Abstract
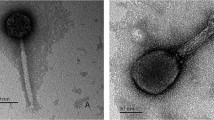
FiveRhizobium meliloti bacteriophages isolated from soil or lysogenic bacteria and belonging to Bradley's group B or theSiphoviridae family of tailed phaes were studied. They are of identical morphology, showing isometric heads and long, noncontractile tails with transverse bars. They are temperate and closely related by host range, DNA restriction endonuclease patterns and homology, DNA mass, serological properties, adsorption velocity, and latent period. However, the phages can be divided into three groups on the basis of burst size and frequency of lysogenization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Ackermann HW (1978) La classification des phages d'Agrobacterium etRhizobium. Pathol Biol 26:507–512
Adams MH (1959) Bacteriophages. New York: Interscience Publishers Inc.
Atkins GJ (1973) Some bacteriophages active againstRhizobium trifolii strain W19. J Virol 12:149–156
Barnet YM (1972) Bacteriophages ofRhizobium trifolii. I. Morphology and host range. J Gen Virol 15:1–15
Barnet YM (1980) The effect of rhizobiophages on populations ofRhizobium trifolii in the root zone of clover plants. Can J Microbiol 26:572–576
Beringer JE (1974) R factor transfer inR. leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol 84:188–198
Bradley DE (1967) Ultrastructure of bacteriophages and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev 31:230–314
Dhar B, Singh BD, Singh RB, Singh RM, Singh VP, Srivastava JS (1978) Isolation and characterization of a virus (RL1) infective onRhizobium leguminosarum. Arch Microbiol 119:263–267
Evans J, Barnet YM, Vincent JM (1979a) Effect of a bacteriophage on the colonization and nodulation of clover roots by a strain ofRhizobium trifolii. Can J Microbiol 25:968–973
Evans J, Barnet YM, Vincent JM (1979b) Effect of a bacteriophage on the colonization and nodulation of clover roots by paired strains ofRhizobium trifolii Can J Microbiol 25:974–978
Gregory DW, Pirie BJS (1973) Wetting agents for biological electron microscopy. I. General considerations and negative staining. J Microsc 99:251–265
Hassani L (1983) La lysogénie chezRhizobium meliloti. Thesis n°1059 Université des Sciences et Techniques de Lille Flandres-Artois 59655 Villeneuve d'Ascq Cedex France
Kowalski M (1967) Transduction inRhizobium meliloti. Acta Microbiol Pol 16:7–12
Kowalski M (1976) Transduction of effectiveness inRhizobium meliloti. In: P.S. Nutman (ed.) Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation in Plants 63–67 Cambridge University Press London
Kowalski M, Denarie J (1972) Transduction d'un gène contrôlant l'expression de la fixation de l'azote chezR. meliloti. C R Acad Sci Ser D 275:141–144
Krsmanovic-Simic D, Werquin M (1973) Etude des bactériophages deRhizobium meliloti. C R Acad Sci Ser D 276:2745–2748
Lesley SM (1982) A bacteriophage typing system forRhizobium meliloti. Can J Microbiol 28:180–189
Luftig R (1967) An accurate measurement of the catalase crystal period and its use as an internal marker for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 20:91–102
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook JS (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Matthews REF (1982) Classification and nomenclature of viruses. Fourth Report of the International Committee on Nomenclature of Viruses. Intervirology 17:1–199
Meyers JA, Sanchez D, Elwell LP, Falkow S (1976) Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol 127:1529–1537
Radloff R, Bauer W, Vinograd J (1967) A dye-buoyant density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Biochemistry 57:1514–1521
Rigby PWJ, Dieckmann M, Rhodes C, Berg P (1977) Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activityin vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol 113:237–251
Silhavy TJ, Bermann ML, Enquist LW (1974) Experiments with gene fusions. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Staniewski R, Kowalski M, Gorzkowska K (1963) The rate of phage adsorption onRhizobium cells. Acta Microbiol Pol 12:184–187
Stent GS (1963) Molecular biology of bacterial viruses. San Francisco: Freeman
Svab Z, Kondorosi A, Orosz L (1978) Specialized transduction of a cysteine marker byRhizobium meliloti 16–3. J Gen Microbiol 106:321–327
Werquin M, Ben Brahim T, Krsmanovic-Simic D (1977) Etude des bactériophages deRhizobium meliloti. C R Acad Sci Ser D 284:1851–1854
Werquin M, Defives C, Hassani L, Andriantsimiavona-Otonia M (1984) Large scale preparation ofRhizobium meliloti bacteriophages by fermenter culture. J Virol Methods 8:155–160
Yamamoto KR, Alberts BM, Benzinger R, Lawhorne L, Treiber G (1970) Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to largescale virus purification. Virology 40:734–744
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Werquin, M., Ackermann, HW. & Levesque, R.C. Characteristics and comparative study of fiveRhizobium meliloti bacteriophages. Current Microbiology 18, 307–311 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01575946
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01575946