Abstract
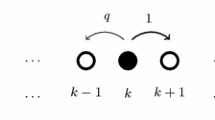
A simple two-species asymmetric exclusion model is introduced. It consists of two types of oppositely charged particles driven by an electric field and hopping on an open chain. The phase diagram of the model is calculated in the meanfield approximation and by Monte Carlo simulations. Exact solutions are given for special values of the parameters defining its dynamics. The model is found to exhibit two phases in which spontaneous symmetry breaking takes place, where the two currents of the two species are not equal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Katz, J. L. Lebowitz, and H. Spohn, Nonequilibrium steady states of stochastic lattice gas models of fast ionic conductors,J. Stat. Phys. 34:497 (1984).
H. Spohn,Large Scale Dynamics of Interacting Particles (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1991).
B. Schmittmann and R. K. P. Zia, Statistical mechanics of driven diffusive systems, inPhase Transitions and Critical Phenomena, C. Domb and J. Lebowitz, eds. (Academic, London, 1994).
P. Meakin, P. Ramanlal, L. M. Sander and R. C. Ball, Ballistic deposition on surfaces,Phys. Rev. A34:5091–5103 (1986).
J. Kertész and D. E. SpohnPhys. Rev. Lett. 62:2571 (1989).
J. Krug and H. Spohn, Anomalous fluctuations in the driven and damped sine-Gordon chain,Europhys. Lett. 8:219–224 (1989).
J. Krug and H. Spohn, inSolids far from Equilibrium, C. Godrèche ed. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1991).
D. Kandel and D. Mukamel, Defects, interface profile and phase transitions in growth models,Europhys. Lett. 20:325–329 (1992).
T. M. Liggett,Interacting Particle Systems (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1985).
B. Schmittmann, K. Hwang, and R. K. P. Zia, Onset of spatial structures in biased diffusion of two species,Europhys. Lett. 19:19 (1992).
D. P. Foster and C. Godrèche, Finite-size effects for phase segregation in a two-dimensional asymmetric exclusion model with two species,J. Stat. Phys. 76:1169 (1994).
J. Krug, Boundary-induced phase transitions in driven diffusive systems,Phys. Rev. Lett. 67:1882–1885 (1991).
D. Kandel, G. Gershinsky, D. Mukamel, and B. Derrida, Phase transitions induced by a defect in a growing interface model,Physica Scripta T49:622 (1993).
E. D. Andjel, M. Bramson, and T. M. Liggett, Shocks in the asymmetric simple exclusion process,Prob. Theory Rel. Fields 78:231–247 (1988).
A. DeMasi, C. Kipnis, E. Presutti, and E. Saada, Microscopic structure at the shock in the simple asymmetric exclusion process,Stochastics Stochastics Rep. 27:151–165 (1988).
P. A. Ferrari, C. Kipnis, and E. Saada, Microscopic structure traveling waves for asymmetric simple exclusion process,Ann. Prob. 19:226–244 (1991).
C. Boldrighini, G. Cosimi, S. Frigio, and M. G. Nuñes, Computer simulation of shock waves in the completely asymmetric simple exclusion process,J. Stat. Phys. 55:611–623 (1989).
S. A. Janowsky and J. L. Lebowitz, Finite-size effects and shock fluctuations in the asymmetric simple-exclusion process,Phys. Rev. A45:618–625 (1992).
B. Derrida, E. Domany, and D. Mukamel, An exact solution of a one dimensional asymmetric exclusion model with open boundaries,J. Stat. Phys. 69:667–687 (1992).
B. Derrida, M. R. Hakim, V. Evans, and V. Pasquier, Exact solution of a 1D asymmetric exclusion model using a matrix formulation,J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 26:1493–1517 (1993).
G. Schütz, and E. Domany, Phase transitions in a exactly soluble one-dimensional exclusion process,J. Stat. Phys. 72:277–296 (1993).
B. Derrida, S. A. Janowsky, J. L. Lebowitz, and E. R. Speer, Microscopic-shock profiles: Exact solution of a non-equilibrium system,Europhys. Lett. 22:651–656 (1993); Exact solution of the totally asymmetric simple exclusion process: Shock profiles,J. Stat. Phys. 73:813 (1993).
M. R. Evans, D. P. Foster, C. Godrèche, and D. Mukamel, Spontaneous symmetry breaking in a one-dimensional driven diffusive system,Phys. Rev. Lett. 74:208–211 (1995).
M. Rubinstein, Discretized model of entangled-polymer dynamics,Phys. Rev. Lett. 59:1496–1949 (1987).
T. A. J. Duke, Tube model of field-inversion electrophoresis,Phys. Rev. Lett. 62:2877–2880 (1989).
B. Widom, J. L. Viovy, and A. D. Defontaines, Repton model of gel electrophoresis and diffusion,J. Phys. I. (France) 1:1759–1784 (1991).
J. M. J. van Leeuwen, and A. Kooiman, The drift velocity in the Rubinstein-Duke model for electrophoresis,Physica A 184:79–97 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Evans, M.R., Foster, D.P., Godrèche, C. et al. Asymmetric exclusion model with two species: Spontaneous symmetry breaking. J Stat Phys 80, 69–102 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02178354
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02178354