Summary
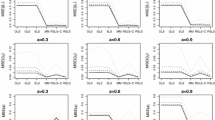
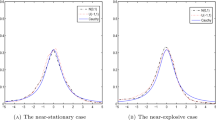
A non-linear AR(1) process is investigated when the associated white noise has a rectangular distribution. The process is a modification of the logistic model and an important feature is that it is possible to derive explicit formulae for extrapolation. Some properties of the extrapolation are derived and it is proved that the least squares extrapolationm steps ahead converges to a constant asm→∞. The least squares extrapolation is compared with the naïve extrapolation and the differences between them are shown to be small in some examples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aase, K. K. (1983). Recursive estimation in non-linear time series models of autoregressive type.J. Roy. Statist. Soc. B 45, 228–237.
Doob, J. L. (1953).Stochastic Processes. New York: Wiley.
Pemberton, J. (1987). Exact least squares multi-step prediction from nonlinear autoregressive models.J. Time Ser. Anal. 8, 443–448.
Tong, H. (1990).Non-linear Time Series. Oxford: University Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andel, J. On least-squares and naïve extrapolations in a non-linear AR(1) process. Test 6, 91–100 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02564427
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02564427