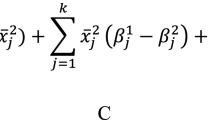Abstract
The purpose of this research is to introduce a new approach to the decomposition of the Gini ratio into three components, supporting them with economic and statistical rigorous interpretations. The three components are: (i) the Gini inequalitywithin subpopulations; (ii) thenet contribution of the extended Gini inequalitybetween subpopulations; and (iii) the contribution of theintensity of transvariation between subpopulations. These components are weighted by the product of the population shares times the income shares of the corresponding subpopulations where the weights add to one.
The decomposition introduced in this research is applied to the 1990 U.S. family income distribution. The population of families is disaggregated by types into the following subpopulations: (a) married-couple families; (b) male householder, no wife present; and (c) female householder, no husband present.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharya N, Mahalanobis B (1967) Regional disparities in household consumption in India. Journal of the American Statistical Association 62:143–161
Blackorby C, Donaldson D, Auersperg M (1981) A new procedure for the measurment of inequality within and among population subgroups. Canadian Journal of Economics 14:665–685
Bourguignon F (1979) Decomposable income inequality measures. Econometrica 47:901–920
Cowell FA (1980) On the structure of additive inequality measures. Review of Economic Studies 47:521–531
Cowell FA, Kuga K (1981) Additivity and the entropy concept: An axiomatic approach to inequality measurement. Journal of Economic Theory 25:131–143
Dagum C (1959) Transvariazione fra più di due distribuzioni. In: Gini, C. (ed.) Memorie di metodologia statistica. Vol II, Libreria Goliardica, Roma
Dagum C (1960) Teoría de la transvariación, sus aplicaciones a la economía. Metron XX:1–206
Dagum C (1961) Transvariación en la hipotesis de variables aleatorias normales multidimensionales. Proceedings of the International Statistical Institute, Vol. XXXVIII, Book 4, Tokyo, pp. 473–486
Dagum C (1980) Inequality measures between income distributions with applications. Econometrica 48 (7):1791–1803
Dagum C (1987a) Gini ratio. The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, Vol. 2, MacMillan Press, London, pp. 529–532
Dagum C (1987b) Measuring the economic affluence between populations of income receivers. Journal of Business and Economic Statistics 5, 1:5–12
Dagum C (1990) Generation and properties of income distribution functions. In: Dagum C, Zenga M (eds.) Income and Wealth Distribution, Inequality and Poverty, Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg, pp. 1–17
Dagum C (1996) A systemic approach to the generation of income distribution models. Journal of Income Distribution 6 (1):105–126
Das T, Parikh A (1982) Decomposition of inequality measures and a comparative analysis. Empirical Economics 7:23–48
Frosini BV (1989) Aggregate units, within-group inequality and the decomposition of inequality measures. Statistica 49 (3):349–369
Frosini BV (1990) Ordinal decomposition of inequality measures in case of Dagum distributions. In: Dagum C, Zenga M (eds.) Income and Wealth Distribution, Inequality and Poverty, Springer-Verlag Berlin-Heidelberg, pp. 215–227
Gini C (1912) Variabilità e mutabilità, In: Memorie di Metodologia Statistica, Vol. 1, Variabilità e Concentrazione. Libreria Eredi Virgilio Veschi, Rome, pp. 211–382
Gini C (1916) Il concetto di transvariazione e le sue prime applicazioni. Giornale degli Economisti e Rivista di Statistica, In: Gini C (ed.) (1959) pp. 21–44
Gini C (ed.) (1959) Transvariazione, Vol. 2. Libreria Goliardica, Rome
Pyatt G (1976) On the interpretation and disaggregation of Gini coefficients. The Economic Journal 86:243–254
Rao VM (1969) Two decompositions of concentration ratio. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, CXXXII. A:418–425
Shorrocks AF (1980) The class of additively decomposable inequality measures. Econometrica 48:613–625
Shorrocks AF (1982) On the distance between income distributions. Econometrica 50:1337–1339
Shorrocks AF (1984) Inequality decomposition by population subgroups. Econometrica 53:1369–1386
Silber J (1989) Factor components, population subgroups, and the computation of the Gini index of inequality. Review of Economics and Statistics 71:107–115
Theil H (1967) Economics and information theory. North-Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam
U.S. Bureau of the Census (1991) Money income of households, families, and person in the United States: 1990. Current Population Reports, Series P-60, N.174, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C.
Yitzhaki S, Lerman RI (1991) Income stratification and income inequality. Review of Income and Wealth 37 (3):313–329
Yitzhaki S (1994) Economic distance and overlapping of distributions. Journal of Econometrics 61:147–159
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dagum, C. A new approach to the decomposition of the Gini income inequality ratio. Empirical Economics 22, 515–531 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01205777
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01205777
Key Words
- Relative economic affluence
- Extended Gini ratio between income distributions
- Intensity of transvariation
- Gini mean difference between income distributions