Abstract
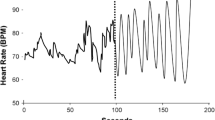
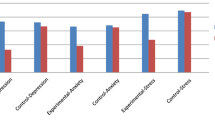
This study investigated effects of EMG-assisted relaxation training on the academic performance, locus of control, and self-esteem of hyperactive junior high school-age boys. Twenty-four subjects each were randomly assigned to the treatment and control condition. Treatment consisted of six 20 to 25-minute sessions conducted biweekly. Pretreatment frontalis EMG, math, reading, and language performance, locus of control, and self-esteem were assessed for both groups. Outcome measures were again obtained on these dependent variables 2 weeks after the last treatment session. Experimental subjects demonstrated significantly higher posttreatment reading and language performance. Math performance gain did not reach statistical significance. A significant internal shift in locus of control was observed; however, self-esteem did not improve to that level. These outcomes correlated with significantly lower posttreatment frontalis EMG in the experimental group. EMG level did not change during the course of this study for control subjects. Implications of these findings are discussed in terms of existent research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman, D. T., Dykman, R. A., & Peters, J. E. (1977). Teenage status of hyperactive and non-hyperactive learning disabled boys.American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 47 577–596.
Ayllon, T., Layman, D., & Kandel, H. (1975). A behavioral-educational alternative to drug control of hyperactive children.Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 8 137–147.
Ballard, K. D., & Glynn, T. (1975). Behavioral self-management in story writing with elementary school children.Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 8 387–398.
Barkley, R., & Ullman, D. (1975). A comparison of objective measures of activity and distractibility in hyperkinetic and nonhyperkinetic children.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychiatry, 3 231–244.
Bhatara, V., Arnold, L. E., Lorance, T., & Gupta, D. (1979). Muscle relaxation therapy in hyperkinesis: Is it effective?Journal of Learning Disabilities, 12 182–186.
Braud, L. W. (1978). The effects of frontal EMG biofeedback and progressive relaxation upon hyperactivity and its behavioral concomitants.Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 3 69–89.
Braud, L. W., Lupin, M. N., & Braud, W. G. (1974).The use of EMG (electromyographic) biofeedback in the control of hyperactivity. Paper presented at the meeting of the International Convention for Learning Disabilities, Houston.
Budzynski, T. H., & Stoyva, J. (1969). An instrument for producing deep muscle relaxation by means of analog information feedback.Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 2 231–237.
Christensen, D. E. (1975). Effects of combination methylphenidate and a classroom token system in modifying hyperactive behavior.American Journal of Mental Deficiency, 80 266–276.
Cobb, D. E., & Evans, J. R. (1981). The Use of biofeedback techniques with school-aged children exhibiting behavioral and/or learning problems.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 9 251–281.
Conners, C. K. (1973). Rating scales for use in drug studies with children.Psychopharmocological Bulletin, 15 24–84.
Conrad, P. (1975). The discovery of hyperkinesis: Notes on medication of deviant behavior.Social Problems, 4 12–21.
Coopersmith, C. (1967).The antecedents of self-esteem. San Francisco: Freeman.
Cruickshank, W. M. (1977). Least restrictive placement: Administrative wishful thinking.Journal of Learning Disabilities, 10 193–194.
Denkowski, K. M. (1981).The relative effects of progressive relaxation and EMG biofeedback training on the disruptive behavior, academic achievement, and locus of control of hyperactive children. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of Houston.
Douglas, V. I. (1974). Sustained attention and impulse control: Implications for the handicapped child. J. A. Swets & L. L. Elliott (Eds.),Psychology and the handicapped child. Washington, D.C.: Office of Education.
Douglas, V. I., Parry, P., Marton, P., & Garson, C. (1976). Assessment of a cognitive training program for hyperactive children.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 4 389–410.
Dunn, F. M., & Howell, R. J. (1982). Relaxation training and its relationship to hyperactivity in boys.Journal of Clinical Psychology, 38 92–100.
Epstein, R., & Komorita, S. S. (1970). Self-esteem, success-failure, and locus of control in negro children.Developmental Psychology, 4 2–8.
Ferritor, D. E., Buckholdt, D., Hamblin, R. L., & Smith, L. (1972). The noneffects of contingent reinforcement for attending behavior or work accomplished.Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 5 7–17.
Firestone, P., & Douglas, V. I. (1975). The effects of rewards and punishment times and automatic activity in hyperactive and normal children.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 3 201–216.
Fitch, G. (1970). Effects of self-esteem, perceived performance, and choice on causal attribution.Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 16 311–315.
Freibergs, V., & Douglas, V. I. (1969). Concept learning in hyperactive and normal children.Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 74 388–395.
Gittelman R., Abikoff, H., Pollack, D. F., Klein, S., Katz, S., & Mattes, J. (1980). A controlled trial of behavior therapy and methylphenidate for hyperactive children. In C. K. Whalen & B. Henker (Eds.),Hyperactive children. New York: Academic Press.
Gittelman-Klein, R., Klein, D. F., Abikoff, H., Katz, S., Gloisten, A. C., & Kates, W. (1976). Relative efficacy of methylphenidate and behavior modification in hyperactive children.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 4 361–379.
Hampstead, W. J. (1979). The effects of EMG-assisted relaxation training with hyperkinetic children: A behavioral alternative.Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 4 113–125.
