Abstract
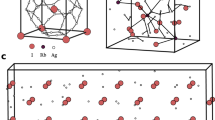
The so-called superionic conductors represent a class of solid materials showing an unusually high ionic conductivity. Their structure is characterized by strong disorder in the sublattice of conducting ions. We shall describe the dynamic properties of the partially disordered state on the basis of two classes of theoretical models. For stochastic lattice gases we discuss the behavior of various time-correlation functions relevant for inelastic neutron- and light-scattering experiments and for tracer-diffusion measurements. In addition we study a system of interacting Brownian particlés in the presence of a periodic potential as a model for optimized (AgI-type) ionic conductors. A mean-field theory is developed which implies a relationship between the conductivity and structural properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. B. Salamon, ed.,Physics of Superionic Conductors (Springer, Berlin, 1979), and references therein.
K. Funke, inAdvances in Solid State Physics, Vol. 20, J. Treusch, ed. (Vieweg, Braunschweig, 1980), p. 1.
S. M. Shapiro and F. Reidinger, inPhysics of Superionic Conductors, M. B. Salamon, ed. (Springer, Berlin, 1979), p. 45.
M. J. Gillan,Solid State Ionics 9 & 10:755 (1983), and references therein.
Y. Tsuchiya, S. Tamaki, and Y. Waseda,J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 12:5361 (1979).
W. Dieterich, P. Fulde, and I. Peschel,Adv. Phys. 29:527 (1980).
G. Alefeld and J. Völkl, eds.,Hydrogen in Metals I (Springer, Berlin, 1978), and references therein.
A. Sadiq and K. Binder, preprint.
L. Pietronero and E. Tosatti, eds.,Physics of Intercalation Compounds (Springer, Berlin, 1981), and references therein.
P. M. Richards, inFast Ion Transport in Solids, Electrodes and Electrolytes, P. Vashishta, J. N. Mundy, and G. K. Shenoy, eds. (North-Holland, New York, 1979), p. 349.
W. Dieterich and I. Peschel,J. Phys. C: Solid State Phys. 16:3843 (1983).
R. J. Nemanich, R. M. Martin, and J. C. Mikkelsen, Jr., inFast Ion Transport in Solids, Electrodes and Electrolytes, P. Vashishta, J. N. Mundy, and G. K. Shenoy, eds. (North-Holland, New York, 1979), p. 547.
H. Harder, Diplomarbeit, Konstanz, 1984.
G. E. Murch,Solid State Ionics 7:177 (1982).
P. A. Fedders and O. F. Sankey,Phys. Rev. B 18:5938 (1978).
N. Nakazato and K. Kitahara,Progr. Theor. Phys. 64:2261 (1980).
R. A. Tahir-Kheli and J. R. Elliott,Phys. Rev. B 27:844 (1983).
D. K. Chaturvedi,Phys. Rev. B 28:6868 (1983).
R. Zwanzig, inLectures in Theoretical Physics, Vol. 3 (Interscience, New York, 1961); H. Mori,Progr. Theor. Phys. 34:399 (1965).
H. J. de Bruin and G. E. Murch,Philos. Mag. 27:1475 (1973).
G. E. Murch, inAtomic Diffusion Theory in Highly Defective Solids (Aedermannsdorf, Trans Tech SA, 1980).
K. W. Kehr, R. Kutner, and K. Binder,Phys. Rev. B 23:4931 (1981).
H. Sato and R. Kikuchi,J. Chem. Phys. 55:677, 702 (1971).
K. W. Kehr and K. Binder, inMonte Carlo Methods in Statistical Physics II, K. Binder, ed. (Springer, Berlin, 1984), Chap. 6.
S. Katz, J. L. Lebowitz, and H. Spohn,J. Stat. Phys. 34:497 (1984).
H. Singer and I. Peschel,Z. Phys. B39:333 (1980).
A. Bunde, D. K. Chaturvedi, and W. Dieterich,Z. Phys. B47:209 (1982).
R. Zeyher,Z. Phys. B31:127 (1978).
D. K. Chaturvedi and W. Dieterich,Z. Phys. B49:17 (1982).
A. Bunde and W. Dieterich,Phys. Rev. B, in press.
L. Onsager,Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 46:241 (1945).
T. Geisel,Phys. Rev. B 20:4294 (1979).
S. H. Jacobsen, M. A. Ratner, and A. Nitzan,J. Chem. Phys. 77:5752 (1982).
G. Radons, T. Geisel, and J. Keller,Solid State Ionics 13:75 (1984).
W. Dieterich, T. Geisel, and I. Peschel,Z. Phys. B29:5 (1978).
H. Risken and H. D. Vollmer,Z. Phys. B31:209 (1978).
H. Risken,The Fokker-Planck Equation, Methods of Solution and Applications (Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, 1983).
W. Hess and R. Klein,Adv. Phys. 32:173 (1983), and references therein.
U. Thomas and W. Dieterich, in preparation.
S. E. Trullinger, M. D. Miller, R. A. Guyer, A. R. Bishop, F. Palmer, and J. A. Krumhansl,Phys. Rev. Lett. 40:206 (1978).
M. Imada,J. Phys. Soc. Japan 49:1247 (1980).
N. H. March and M. P. Tosi,Atomic Dynamics in Liquids (MacMillan, London, 1976).
V. Ambegaokar and B. I. Halperin,Phys. Rev. Lett. 22:1364 (1969).
J. C. Wang and D. F. Pickett,J. Chem. Phys. 65:5378 (1976).
A. Bunde,Z. Phys. B44:225 (1981).
H. Schulz and U. H. Zucker,Solid State Ionics 5:41 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dieterich, W. Superionic conductors. J Stat Phys 39, 583–596 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01008353
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01008353