Summary
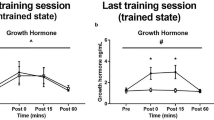
Five normal men performed seven sets of seven squats at a load equal to 80% of their seven repetition maximum. Plasma growth hormone (GH) and lactate levels increased during and after the completion of the exercise. A significant (r=0.93, P<0.001) linear correlation was found between GH changes and the corresponding oxygen Demand/Availability (D/A) ratio expressed by \(\left[ {\int\limits_0^x {\dot V_{O_2 } } \cdot dt} \right] \cdot f\) (where f=[lactate at time x]/[lactate at time 0]). A retrospective examination of previously published data from our laboratory and others also demonstrated the existence of a significant correlation between changes in plasma GH levels and the D/A ratios over a wide variety of exercise; aerobic and anaerobic, continuous and intermittent, weight lifting and cycling, in both fit and unfit subjects under normoxic and hypoxic conditions. It is suggested that the balance between oxygen demand and availability may be an important regulator of GH secretion during exercise.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeLorme L, Watkins AL (1948) Techniques of progressive resistance exercise. Arch Phys Med 29: 263–273
Galbo H (1983) Hormonal and metabolic adaptation to exercise. Thieme, Stuttgart, New York: 40–45
Karagiorgos A, Garcia JF, Brooks GA (1979) Growth hormone response to continuous and intermittent exercise. Med Sci Sports 11: 302–307
Kindermann W, Schnabel A, Schmitt WM, Biro G, Cassens J, Weber F (1982) Catecholamines, growth hormone, cortisol, insulin and sex hormones in anaerobic and aerobic exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 49: 389–399
Koivisto V, Hendler R, Nadel E, Felig P (1982) Influence of physical training on the fuel-hormone response to prolonged low intensity exercise. Metabolism 31: 192–197
Kozlowski SJ, Chwalbinska-Moneta M, Vigas K, Kaciuba-Vscilko H, Nazar K (1983) Greater serum growth hormone response to arm than leg exercise performed at equivalent oxygen uptake. Eur J Appl Physiol 52: 131–135
Lassarre C, Girard F, Durand J, Raynaud J (1974) Kinetics of human growth hormone during submaximal exercise. J Appl Physiol 37: 826–830
Longhurst J, Zelis R (1979) Cardiovascular responses to local hind limb hypoxemia: relation to the exercise reflex. Am J Physiol 237: H359-H365
McCloskey DL, Mitchell JH (1972) Reflex cardiovascular and respiratory responses originating in exercising muscle. J Physiol 224: 173–186
Raynaud J, Dronet L, Martineaud JP, Bordachar J, Coudert J, Durant J (1981) Time course of plasma growth hormone during exercise in humans at altitude. J Appl Physiol 50: 229–233
Shephard RJ, Sidney KH (1975) Effects of physical exercise on plasma growth hormone and cortisol levels in human subjects. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 3: 1–30
Stegeman J, Kenner T (1971) A theory on heart rate control by muscular metabolic receptors. Arch Kreisl-Forsch 63: 186–214
Sutton JR (1977) Effect of acute hypoxia on the hormonal response to exercise. J Appl Physiol 42: 587–592
Sutton JR (1978) Hormonal and metabolic responses to exercise in subjects of high and low work capacities. Med Sci Sports 10: 1–6
VanHelder WP, Goode RC, Radomski MW (1984a) Effect of anaerobic and aerobic exercise of equal duration and work expenditure on plama growth hormone levels. Eur J Appl Physiol 52: 255–257
VanHelder WP, Radomski MW, Goode RC (1984b) Growth hormone responses during intermittent weight lifting exercise in men. Eur J Appl Physiol 53: 31–34
VanHelder WP, Radomski MW, Goode RC, Casey K (1985) Hormonal and metabolic response to three types of exercise of equal duration and external work output. Eur J Appl Physiol 54: 337–342
VanHelder WP, Casey K. Goode RC, Radomski MW (1986) Growth hormone regulation in two types of aerobic exercise of equal oxygen uptake. Eur J Appl Physiol 55: 236–239
Vigas M, Nemeth S, Jurcovicova J, Mikulaj L, Komadel L (1974) The importance of lactate in exercise-induced growth hormone release in men. In: Luft R, Yalow RS (Eds) Radioimmunoassay, methodology and applications in physiology and in clinical studies. Horm Metab Res [Suppl] 5: 166–169
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
DCIEM No. 87-P-27
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
VanHelder, W.P., Casey, K. & Radomski, M.W. Regulation of growth hormone during exercise by oxygen demand and availability. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 56, 628–632 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00424801
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00424801