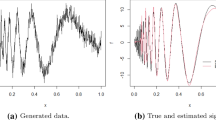
Abstract
A blockwise shrinkage is a popular procedure of adaptation that has allowed the statisticians to establish an impressive bouquet of asymptotic mathematical results and develop softwares for solving practical problems. Traditionally risks of the estimates are studied via upper bounds that imply sufficient conditions for a blockwise shrinkage procedure to be minimax. This article suggests to analyze the estimates via exact (non-asymptotic) lower bounds established for a no-signal setting. The approach complements the familiar minimax, Bayesian and numerical analysis, it allows to find necessary conditions for a procedure to attain desired rates, and it sheds a new light on popular choices of blocks and thresholds recommended in the literature. Mathematical results are complemented by a numerical study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramovich, F., Besbeas, P. and Sapatinas, T. (2002). Empirical Bayes approach to block wavelet function estimation,Computational Statistics and Data Analysis,39, 435–451.
Brown, L. D., Low, M. G. and Zhao, L. H. (1997). Superefficiency in nonparametric function estimation,The Annals of Statistics,25, 2607–2625.
Cai, T. (1999). Adaptive wavelet estimation: a block thresholding and oracle inequality approach,The Annals of Statistics,27, 898–924.
Cai, T. (2002). On block thresholding in wavelet regression: Adaptivity, block size, and threshold level,Statistical Sinica,12, 1321–1273.
Cai, T. and Silverman, B. (2000). Incorporating information on neighboring coefficients into wavelet estimation,Sankhyā Series B,63, 127–148.
Cai, T., Low, M. and Zhao, L. (2000) Sharp adaptive estimation by a blockwise method, Tech. Report, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Cavalier, L. and Tsybakov, A. (2001). Penalized blockwise Stein’s method, monotone oracles and sharp adaptive estimation,Mathematical Methods of Statistics,10, 247–282.
Chiken, E. (2003). Block thresholding and wavelet estimation for nonequispaced samples.Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference,16, 113–129.
DeCanditiis, D. and Vidakovic, B. (2004). Wavelet Bayesian block shrinkage via mixture of normal-inverse gamma priors,Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics,12 (to be published).
Delyon, B. and Juditsky, A. (1996). On minimax wavelet estimators,Journal of Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis,3, 215–228.
Donoho, D. L. (1995). De-Noising by soft thresholding,IEEE Transactions of Information Theory,41, 613–627.
Donoho, D. L. and Johnstone, I. M. (1994). Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage,Biometrika,81, 425–455.
Donoho, D. L. and Johnstone, I. M. (1995). Adapting to unknown smoothness via wavelet shrinkage,Journal of American Statistical Association,90, 1200–1224.
Downie, T. R. and Silverman, B. M. (1998). The discrete multiple discrete transform and threshold methods,IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,46, 2558–2561.
Efromovich, S. (1985). Nonparametric estimation of a density with unknown smoothness,Theory of Probability and Applications,30, 557–568.
Efromovich, S. (1986). Adaptive algorithm for nonparametric regression,Procedures of Second IFAC Symposium on Stochastic Control, 112–114, Science, Vilnuis.
Efromovich, S. (1999)Nonparametric Curve Estimation: Methods, Theory and Applications, Springer, New York.
Efromovich, S. (2000). Can adaptive estimators for Fourier series be of interest to wavelets?Bernoulli,6, 699–709.
Efromovich, S. (2001). Multiwavelets and signal denoising,Sankhyā Series B,23, 367–393.
Efromovich, S. and Pinsker, M. (1984). A learning algorithm for nonparametric filtering,Automation and Remote Control,24, 1434–1440.
Efromovich, S. and Pinsker, M. (1986). Adaptive algorithm of minimax nonparametric estimating spectral density,Problems of Information Transmission,22, 62–76.
Efromovich, S. and Pinsker, M. (1996). Sharp-optimal and adaptive estimation for heteroscedastic nonparametric regression,Statistica Sinica,6, 925–945.
Hall, P., Kerkyacharian, G. and Picard, D. (1998). Block threshold rules for curve estimation using kernel and wavelet methods,The Annals of Statistics,26, 922–942.
Hall, P., Kerkyacharian, G. and Picard, D. (1999). On the minimax optimality of block thresholded wavelet estimators,Statistica Sinica,9, 33–50.
Härdle, W., Kerkyacharian, G., Picard, D. and Tsybakov, A. (1998).Wavelets, Approximation, and Statistical Applications, Springer, New York.
Johnstone, I. (1998).Function Estimation in Gaussian Noise. Sequence Models, Draft of Monograph, University of Stanford, California.
Juditsky, A. (1997). Wavelet estimators: Adapting to unknown smoothness,Mathematical Methods of Statistics,6, 1–25.
Lehmann, E. L. and Casella, G. (1998).Theory of Point Estimation, 2nd ed., Springer, New York.
Mallat, S. (1999).A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing, University Press, New York.
Nemirovski, A. (2000).Topics in Non-Parametric Statistics, Lecture Notes in Mathematics,1738, Springer, New York.
Robbins, H. (1955). A remark on Stirling’s formula,American Mathematics Monthly,62, 26–29.
Tsybakov, A. (2002). Discussion on random rates in anisotropic regression,The Annals of Statistics,30, 379–385.
Vidakovic, B. (1999).Statistical Modeling by Wavelets, Springer, New York.
Wahba, G. (1990).Spline Models for Observational Data, SIAM, Philadelphia.
Zhang, C.-H. (2002). Minimax compound estimation, Tech. Report, Rutgers University, New Jersey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by NSF Grants DMS-9971051 and DMS-0243606.
About this article
Cite this article
Efromovich, S. Analysis of blockwise shrinkage wavelet estimates via lower bounds for no-signal setting. Ann Inst Stat Math 56, 205–223 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02530542
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02530542