Abstract
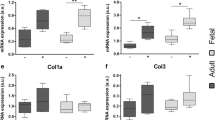
Adult dermal wounds, in contrast to fetal wounds, heal with the formation of scar tissue. A crucial factor in determining the degree of scarring is the ratio of types I and III collagen, which regulates the diameter of the combined fibers. We developed a reaction-diffusion model which focuses on the control of collagen synthesis by different isoforms of the polypeptide transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ). We used the model to investigate the current controversy as to whether the fibroblasts migrate into the wound from the surrounding unwounded dermis or from the underlying subcutaneous tissue. Numerical simulations of a spatially independent, temporal model led to a value of the collagen ratio consistent with that of healthy tissue for the fetus, but corresponding to scarring in the adult. We investigated the effect of topical application of TGFβ and show that addition of isoform 3 reduces scar tissue formation, in agreement with the experiment. However, numerical solutions of the reaction-diffusion system do not exhibit this sensitivity to growth factor application. Mathematically, this corresponds to the observation that behind healing wavefront solutions, a particular healed state is always selected independent of transients, even though there is a continuum of possible positive steady states. We explain this phenomenon using a caricature system of equations, which reflects the key qualitative features of the full model but has a much simpler mathematical form. Biologically, our results suggest that the migration into a wound of fibroblasts and TGFβ from the surrounding dermis alone cannot account for the essential features of the healing process, and that fibroblasts entering from the underlying subcutaneous tissue are crucial to the healing process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adzick, N. S. and M. T. Longaker. 1992. Characteristics of fetal tissue repair. InFetal Wound Healing, N. S. Adzick and M. T. Longaker (Eds). New York: Elsevier, pp. 53–70.
Appling, W. D., W. R. O'Brien, D. A. Johnston and M. Duvie. 1989. Synergistic enhancement of type I and III collagen production in cultured fibroblasts by transforming growth factor-β and ascorbate.FEBS Lett. 250, 541–544.
Armstrong, J. R. and M. W. J. Ferguson. 1995. Ontogeny of the skin and the transition from scar-free to scarring phenotype during wound healing in the pouch young of a marsupial,Monodelphis domestica.Dev. Biol. 169, 242–260.
Bard, J. B. L. and E. D. Hay. 1975. The behaviour of fibroblasts from the developing avian cornea: morphology and movementin situ andin vitro.J. Cell Biol. 67, 400–418.
Canosa, J. 1973. On a nonlinear diffusion equations describing population growth.IBM J. Res. Dev. 17, 307–313.
Chaplain, M. A. J., S. M. Giles, B. D. Sleeman and R. J. Jarvis. 1995. A mathematical analysis of a model for tumour angiogenesis.J. Math. Biol. 33, 744–770.
Chen, R. H., R. Ebner and R. Derynck. 1993. Inactivation of the type II receptor reveals two receptor pathways for the diverse TGFβ activities.Science 260, 1335–1338.
Crosson, C. E., R. W. Klyce and R. W. Beuerman. 1986. Epithelial wound closure in the rabbit cornea.Invest. Ophthal. Vis. Sci. 27, 464–473.
Dale, P. D., P. K. Maini and J. A. Sherratt. 1994. Mathematical modelling of corneal epithelial wound healing.Math. Biosci. 124, 127–147.
Dale, P. D., J. A. Sherratt and P. K. Maini. 1996. A mathematical model for collagen fibre formation during foetal and adult dermal wound healing.Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 263, 653–660.
Ferguson, M. W. J. and G. F. Howarth. 1992. Marsupial models of scarless fetal wound healing. InFetal Wound Healing, N. S. Adzick and M. T. Longaker (Eds). New York: Elsevier, pp. 95–124.
Fisher, R. A. 1937. The wave of advance of advantageous genes.Ann. Eugen. 7, 353–369.
Flint, M. H., A. S. Craig, H. C. Reilly, G. C. Gillard and D. A. D. Parry. 1984. Collagen fibril diameters and glycosaminoglycan content of skins—indices of tissue maturity and function.Connect. Tissue Res. 13, 69–81.
Jeffrey, J. J. 1992. Collagen degradation. InWound Healing: Biochemical and Clinical Aspects, I. K. Cohen, R. F. Diegelmann and W. J. Lindblad (Eds). Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders, pp. 177–194.
Knight, K. R., D. A. Lepore, R. S. C. Horne, M. Ritz, J. V. Hurley, S. Kumta and B. M. O'Brien, 1993. Collagen content of uninjured skin and scar tissue in fetal and adult sheep.Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 74, 583–591.
Kolmogoroff, A., I. Petrovsky and N. Piscounoff. 1937. Etude de l'équation de la diffusion avec croissance de la quantité de matière et son application à un problème biologique.Moscow Univ. Bull. Math. 1, 1–25.
Krieg, T. 1995. Collagen in the healing wound.Wounds 7, A5-A12.
Krummel, T. M., B. A. Michna, B. L. Thomas, M. B. Sporn, J. M. Nelson, A. M. Salzberg, I. K. Cohen and R. F. Diegelmann. 1988. Transforming growth factor beta induces fibrosis in a fetal wound model.J. Pediatr. Surg. 23, 647–652.
Lin, R. Y., K. M. Sullivan, P. A. Argenta, M. Meuli, H. P. Lorenz and N. S. Adzick. 1995. Exogenous transforming growth factor beta amplifies its own expression and induces scar formation in a model of human fetal skin repair.Annal Surg. 222, 146–154.
