Abstract
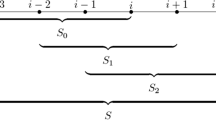
A parallel multischeme computation in the solutions of differential equation initial-value problems has been studied. The mathematical switch of computation history is used successfully in the identification of the best approximation among all available ones at a computing step. A solution correction factor is also developed to achieve an extra four digits in solution accuracy. Based on our results, if the truncation error of computation history as we defined it can be properly utilized, then a computation engaging high-order schemes or using fine grids may be unnecessary.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames, W. F. (1976).Numerical Method for Partial Differential Equations, Academic Press, New York.
Chiang, Y. F. (1986). Use of mathematical switch to solve differential equation problems, ACM SIGNUM Newsletter, October, pp. 20–33.
Chiang, Y. F., Ma, J. S., Hu, K. L., and Chang, C. Y. (1988). Parallel multischeme computation,J. Sci. Comput. 3(3), 289–306.
Chiang, Y. F. (1988). Truncation and accumulated errors in wave propagation,J. Comput. Phys. 79(2), 353–372.
Chiang, Y. F. (1984). Pointwise work convergence for solving linear hyperbolic system with discontinuous initial data, Research Report No. 6, CIS, New Jersey Institute of Technology.
Courant, R., and Hilbert, D. (1953).Methods of Mathematical Physics, Interscience Publishers, New York.
Hamming, R. W. (1962).Numerical Methods for Scientists and Engineers, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Morris, J. LI. (1985).Computational Method in Elementary Numerical Analysis, Wiley-Interscience, New York.
Petzoid, L. (1984). Automatic selection of methods for solving stiff and nonstiff systems of ordinary differential equations,SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comp. 4(1), 136–148.
Richter, G. R., and Falk, R. S. (1984). An analysis of a finite element methods for hyperbolic equations,Adv. Comput. Methods Partial Differential Equations V, 297–301.
Richtmyer, R. D., and Morton, K. W. (1969).Difference Methods for Initial Value Problems, Interscience Publishers, New York.
Roache, P. J. (1977).Computational Fluid Dynamics, Hermosa Publishers.
Ultra Computer (1987). Documentation Note No. 2: How to write parallel programs for the NYU Ultra Computer prototype.
Vichnevetsky, R. (1981).Computer Methods for Partial Differential Equations, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey.
Vichnevetsky, R., and Bowles, J. B. (1982).Fourier Analysis of Numerical Approximations of Hyperbolic Equations, SIAM, Philadelphia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiang, Yl.F., Lai, JF. Parallel multischeme computation with the switch of computation history. J Sci Comput 5, 35–53 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01063425
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01063425