis of acute leukemia. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 89:341–346; 1988.
Locker, J.; Nalesnik, M. Molecular genetic analysis of lymphoid tumors arising after organ transplantation. Am. J. Pathol. 135:977–987; 1989.
Miller, G. Epstein-Barr virus, biology, pathogenesis, and medical aspects. In: Fields, B. N.; Knipe, D. M., eds. Virology. New York: Raven Press; 1990:1921–1958.
Mitelman, F. Marker chromosome 14q+ in human cancer and leukemia. Adv. Cancer Res. 34:141–171; 1981.
Nakamine, H.; Masih, A. S.; Okano, M., et al. Characterization of clonality of Epstein-Barr virus-induced human B lymphoproliferative disease in mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Am. J. Pathol. 142:139–147; 1993.
Nalesnik, M. A.; Jaffe, R.; Starzl, T. E., et al. The pathology of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders occurring in the setting of cyclosporine A-prednisone immunosuppression. Am. J. Pathol. 133:173–192; 1988.
Nilsson, K.; Klein, G. Phenotypic and cytogenetic characteristics of human B-lymphoid cell lines and their relevance for the etiology of Burkitt’s lymphoma. Adv. Cancer Res. 37:319–380; 1982.
Nilsson, K.; Ponten, J. Classification and biological nature of established human hematopoietic cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 15:321–341; 1975.
Penn, I. Host origin of lymphomas in organ transplant recipients. Transplantation 27:214; 1979.
Picker, L. J.; Weiss, L. M.; Medeiros, L. J., et al. Immunophenotypic criteria for the diagnosis of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Am. J. Pathol. 128:181–200; 1987.
Purtilo, D. T.; Strobach, R. S.; Okano, M., et al. Biology of disease. Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphoproliferative disorders. Lab. Invest. 67:5–23; 1992.
Randhawa, P. S.; Markin, R. S.; Starzl, T. E., et al. Epstein-Barr virus-associated syndromes in immunosuppressed liver transplant recipients. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 14:538–547; 1990.
Rickinson, A. B.; Finnerty, S.; Epstein, M. A. Comparative studies on adult donor lymphocytes infected by EB virus in vivo or in vitro: origin of transformed cells arising in co-cultures with foetal lymphocytes. Int. J. Cancer 19:775–782; 1977.
Rijken, A.; Dekker, A.; Taylor, S., et al. Diagnostic value of DNA analysis in effusions by flow cytometry and image analysis. A prospective study on 102 patients as compared with cytologic evaluation. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 95:6–12; 1991.
Rooney, C. M.; Gregory, C. D.; Rowe, M., et al. Endemic Burkitt’s lymphoma: phenotypic analysis of tumor biopsy cells and of derived tumor cell lines. JNCI 77:681–687; 1986.
Rowe, D. T.; Rowe, M.; Evan, G. I., et al. Restricted expression of EBV’s latent genes and T-lymphocyte-detected membrane antigen in Burkitt’s lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 5:2599–2607; 1986.
Sherer, M. E.; Shekhter-Levin, S.; Krause, J. R., et al. Atypical (7; 19) translocation in acute myelomonocytic leukemia. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 57:169–173; 1991.
Starzl, T. E.; Nalesnik, M. A.; Porter, K. A. Reversibility of lymphomas and lymphoproliferative lesions developing under cyclosporinsteroid therapy. Lancet 1:583–587; 1984.
Steel, C. M.; Shade, M.; Woodward, M. A. Chromosome aberrations acquired in vitro by human B-cell lines. I. Gains and losses of material. JNCI 65:95–99; 1980.
Steel, C. M.; Woodward, M. A.; Davidson, C., et al. Non-random chromosome gains in human lymphoblastoid cell lines. Nature 270:349–351; 1977.
Swinnen, L. J.; Costanzo-Nordin, M. R.; Fisher, S. G., et al. Increased incidence of lymphoproliferative disorders after immunosuppression with the monoclonal antibody OKT3 in cardiac-transplant recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 323:1723–1728; 1990.
Tursz, T.; Rousselet, G.; Busson, P., et al. Role of cytokines in EBV-infected cell growth. In: Ablashi, D. V., ed. Epstein-Barr virus and human disease. Clifton, NJ: Humana Press; 1990:133–141.
Xia, X.; Lee, H. K.; Clark, S. C., et al. Recombinant interleukin IL-2-induced human B cell differentiation is mediated by autocrine IL-6. Eur. J. Immunol. 19:2275–2281; 1989.
Young, L.; Alfieri, C.; Hennessy, K., et al. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus transformation-associated genes in tissues of patients with EBV lymphoproliferative disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 321:1080–1085; 1989.
Yunis, E. J.; Agostini, R. M.; Atchison, R. W. An atlas of viral particles from human specimens. Perspect. Pediatr. Pathol. 4:387–429; 1978.
Zech, L.; Haglund, U.; Nilsson, K., et al. Characteristic chromosomal abnormalities in biopsies and lymphoid-cell lines from patients with Burkitt and non-Burkitt lymphomas. Int. J. Cancer 17:47–56; 1976.
Zutter, M. M.; Martin, P. J.; Sale, G. E., et al. Epstein-Barr virus lymphoproliferation after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 72:520–529; 1988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Randhawa, P.S., Zeevi, A., Alvares, C. et al. Morphologic and immunophenotypic characterization of a cell line derived from liver tissue with epstein-barr virus associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Animal 30, 400–406 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02634361
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02634361