Abstract
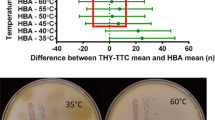
The macro-test for slime production by coagulase-negative staphylococci was adapted to a spectrophotometric micro-test assay to obtain more objective and quantitative information on slime production. A total of 135 isolates of coagulase-negative staphylococci (70 macro-test-positive and 65 macro-test-negative) were tested by both methods. The quantitative micro-test optical density readings were (mean ±SD) 1.176 ± 0.294 and 0.130 ± 0.095 for the macro-test-positive and -negative groups, respectively. The micro-test was reproducible and demonstrated quantitative differences in slime production among the different species of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Aside fromStaphylococcus epidermidis, the majority of the coagulase-negative staphylococci had very low optical density readings, indicating little or no slime production under the conditions employed in this assay. This test allows one to study the relative production of slime by different strains and species of coagulase-negative staphylococci, and may be useful in studying the effects of different conditions, such as antibiotic exposure, on slime production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christensen, G.D., Bisno, A.L., Parisi, J.T., McLaughlin, B., Hester, M.G., Luther, R.W. Nosocomial septicemia due to multiple antibiotic-resistentStaphylococcus epidermidis. Annals of Internal Medicine 1982, 96: 1–10.
Wade, J.C., Schimpff, S.C., Newman, K.A., Wiernik, P.H. Staphylococcus epidermidis: An increasing cause of infection in patients with granulocytopenia. Annals of Internal Medicine 1982, 97: 503–508.
Winston, D.J., Dudnick, D.V., Chapin, M., Ho, W.G., Gale, R.P., Martin, W.J. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal bacteremia in patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy. Archives of Internal Medicine 1982, 143: 32–36.
Sherertz, R.J., Falk, R.J., Huffman, K.A., Thomann, C. A., Mattern, W.D. Infections associated with subclavian Uldall catheters. Archives of Internal Medicine 1983, 143: 52–56.
Christensen, G.D., Simpson, W.A., Bisno, A.L., Beachy, E.H. Adherence of slime-producing strains ofStaphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infection and Immunity 1982, 37: 318–326.
Christensen, G.D., Parisi, J.T., Bisno, A.L., Simpson, W.A., Beachy, E.H. Characterization of clinically significant strains of coagulase-negative staphylococci. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1983, 18: 258–269.
Franson, T.R., Sheth, N.K., Rose, H.D., Sohnle, P.G. Scanning electron microscopy of bacteria adherent to intravascular catheters. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1984, 20: 500–505.
Peters, G., Locci, R., Pulverer, G. Adherence and growth of coagulase-negative staphylococci on surfaces of intravenous catheters. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1982, 14: 479–482.
Davenport, D.S., Massanari, R.M., Pfaller, M.A., Bale, M.J., Streed, S.A., Hierholzer, W.J. Usefulness of a test for slime production as a marker for clinically significant infections with coagulase-negative staphylococci. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1986, 153: 332–339.
Ishak, M.A., Groschel, D.H.M., Mandell, G.L., Wenzel, R.P. Association of slime with pathogenicity of coagulase-negative staphylococci causing nosocomial septicemia. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1985, 22: 1025–1029.
Christensen, G.D., Simpson, W.A., Younger, J.J., Baddour, L.M., Barrett, F.F., Melton, D.M., Beachey, E.H. Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1985, 22: 996–1006.
Galen, R.S., Gambino, S.R. Beyond normality: the predictive value and efficiency of medical diagnosis. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1975.
Kloos, W.E. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clinical Microbiology Newsletter 1982, 4: 75–79.
Parisi, J.T. Coagulase-negative staphylococci and the epidemiological typing ofStaphylococcus epidermidis. Microbiology Reviews 1985, 49: 126–139.
Pfaller, M.A. Immunoassays for measurement of antimicrobial agents in body fluids. In: Jorgensen, J.H. (ed.): Automation in clinical microbiology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 1987, p. 121–137.
Stobberingh, E.E., Houben, A.W., Van Boven, C.O.A. Comparison of different tobramycin assays. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1982, 15: 795.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pfaller, M., Davenport, D., Bale, M. et al. Development of the quantitative micro-test for slime production by coagulase-negative staphylococci. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 7, 30–33 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01962167
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01962167