Abstract
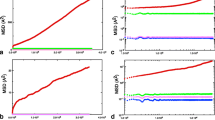
We discuss a simplified version of an ice lattice which consists of an alternating sequence of heavy and light masses. The light masses (protons) are each subject to a bistable potential caused by the heavy masses (oxygens). The protons interact with one another, as do the heavy ions. The interactions between the protons and the oxygens modulate the bistable proton potential. This system is known to exhibit kink and antikink solutions associated with mobile ionic defects accompanied by a lattice distortion. We show that at finite temperatures and in the presence of a constant external field on the protons, the defect velocity is a nonmonotonic function of the temperature, reflecting an interesting interplay of thermal effects (noise) and the constant deterministic external forcing in this nonlinear system. We discuss extensions of the model to higher dimensions, and present preliminary results for the proton motion in such networks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. I. Dykman, D. G. Luchinsky, R. Mannella, P. V. E. McClintock, N. D. Stein, and N. G. Stocks,J. Stat. Phys. 70:463 (1992).
V. Ya. Antonchenko, A. S. Davydov, and A. V. Zolotaryuk,Phys. Stat. Sol. (b) 115:631 (1983).
M. Peyrard, St. Pnevmatikos, and N. Flytzanis,Phys. Rev. A 36:903 (1987).
St. Pnevmatikos,Phys. Rev. Lett. 60:1534 (1988).
G. P. Tsironis and St. Pnevmatikos,Phys. Rev. B 39:7161 (1989).
A. Zolotaryuk and St. Pnevmatikos,Phys. Lett. A 143:233 (1990).
P. S. Lomdahl and W. C. Kerr,Phys. Rev. Lett. 55:1235 (1985).
K. Lindenberg and B. J. West,The Nonequilibrium Statistical Mechanics of Open and Closed Systems (VCH, New York, 1990).
E. S. Nylund and G. P. Tsironis,Phys. Rev. Lett. 66:1886 (1991).
P. B. Hobbs,Ice Physics (Clarendon, Oxford, 1974).
H. Engelheart, B. Bullemer, and N. Riehl,Physics of Ice, N. Riehl, B. Bullemer, and H. Engelheart, eds. (Plenum Press, New York, 1969).
B. Klar, B. Hingerty, and W. Saenger,Acta Cryst. B 36:1154 (1980); W. Saenger, Ch. Betzel, B. Hingerty, and G. M. Brown,Nature 296:581 (1982).
H. Morgan and R. Pethig,Int. J. Quantum Chem. Quantum Biol. Symp. 11:209 (1984).
W. Stoeckenius and W. H. Kunau,J. Cell Biol. 38:337 (1968); D. Osterhelt and W. Stoeckenius,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 70:2853 (1973).
H. Merz and G. Zundel,Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 156:86 (1981).
P. C. Jordan,J. Phys. Chem. 91:6582 (1987).
S. F. Fornili, D. P. Vercantern, and E. Clementi,Biochem. Biophys. Acta 771:151 (1984); D. H. J. Mackay, P. H. Berens, K. R. Wilson, and A. T. Hagler,Biophys. J. 46:229 (1984).
J. F. Nagle and S. Tristram-Nagle,J. Membrane Biol. 74:1 (1983).
St. Pnevmatikos, A. V. Savin, and A. V. Zolotaryuk, inNonlinear Coherent Structures, M. Barthes and J. Léon, eds. (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nylund, E., Lindenberg, K. & Tsironis, G. Proton dynamics in hydrogen-bonded systems. J Stat Phys 70, 163–181 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01053961
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01053961