Abstract
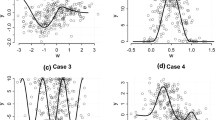
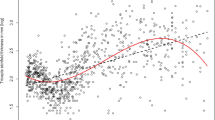
We propose three statistics for testing that a predictor variable has no effect on the response variable in regression analysis. The test statistics are integrals of squared derivatives of various orders of a periodic smoothing spline fit to the data. The large sample properties of the test statistics are investigated under the null hypothesis and sequences of local alternatives and a Monte Carlo study is conducted to assess finite sample power properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buckley, M. J. (1991). Detecting a smooth signal: optimality of cusum based procedures,Biometrika,78, 253–262.
Buckley, M. J. and Eagleson, G. K. (1988). An approximation to the distribution of quadratic forms in normal random variables,Austral. J. Statist.,30, 149–163.
Chen, J. C. (1992). Testing goodness of fit of polynomial models via spline smoothing techniques, Ph.D. Dissertation, Texas A&M University (unpublished).
Cox, D. D. and Koh, E. (1989). A smoothing spline based test of model adequacy in polynomial regression,Ann. Inst. Statist. Math.,41, 383–400.
Cox, D. D., Koh, E., Wahba, G. and Yandell, B. (1988). Testing the (parametric) null model hypothesis in (semiparametric) partial and generalized spline models,Ann. Statist.,16, 113–119.
De Jong, P. (1987). A central limit theorem for generalized quadratic forms,Probab. Theory Related Fields,25, 261–277.
Eubank, R. L. (1988).Spline Smoothing and Nonparametric Regression, Marcel Dekker, New York.
Eubank, R. L. and Hart, J. D. (1992). Testing goodness-of-fit in regression via order selection criteria,Ann. Statist.,20, 1412–1425.
Eubank, R. L. and Hart, J. D. (1993). Commonality of cusum, von Neumann and smoothing-based goodness-of-fit tests,Biometrika,80, 89–98.
Eubank, R. L. and LaRiccia, V. N. (1993). Testing for no effect in nonparametric regression,J. Statist. Plann. Inference,36, 1–14.
Eubank, R. L. and Spiegelman, C. H. (1990). Testing the goodness of fit of a linear model via nonparametric regression techniques,J. Amer. Statist. Assoc.,85, 387–392.
Gasser, T., Sroka, L. and Jennen-Steinmetz, C. (1986). Residual variance and residual pattern in nonlinear regression,Biometrika,73, 625–633.
Graybill, F. A. (1976).Theory and Application of the Linear Model, Duxbury Press, Boston.
Hall, P., Kay, J. W. and Titterington, D. M. (1990). Asymptotically optimal difference-based estimation of variance in nonparametric regression,Biometrika,77, 521–528.
Härdle, W. and Mammen, E. (1988). Comparing nonparametric versus parametric regression fits (unpublished).
Hart, J. D. and Wehrly, T. E. (1992). Kernel regression when the boundary region is large, with an application to testing the adequacy of polynomial models.J. Amer. Statist. Assoc.,87, 1018–1024.
Jayasuriya, B. R. (1990). Testing for polynomial regression using nonparametric regression techniques, Ph.D. Dissertation, Texas A&M University.
Kleinbaum, D. G., Kupper, L. L. and Muller, K. E. (1988).Application Regression Analysis and Other Multivariable Methods, PWS-KENT Publishing, Boston.
Müller, H. G. (1992). Goodness-of-fit diagnostics for regression models,Scand. J. Statist.,19, 157–172.
Munson, P. J. and Jernigan, R. W. (1989). A cubic spline extension of the Durbin-Watson test,Biometrika,76, 39–47.
Raz, J. (1990). Testing for no effect when estimating a smooth function by nonparametric regression: a randomization approach,J. Amer. Statist. Assoc.,85, 132–138.
Rice, J. (1986). Bandwidth choice for differentiation,J. Multivariate Anal.,19, 251–264.
Rice, J. and Rosenblatt, M. (1981). Integrated mean squared error of a smoothing spline,J. Approx. Theory,33, 353–369.
Staniswalis, J. G. and Severini, T. A. (1991). Diagnostics for assessing regression models,J. Amer. Statist. Assoc.,86, 684–692.
von Neumann, J. (1941). Distribution of the ratio of the mean squared successive difference to the variance,Ann. Math. Statist.,12, 367–395.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, JC. Testing for no effect in nonparametric regression via spline smoothing techniques. Ann Inst Stat Math 46, 251–265 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01720583
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01720583