Martin, P., J. Hopkinson-Woolley and J. McCluskey. 1992. Growth factors and cutaneous wound repair.Progr. Growth Factor Res. 4, 25–44.
Mast, B. A., J. M. Nelson and T. M. Krummel. 1992. Tissue repair in the mammalian fetus. InWound Healing: Biochemical and Clinical Aspects, I. K. Cohen, R. F. Diegelmann and W. J. Lindblad (Eds). Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders, pp. 326–343.
McDonald, J. A. 1988. Fibronectin: a primitive matrix. InThe Molecular and Cellular Biology of Wound Repair, R. A. F. Clark and P. M. Henson (Eds). New York: Plenum, pp. 405–436.
Merkel, J. R., B. R. DiPaolo, G. C. Hallock and D. C. Rice 1988. Type I and type III collagen content of healing wounds in fetal and adult rates.Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 187, 493–497.
Morgan, C. J. and W. J. Pledger. 1992. Fibroblast proliferation. InWound Healing: Biochemical and Clinical Aspects, I. K. Cohen, R. F. Diegelmann and W. J. Lindblad (Eds). Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders, pp. 63–76.
Murphy, P. G., B. J. Loitz, C. B. Frank and D. A. Hart. 1994. Influence of exogenous growth factors on the synthesis and secretion of collagen type-I and type-III by explants of normal and healing rabbit ligaments.Biochem. Cell Biol. 72, 403–409.
Murray, J. D., R. T. Tranquillo and P. K. Maini. 1988. Mechanochemical models for generating biological pattern and form in development.Phys. Rep. 171, 59–84.
Olsen, L., J. A. Sherratt and P. K. Maini. 1996. A mathematical model for fibro-proliferative wound healing disorders.Bull. Math. Biol.,58, 787–808.
Olsen, L., P. K. Maini, J. A. Sherratt and B. Marchant. (in press). Simple modelling of extracellular matrix alignment in dermal wound healing. I. Cell flux induced alignment.
Peacock, E. E. 1984Wound Repair. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders.
Pierce, G. F., D. Brown and T. A. Mustoe. 1991. Quantitative analysis of the inflammatory cell influx, procollagen type I synthesis, and collagen cross-linking in incisional wounds: influence of PDGF-BB and TGF-β1 therapy.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 117, 373–382.
Roberts, A. B. and M. B. Sporn. 1990. The transforming growth factor-βs. InPeptide Growth Factors and Their Receptors, M. B. Sporn and A. B. Roberts (Eds). Berlin: Springer-Verlag, pp. 419–472.
Rothe, F. 1978. Convergence to travelling fronts in semilinear parabolic equations.Proc. R. Soc. Edin. 80A, 213–234.
Shah, M., D. M. Foreman and M. W. J. Ferguson. 1992. Control of scarring in adult wounds by neutralising antibody to transforming growth factor β.Lancet 339, 213–214.
Shah, M., D. M. Foreman and M. W. J. Ferguson. 1994. Neutralizing antibody to TGFβ(1,2) reduces scarring in adult rodents.J. Cell Sci. 107, 1137–1157.
Shah, M., D. M. Foreman and M. W. J. Ferguson. 1995. Neutralization of TGFβ1 and TGFβ2 or exogenous addition of TGFβ3 to cutaneous rat wounds scarring.J. Cell Sci. 108, 985–1002.
Sherratt, J. A. and J. D. Murray. 1990. Models of epidermal wound healing.Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 241, 29–36.
Sinclair, R. D. and T. J. Ryan. 1994. Proteolytic enzymes in wound healing: the role of enzymatic debridement.Austr. J. Dermatol. 35, 35–41.
Streuli, C. H., C. Schmidhauser, M. Kobrin, M. J. Bissell and R. Derynck. 1993. Extracellular matrix regulates expression of the TGF-β1 gene.J. Cell Biol.,120, 253–260.
Stricklin, G. P., E. A. Bauer and J. J. Jeffrey. 1978. Human skin collagenase: chemical properties of precursor and active forms.Biochemistry 17, 2331–2337.
Varedi, M., E. E. Tredget, P. G. Scott, Y. J. Shen and A. Ghahary. 1995. Alteration in cell morphology triggers transforming growth factor beta 1, collagenase, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases I expression in normal and hypertrophic scar fibroblasts.J. Invest. Dermatol. 104, 118–123.
Whitby, D. J. and M. W. J. Ferguson. 1991. Immunohistochemical localization of growth factors in fetal wound healing.Dev. Biol. 147, 207–215.
Whitby, D. J. and M. W. J. Ferguson. 1992. Immunohistochemical studies of the extracellular matrix and soluble growth factors in fetal and adult wound healing. InFetal Wound Healing, N. S. Adzick and M. T. Longaker (Eds). New York: Elsevier, pp. 161–176.
Zhang, K., W. Garner, L. Cohen, J. Rodriguez and S. Phan. 1995. Increased type I and type III collagen and transforming growth factor β-1 messenger RNA and protein in hypertrophic burn scar.J. Invest. Dermatol. 104, 750–754.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dale, P.D., Sherratt, J.A. & Maini, P.K. Role of fibroblast migration in collagen fiber formation during fetal and adult dermal wound healing. Bltn Mathcal Biology 59, 1077–1100 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02460102
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02460102