Abstract
A phylogenetic study of the isopenicillin-N-synthetase (IPNS) gene sequence from prokaryotic and lower eukaryotic producers of β-lactam antibiotics by means of a maximum-likelihood approach has been carried out. After performing an extensive search, rather than invoking a global molecular clock, the results obtained are best explained by a model with three rates of evolution. Grouped in decreasing order, these correspond toA. nidulans and then to the rest of the eukaryotes and prokaryotes, respectively. The estimated branching date between prokaryotic and fungal IPNS sequences (852 ±106 MY) strongly supports the hypothesis that the IPNS gene was horizontally transferred from bacterial β-lactam producers to filamentous fungi.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1974) A new look at the statistical model identification. Inst Electrical Electronics IEEE Trans Autom Contr AC-19:716–723
Cohen G, Shiffman D, Mavarech M, Aharonowitz Y (1990) Microbial isopenicillin N synthase genes: structure, function, diversity and evolution. Trends Biotechnol 8:105–111
Coque JJR, Martín JF, Calzada JG, Liras P (1991a) The cephamycin biosynthetic genepcbAB, encoding a large multidomain peptide synthetase, andpcbC ofNocardia lactamdurans are clustered together in an organization different from the same genes inA. chrysogenum andP. chrysogenum. Mol Microbial 5:1125–1133
Coque JJR, Liras P, Laiz L, Martín IF (1991b) A gene encoding lisyne 6-aminotransferase, which forms the β-lactam precursor α-aminoadipic acid, is located in the cluster of cephamycin biosynthetic genes inNocardia lactamdurans. J Bacteriol 173:6258–6264
Dyer BD, Obar RA (1994) Tracing the history of eukaryotic cells. Columbia University Press, New York
Elander RP (1983) Strain improvement and preservation of β-lactam producing microorganisms. In: Demain AL, Solomon NA (eds) Antibiotic containing the β-lactam structure I. Springer, Berlin, p 97
Felsenstein J (1990) PHYLIP manual. Version 3.3. University of California Press, Berkeley
Fitch WM (1970) Distinguishing homologous from analogous proteins. Syst Zool 19:99–113
Gray GS, Fitch WM (1983) Evolution of antibiotic resistance genes: the DNA sequence of a kanamycin resistance gene fromStaphylococcus aureus. Mol Biol Evol 1:57–66
Hasegawa M, Kishino H, Yano T (1985) Dating of the human-ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial DNA. J Mol Evol 22:160–174
Higgins DG, Sharp PM (1989) Fast and sensitive multiple sequence alignments on a microcomputer. Comput Appl Biol Sci 5:151–153
Hori H, Osawa S (1987) Origin and evolution of organisms as deduced from 5S ribosomal RNA sequences. Mol Biol Evol 4:445–472
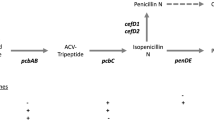
Jensen SE (1986) Biosynthesis of cephalosporins. Crit Rev Biotechnol 3:277–301
Kidwell M (1993) Lateral transfer in natural populations of eukaryotes. Annu Rev Genet 27:235–256
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kishino H, Hasegawa M (1990) Converting distances to time: an application to human evolution. Methods Enzymol 183:550–570
Landan G, Cohen G, Aharonowitz Y, Shuali Y, Graur D, Shiffman D (1990) Evolution of isopenicillin N synthase may have involved horizontal gene transfer. Mol Biol Evol 7:399–406
Lawrence JG, Hard DL (1992) Inference of horizontal genetic transfer from molecular data: an approach using bootstrap. Genetics 131:753–760
Miller JR, Ingolia TD (1989) Cloning and characterization of betalactam biosynthetic genes. Mol Microbiol 3:689–695
Peñalva MA, Moya A, Dopazo J, Ramón D (1990) Sequences of isopenicillin N syntherase genes suggest horizontal gene transfer from prokaryotes to eukaryotes. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 241:161–169
Ram′n D, Carramolino L, Patiño C, Sánchez F, Peñalva MA (1987) Cloning and characterization of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene mediating the formation of the β-lactam ring inAspergillus nidulans. Gene 57:171–181
Roach PL, Clifton IJ, Füilöp V, Harlos K, Barton GJ, Hajdu J, Anderson I, Schofield CJ, Baldwin JE. (1995) Crystal structure of isopenicillin N synthase is the first from a new structural family of enzymes. Nature 375:700–704
Smith DJ, Burnham MKR, Bull JH, Hodgson JE, Ward JM, Browne P, Brown L, Barton B, Earl AJ, Turner G (1990a) β-lactam antibiotic biosynthetic genes have been conserved in clusters in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. EMBO J 9:741–747
Smith DJ, Burnham MKR, Edwards J, Earl AJ, Turner G (1990b) Cloning and heterologous expression of the penicillin biosynthetic gene cluster fromP. chrysogenum. BioTechnology 8:39–41
Smith DJ, Earl AJ, Turner G (1990c) The multifunctional peptide synthetase performing the first step of penicillin biosynthesis inP. chrysogenum is a 421.073 dalton protein similar toBacillus brevis peptide antibiotic synthetases. EMBO J 9:2743–2750
Smith MW, Feng DF, Doolittle RF (1992) Evolution by adquisition: the case for horizontal gene transfers. Trends Biochem Sci 17:489–493
Syvanen M (1994) Horizontal gene transfer: evidence and possible consequences. Annu Rev Genet 28:237–261
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: A. Moya
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buades, C., Moya, A. Phylogenetic analysis of the isopenicillin-N-synthetase horizontal gene transfer. J Mol Evol 42, 537–542 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02352283
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02352283