Abstract
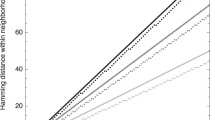
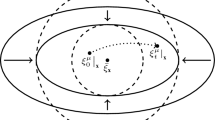
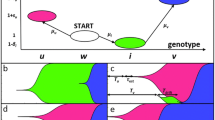
We study in detail a recently proposed simple discrete model for evolution on smooth landscapes. An asymptotic solution of this model for long times is constructed. We find that the dynamics of the population is governed by correlation functions that although being formally down by powers ofN (the population size), nonetheless control the evolution process after a very short transient. The long-time behavior can be found analytically since only one of these higher order correlators (the two-point function) is relevant. We compare and contrast the exact findings derived herein with a previously proposed phenomenological treatment employing mean-field theory supplemented with a cutoff at small population density. Finally, we relate our results to the recently studied case of mutation on a totally flat landscape.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. S. Novella, E. A. Duarte, S. F. Elena, A. Moya, E. Domingo, and J. J. Holland,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:5841 (1995), and references therein.
D. L. Hartle,A Primer of Population Genetics, 2nd ed. (Sinauer, Sunderland, Massachusetts, 1988).
L. Tsimring, H. Levine, and D. A. Kessler,Phys. Rev. Lett. 76:4440 (1996).
M. Eigen and C. Biebricher, InRNA Genetics, E. Domingo, J. J. Holland, and P. Ahlquist, eds. (CPC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 1988).
W. Fontana, W. Schnabl, and P. Schuster,Phys. Rev. A 40:3301 (1989).
S. A. Kaufman,The Origins of Order (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1993).
T. A. Witten and L. M. Sander,Phys. Rev. B 27:5686 (1983).
E. Brener, H. Levine, and Y. Tu,Phys. Rev. Lett. 66:1978 (1991).
T. B. Kepler and A. S. Perelson,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92 (18):8219 (1995).
Y.-C. Zhang, M. Serva, and M. Polikarpov,J. Stat. Phys. 58:849 (1990).
M. Meyer, S. Havlin, and A. Bunde, Preprint (1996).
H. J. Muller,Mutat. Res. 1:2 (1964).
D. E. Goldberg,Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization, and Machine Learning (Addison-Wesley, Reading, 1989).
G. Woodcock and P. Higgs,J. Theor. Biol. 179:61 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kessler, D.A., Levine, H., Ridgway, D. et al. Evolution on a smooth landscape. J Stat Phys 87, 519–544 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181235
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181235