Summary
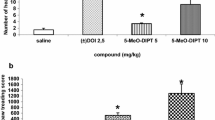
The effect of reducing 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) concentration within various areas of the central dopamine (DA) system on catalepsy has been investigated. The neurotoxin 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine was used to selectively deplete 5-HT in the striatum, nucleus accumbens septi, tuberculum olfactorium or substantia nigra. Localised depletion of 5-HT within the nucleus accumbens septi and substantia nigra reduced the cataleptic effects of the neuroleptic agent fluphenazine, while lesions of the striatum or tuberculum olfactorium were without effect. Each injection of neurotoxin resulted in a 38–47% depletion of 5-HT in the target site: DA levels were not significantly altered. The results suggest that varied dopamine/5-hydroxytryptamine interactions within the nucleus accumbens may contribute to the action of the neuroleptic. The reduction of fluphenazine-induced catalepsy produced by 5-HT depletion within the substantia nigra supports the concept of a controlling influence of 5-HT on nigro-striatal DA function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andén, N.-E., Stock, G.: Effect of clozapine on the turnover of dopamine in the corpus striatum and in the limbic system. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 25, 346–348 (1973)
Bartholini, G.: Differential effect of neuroleptic drugs on dopamine turnover in the extrapyramidal and limbic system. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 28, 429–433 (1976)
Baumgarten, H. G., Victor, S. J., Lowenberg, W.: Effect of intraventricular injection of 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine on regional tryptophan hydroxylase of rat brain. J. Neurochem. 21, 251–253 (1973)
Bird, E. D., Barnes, J., Iversen, L. L., Spokes, E. G., Mackay, A. V. P., Shepherd, M.: Increased brain dopamine and reduced glutamic acid decarboxylase and choline acetyl transferase activity in schizophrenia and related psychoses. Lancet 1977 II, 1157–1159
Carlsson, A., Kehr, W., Lindqvist, M.: Receptor mediated control of dopamine synthesis. In: Neuropsychopharmacology, Proceedings of the IX. Congress of the CINP, Paris (J. R. Boissier H. Hippins and P. Pichot, eds.), pp. 468–471. Amsterdam: Exc. Med. 1975
Carter, C. J., Pycock, C. J.: Possible importance of 5-hydroxytryptamine in neuroleptic-induced catalepsy in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 60, 267P. (1977)
Costall, B., Naylor, R. J.: The importance of the ascending dopaminergic systems to the extrapyramidal and mesolimbic brain areas for the cataleptic action of the neuroleptic and cholinergic agents. Neuropharmacology 13, 353–365 (1974a)
Costall, B., Naylor, R. J.: Mesolimbic involvement with behavioural effects indicating antipsychotic activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 27, 46–58 (1974b)
Costall, B., Naylor, R. J.: Antagonism of the hyperactivity induced by dopamine applied intracerebrally to the nucleus accumbens septi by typical neuroleptics and by clozapine, sulpiride and thioridazine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 35, 161–168 (1976)
Costall, B., Fortune, D., Naylor, R. J., Marsden, C. D., Pycock, C. J.: Serotonergic involvement with neuroleptic catalepsy. Neuropharmacology 14, 859–868 (1975)
Costall, B., Naylor, R. J., Marsden, C. D., Pycock, C. J.: Serotonergic modulation of the dopamine response from the nucleus accumbens. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 28, 523–526 (1976)
Curzon, G., Green, A. R.: Rapid method for the determination of 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in small regions of rat brain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 39, 653–655 (1970)
Daly, J., Fuxe, K., Jonsson, G.: 5,7-Dihydroxytryptamine as a tool for the morphological and functional analysis of central 5-hydroxytryptamine neurons. Res. Commun. Chem. Path. Pharmacol. 7, 175–187 (1974)
De Groot, J.: The rat forebrain in stereotaxic coordinates. Vehr. K. Ned. Akad. Wet. 52, 14–39 (1959)
Dray, A., Gonye, T. J., Oakley, N. R., Tanner, T.: Evidence for the existence of a raphé projection to the substantia nigra in rat. Brain Res. 113, 45–57 (1976)
Fog, R.: On stereotypy and catalepsy. Studies on the effect of amphetamine and neuroleptics in rats. Acta Neurol. Scand. 48, Suppl. 50 (1972)
Fuxe, K.: The distribution of monoamine terminals in the central nervous system. Acta Physiol. Scand. 64, Suppl. 247, 41–85 (1965)
Green, A. R., Grahame-Smith, D. G.: Effects of drugs on the processes regulating the functional activity of brain 5-hydroxytryptamine. Nature 260, 487–491 (1976)
Horton, R. W., Chapman, A. G., Meldrum, B. S.: Regional changes in cerebral GABA concentrations and convulsions produced by D-and by L-allylglycine. J. Neurochem. (in press, 1978)
Kostowski, W., Gumulka, W., Czlonkowski, A.: Reduced cataleptogenic effects of some neuroleptics in rats with lesioned midbrain raphé and pretreated with parachlorophenyl-alanine. Brain Res. 48, 443–446 (1972)
Laverty, R., Sharman, D. F.: The estimation of small quantities of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine in tissues. Br. J. Pharmacol. 24, 538–548 (1965)
Mabry, P. D., Campbell, B. A.: Serotonergic inhibition of catecholamine-induced behavioural arousal. Brain Res. 49, 381–391 (1973)
Maj, J., Mogilnicka, E., Przewlocka, B.: Antagonistic effect of cyproheptadine on neuroleptic-induced catalepsy. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 3, 25–27 (1975)
Marsden, C. A., Curzon, G.: Effects of p-chlorophenylalanine and α-methyltryptophan on behaviour and brain 5-hydroxyindoles. Neuropharmacology 16, 489–494 (1977)
Matthysse, S.: Implications of catecholamine systems of the brain in schizophrenia. Res. Publ. Assoc. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 53, 305–315 (1974)
Naylor, R. J., Olley, J. E.: Modification of the behavioural changes induced by haloperidol in the rat by lesions in the caudate nucleus, the caudate putamen and globus pallidus. Neuropharmacology 11, 81–89 (1972)
Parizek, J., Hassler, R., Bak, I. J.: Light and electron microscopic autoradiography of substantia nigra of rat after intraventricular administration of tritium labelled norepinephrine, dopamine, serotonin and the precursors Z. Zellforsch. 115, 137–148 (1971)
Smythies, J. R.: Recent progress in schizophrenia research. Lancet 1976 II, 136–139
Van Praag, H. M.: The significance of dopamine for the mode of action of neuroleptics and the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. In: Psychobiology of the striatum (A. R. Cools et al., eds.) pp. 155–171. Amsterdam Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press 1977
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carter, C.J., Pycock, C.J. A study of the sites of interaction between dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine for the production of fluphenazine-induced catalepsy. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 304, 135–139 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00495549
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00495549