Abstract
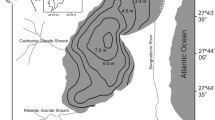
Factors influencing the species composition, distribution and abundance of benthic invertebrates were determined in a eutrophic subarctic lake from April 1978 to April 1979. Collections were made at five stations located at depths of 4 to 13 m. The largest populations of up to 5 × 103 animals m−2 were found in the deepest part of the lake. of the 24 species recorded in this area, the chironomidsProcladius denticulatus, Dicrotendipes modestus, Chironomus decorus andGlyptotendipes barbipes were most common. The strong development of benthos in the profundal zone was attributed to a consistently large supply of food and warm (4 °C) winter temperatures on bottom. Slightly smaller populations (up to 4 × 103 animals, m−2), composed of 19–23 species, occurred in shallower water, a reflection of lower (1.5 °C) winter temperatures. In the anoxic northern part of the lake, only 4–8 species were found in low numbers (400–1 000 animals m−2). This was likely due to low (<5% saturation) oxygen levels in water and high organic content (18.5%) of the sediments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barton, D. R. & Hynes, H. B. N., 1978. Seasonal study of the fauna of bedrock substrates in the wave zones of lakes Huron and Erie. Can. J. Zool. 56: 48–54.
Comita, G. W. & Anderson, G. C., 1959. The seasonal development of a population of Diaptomus ashlandi March, and related phytoplankton cycles in Lake Washington. Limnol. Oceanogr. 4: 37–52.
Darville, R. G. & Harrel, R. C., 1980. Macrobenthos of Pine Island Bayou in the Big Thicket National Preserve, Texas. Hydrobiologia 69: 213–223.
Edmonds, J. S. & Ward, J. V., 1979. Profundal benthos of a multibasic foothills reservoir in Colorado, USA Hydrobiologia 63: 199–208.
Gore, J. A., 1980. Ordinational analysis of benthic communities upstream and downstream of a prairie storage reservoir. Hydrobiologia 69: 33–44.
Johnson, L., 1975. Distribution of fish species in Great Bear Lake, Northwest Territories, with reference to zooplankton, benthic invertebrates, and environmental conditions. J. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 32: 1989–2004.
Jónasson, R. M. & Kristiansen, J., 1967. Primary and secondary production in Lake Esrom. Growth of Chironomus anthracinus in relation to seasonal cycles of phytoplankton and dissolved oxygen. Int. Rev. ges. Hydrobiol. 52: 163–217.
Kajak, Z., 1977. Factors influencing benthos biomass in shallow lake environments. Ekol. Pol. 25: 421–429.
Kajak, Z. & Dusoge, K., 1976. Benthos of Lake Sniardwy as compared to benthos of Lake Mikolajskie and Lake Taltowisko. Ecol. Pol. 24: 77–101.
Larkin, P. A., 1948. Pontoporeia and Mysis in Athabaska, Great Bear and Great Slave Lakes. Bull. Fish. Res. Bd. Can. 78: 1–33.
Lellak, J., 1966. Influences of the removal of the fish population on the bottom fauna of five Elbe backwaters. In: Hydrobiological Studies I. Hrbacek, J., Ed., Prague: Academic Press. pp. 323–359.
Mackey, A. P., 1976. Quantitative studies of the Chironomidae (Diptera) of the Rivers Thames and Kennet. I. The Aorus zone. Arch. Hydrobiol. 78: 240–267.
Maitland, P. S., 1976. The distribution of zoobenthos and sediments in Loch Leven, Kinross, Scotland. Arch. Hydrobiol. 85: 98–125.
McLachlan, A. J. & Contrell, M. A., 1976. Sediment development and its influence on the distribution and tube structure of Chironomus plumosus L. (Chironomidae, Diptera) in a new impoundment. Freshwater Biol. 6: 437–443.
Moore, J. W., 1978. Some factors influencing the diversity and species composition of benthic invertebrate communities in twenty arctic and subarctic lakes. Int. Rev. ges. Hydrobiol. 63: 757–771.
Moore, J. W., 1979. Factors influencing the diversity, species composition and abundance of phytoplankton in twenty one arctic and subarctic lakes. Int. Rev. ges. Hydrobiol. 64: 485–499.
Roback, S. S., 1974. Insects (Arthropoda: Insecta) In: Pollution ecology of freshwater invertebrates, Eds. Hart, C. W. & Fuller, S. L. H., New York: Academic Press, pp. 313–376.
Ruttner, F., 1970. Fundamentals of limnology. Univ. Toronto Press, Toronto.
Utermöhl, H., 1958. Zur Vervollkommnung der quantitativen Phytoplankton — Methodik. Verh. Int. Ver. Limnol. 9: 1–39.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, J.W. Factors influencing the species composition, distribution and abundance of benthic invertebrates in the profundal zone of a eutrophic northern lake. Hydrobiologia 83, 505–510 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02187047
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02187047