Summary
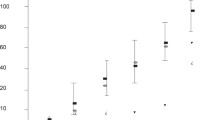
Concentrations of pregnancy-specific β1-glycoprotein (SP-1) were measured in maternal blood and amniotic fluid of patients with a trisomic fetus and compared with that of a cytogenetically normal fetus at weeks 16–19 of pregnancy. The SP-1 concentrations were significantly elevated in the sera of women with a Down's syndrome fetus, whereas amniotic fluid levels were only slightly increased. It is suggested that high levels of maternal SP-1 in the second trimester of pregnancy may be a valuable indicator in the prenatal detection of fetal trisomy 21.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bohn H (1971) Nachweis und Charakterisierung von Schwangerschaftsproteinen in der menschlichen Placenta sowie ihre quantitative immunologische Bestimmung im Serum schwangerer Frauen. Arch Gynäkol 210:440–457
Bohn H (1978) Pregnancy-specific β1-globulin SP1. Scand J Immunol [Suppl 6] 7:119–125
Claussen U, Klein R, Schmidt M (1986) A pipette method for rapid karyotyping in prenatal diagnosis. Prenat Diagn 6:401–408
Crandall BF, Matsumoto M (1986) Routine amniotic fluid alphafetoprotein assay: experience with 40,000 pregnancies. Am J Med Genet 24:143–149
Friedmann W, Cramer B, Vogel M, Baumgärtel H (1984) Immunhistochemische Lokalisation von schwangerschaftsspezifischen β1-Globulin in Plazenten verschiedener Altersstufen. Z Geburtshilfe Perinatol 188:119–122
Heikinheimo M, Seppälä M, Brock DJH (1980) Pregnancy specific β1-glycoprotein and human chorionic gonadotrophin levels in amniotic fluid and in maternal serum in the first half of pregnancy. Oncodev Biol Med 1:71–76
Heikinheimo M, Jalanko H, Leisti J, Kolho KL, Saloen R, Koskull H von, Aula P (1984) Amniotic fluid pregnancy-specific β1-glycoprotein (SP1) in fetal developmental disorders. Prenat Diagn 2: 147–150
Honore LH, Dill FJ, Poland BJ (1976) Placental morphology in spontaneous human abortuses with normal and abnormal karyotypes. Teratology 14:151–166
Horne CHW, Towler CM, Pugh-Hamphreys RGP, Thompson AW, Bohn H (1976) Pregnancy specific β1-glycoprotein — a product of syncytiotrophoblast. Experientia 32:1197–1199
Lin TM, Halbert SP (1976) Placental localisation of human pregnancy-associated plasma proteins. Science 193:1249–1252
Martin AO, Liu K (1986) Implication of “low” maternal serum alphafetoprotein levels: are maternal age risk criteria obsolete? Prenat Diagn 6:243–247
Merkatz IR, Nitowsky HM, Macri JN, Johnson WE (1984) An association between low maternal serum α-fetoprotein and fetal chromosomal abnormalities. Am J Obstet Gynecol 148:886–894
Nicolaides KH, Rodeck CH, Scoothill PW, Warren RC (1986) Why confine chrionic villus (placental) biopsy to the first trimester? Lancet I:543–544
Schönfeld Dimaio M, Baumgarten A, Greenstein RM, Saal HM, Mahoney MJ (1987) Screening for fetal Down's syndrome in pregnancy by measuring maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein levels. N Engl J Med 317:342–346
Sterzig K, Wenske C, Rossmanith W, Benz R (1986) Beta-1-glycoprotein determination in normal and disturbed pregnancy. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 24:65–68
Tabor A, Larsen SO, Nielsen J, Nielsen J, Philip J, Pilgaard B, Videbech P, Norgaard-Pedersen B (1987) Screening for Down's syndrome using an iso-risk curve based on maternal age and serum alpha-fetoprotein. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 94:636–642
Tatra G, Polak S, Nasr F, Dati F (1981) Serum levels of pregnancy specific protein in suspected ectopic pregnancy. Arch Gynecol 230:293–297
Westergaard JG, Teisner B, Hau J, Grudzinskas JG, Chard T (1985) Placental function studies in low birth weight infants with and without dysmaturity. Obstet Gynecol 65:316–318
Würz H, Geiger W, Künzig HJ, Jabs-Lehmann A, Bohn H, Lüben G (1981) Radioimmunoassay of SP1 (pregnancy specific β1-glycoprotein) in maternal blood and in amniotic fluid in normal and pathologic pregnancies. J Perinat Med 9:67–78
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bartels, I., Lindemann, A. Maternal levels of pregnancy-specific β1 (SP-1) are elevated in pregnancies affected by Down's syndrome. Hum Genet 80, 46–48 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00451454
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00451454