Summary
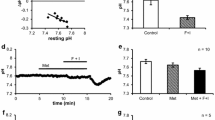
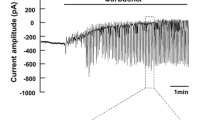
The effect of carbachol on transepithelial potential difference and transepithelial nett electrolyte transport has been studied in the rabbit submaxillary main duct perfusedin vivo andin vitro with bicarbonate saline. The two preparations function similarly, reabsorbing Na, Cl and water and secreting K. In control ducts nett Na reabsorption was 683±55 nmol · cm−2 · min−1 and K secretion was 31.2±2.4 nmol · cm−2 · min−1. Nett water reabsorption was 970±71 nl · cm−2 · min−1 and the hydraulic conductivity was (14.0±1.6)×10−6 ml · cm−2 · s−1 · atm−1. The mean transepithelial potential difference was 13.1±0.8 mV (lumen negative) and, assuming no active transport of Cl, the partial conductance of the duct to Cl was (12.7±2.6)×10−2 mho · cm−2. Carbachol,in vivo andin vitro, caused partial depolarization of the transepithelial potential difference and reduction of nett Na and Cl reabsorption. It was without effect on duct K and HCO3 transport.In vitro, the drug was effective in concentrations as low as 10−7 M and perhaps lower. Atropine was able completely to block the effects of carbachol present at twice the atropine concentration. The results are consistent with the hypothesis that carbachol acts in some way to reduce the sodium conductance of the luminal face of the duct epithelial cell, this response being secondary to an undefined primary action of carbachol on the interstitial face of the cell.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolton, T. B.: The depolarizing action of acetylcholine or carbachol in intestinal smooth muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)220, 647–671 (1972).
Bülbring, E., Jones, A., Tomita, T.:Smooth Muscle. London: Arnold 1970.
Changeux, J. P., Kasai, M., Lee, C. Y.: Use of snake venom toxin to characterize the cholinergic receptor protein. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.)67, 1241–1247 (1970).
Eccles, J. C.:The physiology of synapses. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1964.
Endre, Z. H., Young, J. A.: Acino-tubular balance in the rabbit submaxillary gland. Proc. Aust. Physiol. Pharmacol. Soc.3, No. 2, 160 (1972).
Field, M. J., Young, J. A.: Sodium and potassium transport by the rat submaxillary main duct perfusedin vitro. Proc. Aust. Physiol. Pharmacol. Soc.3, No. 2, 159 (1972).
Frömter, E., Diamond, J.: Route of passive ion permeation in epithelia. Nature (New Biol.)235, 9–13 (1972).
Hayden, L. J., Shagrin, J. M., Young, J. A.: Micropuncture investigation of the anion content of colloid from single rat thyroid follicles. Pflügers Arch.321, 173–186 (1970).
Katz, B.:Nerve, Muscle, Synapse. New York: McGraw-Hill 1966.
Knauf, H.: The isolated salivary duct as a model for electrolyte transport studies. Pflügers Arch.333, 82–94 (1972).
Knauf, H., Frömter, E.: Elektrische Untersuchungen am Hauptausführungsgang der Speicheldrüsen des Menschen. I. Potentialmessung. Pflügers Arch.316, 238–258 (1970).
Knauf, H., Gebler, B., Martin, C. J., Young, J. A.: On the mechanism of action of carbachol on Na+ transport in rabbit submaxillary duct perfusedin vitro. Pflügers Arch.335, R60 (1972).
Martin, C. J., Frömter, E., Gebler, B., Knauf, H., Young, J. A.: The effect of carbachol on electrolyte transport and transepithelial potential differences in the rabbit submaxillary main duct perfusedin vitro. Proc. Aust. Physiol. Pharmacol. Soc.3, No. 1, 64–65 (1972).
Martin, C. J., Frömter, E., Gebler, B., Knauf, H., Young, J. A.: Electrolyte transport in the excurrent duct system of the submaxillary gland. II. Micro perfusion studies on the excretory ductsin vivo andin vitro. In:Oral Physiology, pp. 115–125. N. G. Emmelin and Y. Zotterman, eds. Oxford: Pergamon 1972.
Martin, C. J., Young, J. A.: A microperfusion investigation of the effects of a sympathomimetic and a parasympathomimetic drug on water and electrolyte fluxes in the main duct of the rat submaxillary gland. Pflügers Arch.327, 303–323 (1971).
Paton, W. D. M., Zar, M. A.: The origin of acetylcholine released from guinea pig intestine and longitudinal muscle strips. J. Physiol. (Lond.)194, 13–33 (1968).
Schneyer, L. H.: Secretory processes in perfused excretory duct of rat submaxillary gland. Amer. J. Physiol.215, 664–670 (1968).
Schneyer, L. H., Young, J. A., Schneyer, C. A.: Salivary secretion of electrolytes. Physiol. Rev.52, 720–777 (1972).
Thaysen, J. H., Thorn, N. A., Schwartz, I. L.: Excretion of sodium, potassium, chloride, and carbon dioxide in human parotid saliva. Amer. J. Physiol.178, 155–159 (1954).
Thies, H., Reuther, F. W.: Ein Reagens zum Nachweis von Alkaloiden auf Papierchromatogrammen. Naturwissenschaften91, 230–231 (1954).
Werner, G.: Fermentdefekte als Ursache unterschiedlicher mydriatischer Wirksamkeit von Atropin und Cocain bei Kaninchen. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak.251, 320–334 (1965).
Werner, G., Brehmer, G.: Zur Stereospezifität der (-)-Hyoscyamin-Acylhydrolase des Kaninschens. Hoppe-Seylers Z. physiol. Chem.348, 1640–1652 (1967).
Young, J. A.: Microperfusion investigation of chloride fluxes across the epithelium of the main excretory duct of the rat submaxillary gland. Pflügers Arch.303, 366–374 (1968).
Young, J. A., Frömter, E., Schögel, E., Hamann, K. F.: A microperfusion investigation of sodium resorption and potassium secretion by the main excretory duct of the rat submaxillary gland. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.295, 157–172 (1967).
Young, J. A., Martin, C. J.: The effect of a sympatho- and a parasympathomimetic drug on the electrolyte concentrations of primary and final saliva of the rat submaxillary gland. Pflügers Arch.327, 285–302 (1971).
Young, J. A., Martin, C. J., Asz, M., Weber, F. D.: A microperfusion investigation of bicarbonate secretion by the rat submaxillary gland. The action of a parasympathomimetric drug on electrolyte transport. Pflügers Arch.319, 185–199 (1970).
Young, J. A., Schögel, E.: Micropuncture investigation of sodium and potassium excretion in rat submaxillary saliva. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.291, 85–98 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Preliminary accounts of this work have already been published [13, 14].
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, C.J., Frömter, E., Gebler, B. et al. The effects of carbachol on water and electrolyte fluxes and transepithelial electrical potential differences of the rabbit submaxillary main duct perfusedin vitro . Pflugers Arch. 341, 131–142 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587320
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587320