Abstract
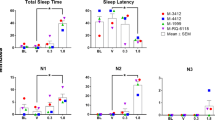
Adult female Sprague-Dawley rats were prepared with chronically implanted cortical and temporal muscle electrodes and i.v. cannulae. Morphine injections of 10 mg/kg were given i.p. to naive rats and to post-addict rats at successive intervals following morphine withdrawal. These intervals extended in a few cases up to one year. In the naive rat, high voltage EEG slow bursts associated with stuporous behavior appeared almost immediately after injection and prevailed for 60–90 min. This phase was followed by continuous EEG and behavioral arousal for another period of 60–90 min, after which sleep appeared. In contrast, morphine challenge to post-addict rats was followed by an EEG and behavioral arousal for as long as 180 min, the degree of which was less pronounced at the longer intervals following withdrawal. The EEG and behavioral arousal of the post-addict rat in response to morphine challenge is reminiscent of similar responses in human postaddicts already reported and may further emphasize the pharmacodynamic factors in morphine addiction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews, H. L.: Brain potentials and morphine addiction. Psychosom. Med. 3, 399–409 (1941).
Beecher, H. K.: Measurement of subjective responses: quantitative effects of drugs. New York: Oxford University Press 1959.
Cochin, J., Kornetsky, C.: Development and loss of tolerance to morphine in the rat after single and multiple injections. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 145, 1–10 (1964).
Eddy, N. B., Leimbach, D.: Synthetic analgesics. II. Dithienylbutenyl—and dithienylbutylamines. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 107, 385–393 (1953).
Green, A. F., Young, P. A., Godfrey, E. J.: A comparison of heat and pressure analgesiometric methods in rats. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 6, 572–585 (1951).
Himmelsbach, C. K.: Clinical studies of drug addiction: Physical dependence, withdrawal and recovery. Arch. intern. Med. 69, 766–772 (1942).
Kay, D. C., Eisenstein, R. B., Jasinski, D. R.: Morphine effects on human REM state, waking state, and NREM sleep. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 14, 404–416 (1969).
Khazan, N.: Longitudinal EEG study of the effects of morphine injections and withdrawal in the morphine dependent rat. Bulletin, Problems of Drug Dependence, NAS-NRC, Thirty-second meeting (1970a) 6827–6836.
—: Declining levels of electrocorticogenesis and their response to morphine in morphine dependent rats. Fed. Proc. 29, 780 (1970b).
—, Colasanti, B.: Decline in the mean integrated electroencephalogram voltage during morphine abstinence in the rat. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 177, 491–499 (1971).
—, Weeks, J. R.: The electroencephalogram (EEG) and the electromyogram (EMG) of self-maintained morphine addicted rats in relation to injections. Pharmacologist 10, 189 (1968).
— —, Schroeder, L. A.: Electroencephalographic, electromyographic and behavioral correlates during a cycle of self maintained morphine addiction in the rat. J Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 155, 521–531 (1967).
Lasagna, L., von Felsinger, J. M., Beecher, H. K.: Drug induced mood changes in man, I. Observations of healthy subjects, chronically ill patients and “postaddicts”. J. Amer. med. Ass. 157, 1006–1020 (1955).
Martin, W. R., Jasinski, D. R., Sapira, J. D., Flanary, H. G., Kelly, O. A., Thompson A. K., Logan, C. R.: The respiratory effects of morphine during a cycle of dependence. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 162, 182–189 (1968).
—, Wikler, A., Eades, C. G., Pescor, F. T.: Tolerance to and physical dependence on morphine in rats. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 4, 247–260 (1963).
Sloan, J. W., Eisenman, A. J.: Long persisting changes in catecholamine metabolism following addiction to and withdrawal from morphine. In: The Addictive States, Ass. Res. nerv. Dis. Proc. 46, 96–105 (1968).
Weeks, J. R.: Experimental morphine addiction: Method for automatic intravenous injections in unrestrained rats. Science 138, 143–144 (1962).
—, Schroeder, L. A., Khazan, N.: Electroencephalographic, electromyographic and behavioral correlates in self-maintained morphine addicted rats. Pharmacologist 6, 183 (1964).
Wikler, A.: Clinical and electroencephalographic studies on the effects of mescaline, N-allylnormorphine and morphine in man. J. nerv. ment. Dis. 120, 157–175 (1954).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by NIMH Grant MH-16693; a preliminary report on this work appeared in Fed. Proc. 30, 277, (1971).
NIMH Postdoctoral Fellow.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khazan, N., Colasanti, B. EEG correlates of morphine challenge in post-addict rats. Psychopharmacologia 22, 56–63 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00401467
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00401467