Abstract
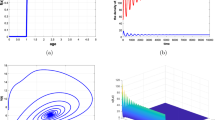
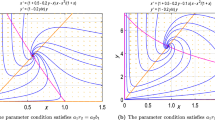
Cannibalism can have a stabilizing effect in a predator-prey system. Contrary to the intuitive expectation cannibalism of the predator leads to an increase of the standing stocks of both, prey and predator.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baretta, J.et al. 1994. ERSEM.Neth. J. Sea Res. preprint.
Breckling, B. 1985. Die Veränderbarkeit der dynamischen Verhaltensqualität des Lotka-Volterra Modells durch Einführung nichtlinearer Ergänzungen-theoretische Konsequenzen.Verhandlungen der Gesellschaft für Ökologie (Bremen 1983). Band XIII 1985.
Den Bosch, F., A. M. van De Roos and W. Gabriel. 1988. Cannibalism as a lifeboat mechanism.J. Math. Biol. 26, 619–933.
Diekmann, O., R. M. Nisbet, W. S. C. Gurney and F. van den Bosch. 1986. Simple mathematical models for cannibalism. A critique and a new approach.Math. Biosc. 78, 21–46.
Cushing, J. M. 1991. A simple model of cannibalism.Math. Biosc. 107, 47–71.
Ebenhöh, W., C. Kohlmeier and P. Radford. 1994. Modelling benthic biology in ERSEM.Neth. J. Sea Res. preprint.
Fraunthal, J. C. 1983. Some simple models of cannibalism.Math. Biosc. 63, 87–98.
Freedman, H. I. 1991.Deterministic Mathematical Models in Population Ecology. Marcel Dekker, New York.
Gabriel, W. 1985a. Can cannibalism be advantageous in cyclopoids? A mathematical model.Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 22, 3164–3168.
Gabriel, W. 1985b. Overcoming food limitations by cannibalism: a model study on cyclopoids.Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. 21, 373–381.
Gabriel, W. 1985c. Simulation komplexer Populationsdynamik. In:Simulationstechnik, D.P.F. Möller (ed.).Informatik Fachberichte.109, 318–324.
Gurtin, M. E. and D. S. Levine. 1982. On populations that cannibalize their young.SIAM J. Appl. Math. 42, 94–108.
Jetschke, G. 1989.Mathematik der Selbstorganisation. Vieweg, 333pp.
Lahndahl, H. D. and B. D. Hansen. 1975. A three stage population model with cannibalism.Bull. math. biol. 37, 11–17.
Lotka, A. J. 1925.Elements of Physical Biology. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkens.
Plis, G. A. 1981. The evolution and dynamics of intraspecific predation.Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 12, 225–251.
REnshaw, E. 1991.Modelling Biological Populations in Space and Time. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Richter, O. 1985.Simulation des Verhaltens ökologischer Systeme. VCH, 219 pp.
Ulanowicz, R. E. 1986.Growth and Development: Ecosystem Phenomenology, pp. 1–203. New York: Springer Verlag.
Volterra, V. 1926. Fluctuations in the abundance of a species considered mathematically.Nature 118, 558–560.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohlmeier, C., Ebenhöh, W. The stabilizing role of cannibalism in a predator-prey system. Bltn Mathcal Biology 57, 401–411 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02460632
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02460632