Abstract
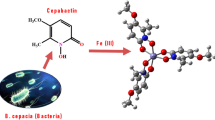
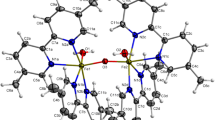
The phytopathogenic bacteriumErwinia chrysanthemi produces the monocatecholate siderophore chrysobactin under conditions of iron deprivation. Only the catecholate hydroxyl groups participate in metal coordination, and chrysobactin is therefore unable to provide full 1:1 coordination of Fe(III). The stoichiometry in aqueous solution is a variable dependent on pH and metal/ligand ratio, in addition to being concentration dependent. At neutral pH and concentrations of about 0.1mm, ferric chrysobactin exists as a mixture of bis and tris complexes. Chrysobactin and its isomers form optically active tris complexes. The dominant configuration depends on the chirality of the amino acid to which the catecholate moiety is attached.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson BF, Buckingham DA, Robertson GB, et al. 1976 Models for the bacterial iron-transport chelate enterochelin.Nature 262, 722–724.
Avdeef A, Sofen SR, Bregante TL, Raymond KN. 1978 Coordination chemistry of microbial iron transport compounds. 19. Stability constants for catechol models of enterobactin.J Am Chem Soc 100, 5362–5370.
Bagg A, Neilands JB. (1987) Molecular mechanism of regulation of siderophore-mediated iron assimilation.Microbial Rev 51, 509–518.
Barclay SJ, Riley PE, Raymond KN. 1982 Dihydroxamate analogues of rhodotorulic acid and an exceptional dimer: preparation and crystal structure of Fe2 [i-C3H7N(O)C(=O)(−CH2−)5−C(=O)N(O)−i-C3 H7]2(μ-OCH3)2.J Am Chem Soc 104, 2011–2018.
Barclay SJ, Huynh BH, Raymond KN. 1984 Coordination chemistry of microbial iron transport compounds. 27. Dimeric iron(III) complexes of dihydroxamate analogues of rhodotorulic acid.Inorg Chem 23, 2011–2018.
Barghouthi S, Young R, Olson MOJ, et al. 1989 Amonabactin, a novel tryptophan-or phenylalanine-containing phenolate siderophore inAeromonas hydrophila.J Bacteriol 171, 1811–1816.
Bergeron RJ, Weimar WJ. 1990 Kinetics of iron acquisition from ferric siderophores byParacoccus denitrificans.J Bacteriol 172, 2650–2657.
Buckingham DA, Clark CR, Weller MG, Gainsford GJ. 1982 A general method for the preparation of crystalline iron(III) and gallium(III) catecholamides; X-ray crystal structure of dipiperidinium bis(ethyl 2,3-dihydroxybenzoylglycinato) (penetane-2,4-dionato)-)ferrate-tetrahydrofuran.J Chem Soc Chem Commun, 779–781.
Carrano CJ, Raymond KN. 1978 Coordination chemistry of microbial iron transport compounds. 10. Characterization of the complexes of rhodotorulic acid, a dihydroxamate siderophore.J Am Chem Soc 100, 5371–5373.
Cass ME, Garrett TM, Raymond KN. 1989 The salicylate mode of bonding in protonated ferric enterobactin analogues.J Am Chem Soc 111, 1677–1682.
Chakraborty RN, Patel HN, Desai SB. 1990 Isolation and partial characterization of catechol-type siderophore fromPseudomonas stutzeri, RC 7.Curr Microbial 20, 283–286.
Enard C, Diolex A, Expert D. 1988 Systemic virulence ofErwinia chrysanthemi 3937 requires a functional iron assimilation system.J Bacteriol 170, 2419–2426.
Hahn FE, McMurry TJ, Hugi A, Raymond KN. 1990 Coordination chemistry of microbial iron transport compounds. 42. Structural and spectroscopic characterization of diastereomeric Cr(III) and Co(III) complexes of desferrithiocin.J Am Chem Soc 112, 1854–1860.
Harris WR, Raymond KN. 1979 Ferric ion sequestering agents. 3. The spectrophotometric and potentiometric evaluation of two new enterobactin analogues: 1,5,9-N′, N″-tris(2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)-cyclotriazatridecane and 1,3,5-N′,N″-tris(2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl (triaminomethylbenzene).J Am Chem Soc 101, 6534–6541.
