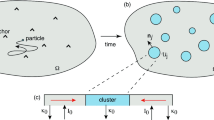
Abstract
Aggregation of membrane molecules is a crucial phenomenon in developing organisms, a classic example being the aggregation of post-synaptic receptors during synaptogenesis. Our understanding of the molecular events involved is improving, but most models of the aggregation or concentration process do not address binding events on the molecular level. An exception is the study of diffusion limited aggregation, in which the aggregation process is simulated on a molecular level. In this analysis, however, important physical parameters such as molecular size, diffusion constant and initial density are not addressed. Thus no predictions about the rate at which such aggregates will form is possible. In the present work the model of diffusion limited aggregation is extended to incorporate these parameters and make the corresponding predictions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, M. J. and M. W. Cohen. Nerve-induced and spontaneous redistribution of acetylcholine receptors on cultured muscle cells.J. Physiol. (Lond). 268, 757–773.
Angelides, K. J., L. W. Elmer, D. Loftus and E. Elson. 1988. Distribution and lateral mobility of voltage-dependent sodium channels in neurons [published erratum appears inJ. Cell Biol. (1989) May;108(5): preceding 2001].J. Cell Biol. 106, 1911–1925.
Axelrod, D., P. Ravdin, D. E. Koppel, J. Schlessinger, W. W. Webb, E. L. Elson and T. R. Podleski. 1976. Lateral motion of fluorescently labeled acetylcholine receptors in membranes of developing muscle fibers.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 4594–4598.
Baker, L. P. and H. B. Peng. 1993. Tyrosine phosphorylation and acetylcholine receptor cluster formation in cultured Xenopus muscle cells.J. Cell Biol. 120, 185–195.
Chao, N. M., S. H. Young and M. M. Poo. 1981. Localization of cell membrane components by surface diffusion into a “trap”.Biophys. J. 36, 139–153.
Dewey, T. G. and M. M. Datta. 1989. Determination of the fractal dimension of membrane protein aggregates using fluorescence energy transfer.Biophys. J. 56, 415–420.
Dubinsky, J. M., D. J. Loftus, G. D. Fischbach and E. L. Elson. 1989. Formation of acetylcholine receptor clusters in chick myotubes: migration or new insertion?J. Cell Biol. 1733–1743.
Edidin, M. 1987. Rotational and lateral diffusion of membrane proteins and lipids: phenomena and function. InCurrent Topics in Membranes and Transport, pp. 91–119. Orlando: Academic Press.
Edwards, C. and H. L. Frisch. 1976. A model for the localization of acetylcholine receptors at the muscle endplate.J. Neurobiol. 7, 377–381.
Gershon, N. D. 1978. Model for capping of membrane receptors based on boundary surface effects.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 1357–1360.
Joe, E. and K. J. Angelides. 1993. Clustering and mobility of voltage-dependent sodium channels during myelination.J. Neurosci. 13, 2993–3005.
Kolb, M., R. Botet and R. Jullien. 1983. Scaling of kinetically growing clusters.Phys. Rev. Lett. 51, 1123–1126.
Kusumi, A., Y. Sako and M. Yamamoto. 1993. Confined lateral diffusion of membrane receptors as studied by single particle tracking (nanovid microscopy). Effects of calcium-induced differentiation in cultured epithelial cells.Biophys. J. 65, 2021–2040.
Mandelbrot, B. B. and C. J. G. Evertsz. 1990. The potential distribution around growing fractal clusters.Nature 348, 143–145.
Meakin, P. 1983. Formation of fractal clusters and networks by irreversible diffusion-limited aggregation.Phys. Rev. Lett. 51, 1119–1122.
Meakin, P. 1987. Noise-reduced diffusion-limited aggregation.Phys. Rev. A 36, 332–339.
Moreira, F., R. R. Freire and C. M. Chaves. 1989. Scaling laws for the noise-reduced diffusion-limited aggregation.Phys. Rev. A 40, 2225–2228.
Muthukumar, M. 1983. Mean-field theory for diffusion-limited cluster formation.Phys. Rev. Let. 50, 839.
Northrup, S. H. and H. P. Erickson. 1992. Kinetics of protein-protein association explained by Brownian dynamics computer simulation.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 3338–3342.
Ossadnik, P. 1991. Multiscaling analysis of large-scale off-lattice DLA.Physica A 176, 454–462.
Peng, H. B., L. P. Baker and Z. Dai. 1993. A role of tyrosine phosphorylation in the formation of acetylcholine receptor clusters induced by electric fields in cultured Xenopus muscle cells.J. Cell Biol. 120, 197–204.
Poo, M.-m. 1982. Rapid lateral diffusion of functional ACh receptors in embryonic muscle cell membrane.Nature 295, 332–335.
Sander, L. M. 1986. Fractal growth processes.Nature 322, 789–793.
Saxton, M. J. 1992. Lateral diffusion and aggregation. A Monte Carlo study.Biophys. J. 61, 119–128.
Saxton, M. J. 1993. Lateral diffusion in an archipelago. Dependence on tracer size.Biophys. J. 64, 1053–1062.
Stenberg, M. and H. Nygren. 1991. Computer simulation of surface-induced aggregation of ferritin.Biophys. Chem. 41, 131–141.
Stollberg, J. 1994. A model for diffusion-limited aggregation in membranes.Com. Mol. Cell. Biophys. 8, 188–198.
Stollberg, J. and S. E. Fraser. 1988. Acetylcholine receptors and concanavalin A-binding sites on cultured Xenopus muscle cells: electrophoresis, diffusion and aggregation.J. Cell. Biol. 197. 1397–1408.
Stollberg, J. and S. E. Fraser. 1990. Local accumulation of acetylcholine receptors is neither necessary nor sufficient to induce cluster formation.J. Neurosci. 10, 247–255.
Stollberg, J. and H. Gordon. 1992. Diffusion-trapping of acetylcholine receptors: a numerical model.Invited Seminar (Keystone Symposia: Synapse formation and function: The neuromuscular junction and the central nervous system).
Tokuyama, M. and K. Kawasaki. 1984. Fractal dimensions for diffusion-limited aggregation.Phys. Lett. 100A, 337–340.
Wallace, B. G. 1991. The mechanism of agrin-induced acetylcholine receptor aggregation.Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. [Biol.] 331, 273–280.
Wallace, B. G. 1994. Staurosporine inhibits agrin-induced acetylcholine receptor phosphorylation and aggregation.J. Cell. Biol. 125, 661–668.
Wallace, B. G., Z. Qu and R. L. Huganir. 1991. Agrin induces phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.Neuron 6, 869–878.
Weaver, D. L. 1983. Diffusion-mediated localization on membrane surfaces.Biophys. J. 41, 81–86.
Witten, T. A., Jr. and P. Meakin. 1983. Diffusion-limited aggregation at multiple growth sites.Phys. Rev. B 28, 5632–5642.
Witten, T. A. and L. M. Sander. 1981. Diffusion-limited aggregation, a kinetic critical phenomenon.Phys. Rev. Lett. 47, 1400–1403.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stollberg, J. Density and diffusion limited aggregation in membranes. Bltn Mathcal Biology 57, 651–677 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02461845
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02461845