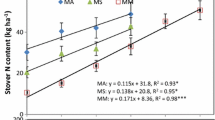
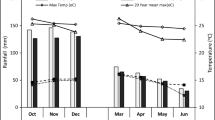
Abstract
Growth and yield components in field-grown maize (Zea mays L.) were enhanced by nitrogen fertilization ranging from 50 to 200 kg N ha−1. Ear diameter, kernel depth, grain: stover ratio, number of ears plant−1, plant height and dry matter production increased as N fertilization rate was increased up to 100 or 150 kg N ha−1. Tasselling in maize was hastened by N fertilization. Increasing plant density from 25000 to 75000 plants ha−1 increased plant height, dry matter production and delayed tasseling but reduced ear diameter, kernel depth, grain: stover ratio and number of ears plant−1. Increased N supply and plant density had no influence on the concentrations of Mn, Zn, Cu, and Fe in ear leaf; except that Mn concentration increased as N fertilization rate was increased up to 150 kg N ha−1. Nitrogen × plant density interactions on the concentrations of the micronutrients in maize ear leaf were not significant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnon I (1975) Mineral nutrition of maize. Bern, Switzerland: International Potash Institute
Bache BW and Rodgers NE (1970) Soil phosphate values in relation to phosphate supply to plants from some Nigerian soils. J Agric Sci, Cambridge 74: 282–290
Chapman HD and Pratt PF (1961) Methods of analysis for soils, plants and waters. Riverside, California: University of California, Division of Agric Science
Douglas JA, Cottie E, Kain WM, O'Connor MB and Douthorn T (1972) Advances in maize production. Proc. Ruakura Farmers Conf., 121-228
Gagra M (1978) Effect of nitrogen fertilization and plant density on stem height of hybrids BcSK 5A, BcSK 21-22 and Pau 200. Poljoprivreda Znanstvena Smotra 44, 347–360 (cited in Soil and Fert. Abstr. 44, No. 571, 1981)
Hamissa MR, Mawadi A, Aziz IA and Hakin AA (1979) Sources of nitrogen for maize. Agric Res 59: 103–112
Iremiren GO and Milbourn GM (1980) Effects of plant density on ear barrenness in maize. Expl Agric 16: 321–326
Jones MJ (1973) The organic matter content of the savanna soils of West Africa. J Soil Sci 24: 42–53
Jordan HV, Laird ICC and Ferguson DD (1959) Growth rate and nutrient uptake by corn in a fertilizer — spacing experiment. Agron J 42: 261–268
Lacatusu R, Dornescu D and Borlan Z (1981) Susceptibility of some maize hybrids to zinc deficiency. Mitteilungen der Deutschen Bodenk. Gesellschaft 32: 399–410
Mohammed MI, Noor MA and Alio AN (1978) The influence of the level of nitrogen fertilizer and spacing on maize in Somalia. Studi e Ricerche 2: 109–115
Powell RD and Webb JR (1972) Effects of high rates of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium fertilizer on maize (Zea mays L.) grain yields. Agron J 64: 653–656
Rathore DN, Kirpal S and Singh BP (1976) Effect of nitrogen and plant population on the yield attributes of maize. Indian J Agric Res 10: 79–82
Sandell EB (1950) Colorimetric determination of trace metals. 2nd ed. New York: Interscience Publishers
Steele KW, McCormick SJ, Pervidal and Brown NS (1981) N, P, K, Mg and S requirements for maize grain production. New Zealand J Expl Agric 9: 243–249
Thompson JW (1962) Effect of fertilizers and soil amendments on the mineral constituents of maize. Soil Sci 94: 323–330
Tyner EH (1946) The relation of corn yields to leaf nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium content. Soil Sci Soc of Amer Proceedings 11: 317–323
Wild A (1971) The potassium status of soils of the savanna zone of Nigeria Expl Agric 7: 257–270
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogunlela, V.B., Amoruwa, G.M. & Ologunde, O.O. Growth, yield components and micronutrient nutrition of field-grown maize (Zea mays L.) as affected by nitrogen fertilization and plant density. Fertilizer Research 17, 189–196 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01050279
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01050279