Harris WR, Carranao CJ, Cooper SR, et al. 1979 Coordination chemistry of microbial iron transport compounds. 19. Stability constants and electrochemical behavior of ferric enterobactin and model complexes.J Am Chem Soc 101, 6097–6104.
Hider RC. 1984, Siderophore mediated absorption of iron.Struct Bonding 58, 25–87.
Jalal MAF, Love SK, van der Helm D. 1986, Siderophore mediated iron(III) uptake inGliocladium virens. 1. Properties ofcis-fusarinine,trans-fusarinine, dimerum acid, and their ferric complexes.J Inorg Biochem 28, 417–430.
Kobaru S, Tsunakawa M, Hanada M, et al. 1983 Bu-2743E, a leucine aminopeptidase inhibitor, produced byBacillus circulans.J Antibiot 35, 1396–1398.
Llinás M, Wilson DM, Neilands JB. 1973 Effect of metal binding on the conformation of enterobactin a proton and carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance study.Biochemistry 12, 3836–3843.
Matzanke BF, Müller-Matzanke G, Raymond KN. 1989 Siderophore-mediated iron transport. In: Loehr TM, ed.Iron Carriers and Iron Proteins. Weinheim: VCH Verlagsgesellschaft; 3–121.
McArdle JV, Sofen SR, Cooper SR, Raymond KN. 1978 Coordination chemistry of microbial iron transport compounds. 13. Preparation and chirality of the rhodium(III)-enterobactin complex and model tris(catecholoato)-rhodate(III) analogues.Inorg Chem 17, 3075–3078.
McBryde WAE. 1964 A spectrophotometric reexamination of the iron(III)-tiron complexes.Can J Chem 42, 1917–1927.
Neilands JB. 1989 Siderophore systems of bacteria and fungi. In: Beveridge TJ, Doyle RJ, eds.Metal Ions and Bacteria. New York: John Wiley and Sons; 141–163.
Neilands JB, Erickson TJ, Rastetter WH. 1981 Stereospecificity of the ferric enterobactin receptor ofEscherichia coli K12.J Biol Chem 256, 3831–3832.
Patel HN, Chakraborty RN, Desai SB. 1988 Isolation and partial characterization of phenolate siderophore fromRhizobium leguminosarum, IARI 102.FEMS Microb Lett 56, 131–134.
Persmark M, Expert D, Neilands JB. 1989 Isolation, characterization, and synthesis of chrysobactin, a compound with siderophore activity fromErwinia chrysanthemi.J Biol Chem 264, 3187–3193.
Rastetter WH, Erickson TJ, Venuti MC. 1981 Synthesis of iron chelators. Enterobactin, enantioenterobactin, and a chiral analogue.J Org Chem 46, 3579–3590.
Raymond KN, Abu-Dari K, Sofen SR. 1980 Stereochemistry of microbial transport compounds.ACS Symp Ser 119, 133–167.
Skorupska A, Choma A, Derylo M, Lorkiewicz Z. 1988 Siderophore containing 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid and threonine formed byRhizobium trifolii.Acta Biochim Pol 35, 119–130.
Tsin-Jao J, Sommer L, Okác A. 1961 Chelate dero-dihydroxybenzoesäuren mit eisen(III).Collect Czech Chem Commun 27, 1170–1190.
van der Helm D, Jalal MAF, Hossain MB. 1987 The crystal structures, conformations, and configurations of siderophores. In: Winkelmann G, van der Helm D, Neilands JB, eds.Iron Transport in Microbes, Plants and Animals. Weinheim: VCH Verlagsgesellschaft; 136–165.
Winkelmann G, Huschka H-G. 1987 Molecular recognition and transport of siderophores in fungi. In: Winkelmann G, van der Helm D, Neilands JB, eds.Iron Transport in Microbes, Plants and Animals. Weinheim: VCH Verlagsgesellschaft; 317–336.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Persmark, M., Neilands, J.B. Iron(III) complexes of chrysobactin, the siderophore ofErwinia chrysanthemi . Biometals 5, 29–36 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01079695
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01079695