Hieronymous, D., & Lindquist, R. (1964). Manual for administrators, supervisors, and counselors.Iowa Test of Basic Skills. Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
Keogh, B. K., & Barkett, C. J. (1980). An educational analysis of hyperactive children's achievement problems. In C. K. Whalen & B. Henker (Eds.),Hyperactive children. New York: Academic Press.
Kerlinger, R. N., & Pedhauzr, E. J. (1973). Multiple regression in behavioral research. New York: Holt, Rinehard & Winston.
Lupin, M. (1977).Peace, harmony, awareness. San Antonio, Texas: Learning Concepts (audio casette program).
Lupin, M., Braud, L. W., Braud, W., & Duer, W. F. (1976). Children, parents and relaxation tapes.Academic Therapy, 12 105–113.
Martin, G., & Powers, R. (1967). Attention span: An operant conditioning analysis.Exceptional Children, 33 565–570.
Masters, J. C., & Mokoros, J. R. (1974). Self-reinforcement processes in children. In H. Reese (Ed.),Advances in child development and behavior (Vol. 9). New York: Academic Press.
Meichenbaum, D. (1976). Cognitive factors in biofeedback therapy.Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 2 201–216.
Nowicki, S., & Strickland, B. (1973). A locus of control scale for children.Journal of Clinical and Consulting Psychology, 40 148–154.
O'Leary, K. D., Pelham, W. E., Rosenbaum, A., & Price, G. H. (1976). Behavior treatment of kinetic children: An experimental evaluation of its usefulness.Clinical Pediatrics, 15 510–515.
Omizo, M., Denkowski, K. M., & Wilson, P. (1980).The effects of biofeedback-induced relaxation training on hyperactive boys. Paper presented at the meeting of the American Psychological Association, Montreal, 1980.
Parry, P., & Douglas, V. I. (1977). The effect of reward on the performance of hyperactive children.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 5 389–410.
Patterson, G. R. (1965). An application of conditioning techniques to the control of hyperactive children. In L. Ullman & L. Krasner (Eds.),Case studies in behavior modification. New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston.
Prinz, R. J., Connor, P. A., & Wilson, C. C. (1981). Hyperactive and aggressive behaviors in childhood: Interwined dimensions.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 9 191–202.
Riddle, K. D., & Rapoport, J. L. (1976). A 2-year followup of 72 hyperactive boys: Classroom behavior and peer acceptance.Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 162 130–134.
Rie, H. E., Rie, E. D., Stewart, S., & Ambuel, J. P. (1976). Effects of methylphenidate on underactive children.Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 44 250–260.
Rotter, J. B. (1966). Generalized expectancies for internal versus external control of reinforcement.Psychological Monographs, 80(1, Whole No. 609).
Rivera, E., & Omizo, M. (1980). An investigation of the effects of relaxation training on attention to task and impuisivity among male hyperactive children.Exceptional Child, 27 21–31.
Sandoval, J. (1977). The measurement of the hyperactive syndrome in children.Review of Educational Research, 47 293–318.
Sandoval, J., Lambert, N. M., & Sassone, D. (1980). The identification and labelling of hyperactivity in children: An interactional model. In C. K. Whalen & B. Henker (Eds.),Hyperactive children. New York: Academic Press.
Schandler, S. L., & Grings, W. W. (1976). An examination of methods for producing relaxation during short-term laboratory sessions.Behaviour Research and Therapy, 14, 419–426.
Seligman, M. E. P.Helplessness. San Francisco: Freeman.
Skinner, B. F. (1972).Cumulative record: A selection of papers. New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Stern, G. S., & Berrenberg, J. L. (1977). Biofeedback training in frontalis muscle relaxation and enhancement of belief in personal control.Biofeedback and Self-Regulation, 2 173–182.
Stewart, M. A., Mendelson, W. B., & Johnson, N. E. (1973). Hyperactive children as adolescents: How they describe themselves.Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 4 3–11.
Stoyva, J. M., & Budzynskii, T. H. (1974). Cultivated low arousal—An anti-stress response? In L. V. DiCara (Ed.),Limbic and autonomic nervous system research. New York: Plenum.
Twardosz, S., & Sajwaj, T. (1972). Multiple effects of a procedure to increase sitting in a hyperactive body.Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 5 73–78.
Varni, J. W. (1976).A cognitive-behavior self-regulation approach to the treatment of the hyperactive child. Unpublished doctoral dissertation, University of California, Los Angeles.
Venables, P. H., & Martin, I. (Eds.) (1967).A survey of psychophysiological methods. Amsterdam: North Holland.
Weiss, G., Kruger, E., Danielson, V., & Elman, M. (1975). Effects of long-term treatment with methylphenidate.Canadian Medical Association Journal, 112 159–165.
Werry, J. S., Sprague, R. L., & Cohen, M. N. (1975). Conners's teacher rating scale for use in drug studies with children: An empirical study.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 3 217–229.
Whelan, C. K., & Henker, B. (Eds.) (1980).Hyperactive children. New York: Academic Press.
Worland, J. (1976). Effects of positive and negative feedback on behavior control in hyperactive and normal boys.Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 4 315–326.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Denkowski, K.M., Denkowski, G.C. & Omizo, M.M. The effects of EMG-assisted relaxation training on the academic performance, locus of control, and self-esteem of hyperactive boys. Biofeedback and Self-Regulation 8, 363–375 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00998746
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00998746