Summary
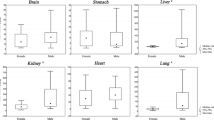
In 101 unselected autopsies, cadmium (Cd) in lung tissue was analyzed by means of flameless atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS). The subjects originated from Bochum (BO), Dortmund (DO), and neighbouring cities in the Ruhr District (BO/DO) as well as from Muenster (MS) and vicinity. The sample included eight persons who had died from bronchial carcinoma. The Cd concentration in lung tissue (CdL) did not show a significant age-dependency. There was only a slight increase of CdL in the age around 50. For males, the median CdL value was found to be 1.32 μg/g dry wt in the age group from 20–45, 1.48 μg/g dry wt from 45–65, and 0.64 μg/g dry wt > 65 (the corresponding means and standard deviations were 1.48 ± 1.22, 1.73 ± 1.42, and 1.18 ± 1.27 μg/g dry wt). CdL in men was twice that in women. There were no differences between the two regions (BO/DO : MS) examined. CdL of the bronchial carcinoma cases were mostly clearly above the expected level, often similar to the Cr and Ni concentration of the same specimens. Besides the amount of inhaled metal aerosols, insufficient lung clearance may play a leading role for their retention in lung parenchyma. However, with regard to the determination of causality between uptake and disease the data are difficult to interpret, in our study due to a lack of enough consistent and reliable data on occupation, environment, and smoking habits, and in general due to a lot of variables which, until now, cannot be sufficiently quantified.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cumbrowski J (1988) Zur Kinetik des Kadmiums im menschlichen Organismus. Z Gesamte Hyg 34:40–43
Cumbrowski J, Raffke W, Ackermann E (1979) Cadmium-burden of humans in various areas of the German Democratic Republic (GDR) from selected viewpoints. In: Bolck F (ed) Kadmium-Symposion 1977. Friedrich-Schiller-Universität, Jena, S 289–294
Drasch G (1983) An increase of cadmium body burden for this century — an investigation on human tissues. Sci Total Environ 26:111–119
Elinder CG, Kjellström R, Friberg L, Lind B, Linnman L (1976) Cadmium in kidney cortex, liver, and pancreas from Swedish autopsies. Arch Environ Health 31:292–302
Ewers U, Brockhaus A, Freier I, Jermann E, Dolgner R (1988) Exposure to cadmium of the West-German population — results of biological monitoring studies 1980–1986. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo [Environmental Toxin Series, vol 2]
Friberg L, Piscator M, Nordberg GF, Kjellström LT (1974) Cadmium in the environment, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Cleveland, OH
Haddock AG, Travis CC (1979) Age dependent biological half-time of cadmium in the renal cortex. In: Hemphill DD (ed) Proc Univ Missouri's Ann Conf on trace substances in environmental health, 4.–7.6.1979. University of Missouri Press, Columbia, pp 190–194
Hahn R, Ewers U, Jermann E, Freier I, Brockhaus A, Schlipköter HW (1987) Cadmium in kidney cortex of inhabitants of North-West Germany: its relationship to age, sex, smoking and environmental pollution by cadmium. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 59:165–176
Hammer DI, Colucci AV, Hasselblad V, Williams WE, Pinkerton C (1973) Cadmium and lead in autopsy tissue. J Occup Med 15:956–963
International Agency for Research on Cancer (1987) Overall evaluations of carcinogenicity: an updating of IARC Monographs, vols 1–42. IARC (ed) IARC Monographs on the evaluation of the carcinogenic risk to humans. Lyon [Suppl 7] pp 139–142
Kollmeier H, Müller KM, Seemann J, Rothe G, Wittig P, Schejbal V, Hummelsheim G (1988) Untersuchungen zur Chrom- und Nickel-Belastung der Lunge. Wirtschaftsverlag NW, Bremerhaven (BAU Forschungsbericht Nr 548, S 1–222)
Kollmeier H, Seemann J, Rothe G, Müller KM, Wittig P (1990) Age, sex, and region adjusted concentrations of chromium and nickel in lung tissue. Br J Ind Med (in press)
Kollmeier H, Witting C, Seemann J, Wittig P, Rothe G (1985) Metallanreicherungen in Humangeweben. Chrom, Nickel, Blei, Cadmium und Zink in Lunge, Leber, Milz und Niere. Wirtschaftsverlag NW, Bremerhaven [BAU Forschungsbericht Nr 347 VI, S 1–150]
Lauwerys R, Hardy R, Job M, Buchet JP, Roels H, Bruaux P, Rondia D (1985) Environmental pollution by cadmium and cadmium body burden: an autopsy study. Toxicol Lett 23:278–289
Lee HY, Oberdörster G (1985) Kinetics of intratracheally instilled CdCl2 and Cd-thionein. Toxicologist 5:178
Oberdörster G (1986) Airborne cadmium and carcinogenesis of the respiratory tract. Scand J Work Environ Health 12:523–537
Oberdörster G, Kordel W (1981) Metallothionein content in lung, liver, and kidney after chronic cadmium oxide and zinc oxide inhalation in rats. In: CEP Consultants. Proc Int Conf on Heavy Metals in the Environment. Edinburgh, pp 502–505
Radermacher L, Prinz B, Rudolph H (1988) Bericht über die Ergebnisse der im Land Nordrhein-Westfalen in der Zeit von Januar 1987 bis Dezember 1987 durchgeführten Staub- und Schwermetallniederschlagsmessungen. LIS (Hrsg) Schriftenreihe. Girardet, Düsseldorf, Heft 66
Schroeder HA, Nason AP, Tipton IH, Balassa JJ (1967) Essential trace metals in man: Zinc. Relation to environmental cadmium. J Chron Dis 20:197–210
Seemann J, Wittig P, Kollmeier H, Muller KM, Schejbal V (1990) Trace metal analysis of chromium and nickel in lung tissue fixed and stored in formalin. Pathol Res Pract 186:197–201
Seemann J, Wittig P, Kollmeier H, Rothe G (1985) Analytische Bestimmung von Cd, Pb, Zn, Cr and Ni in Humangewebe. Lab Med 9:294–299
Seewöster J (1988) Abschlußbericht zum Immissionsmeßprogramm in der Stadt Münster. Stadt Münster (Hrsg) Werkstattberichte zum Umweltschutz. Burlage, Munster, Heft 1
Smith TJ, Anderson RJ, Reading JC (1980) Chronic cadmium exposures associated with kidney function effects. Am J Ind Med 1:319–337
Thun MT, Schnorr TM, Smith AB, Halperin WE, Lemen RA (1985) Mortality among a cohort of US cadmium production workers — an update. J Natl Cancer Inst 74:325–333
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kollmeier, H., Seemann, J., Wittig, P. et al. Cadmium in human lung tissue. Int. Arch Occup Environ Heath 62, 373–377 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00381367
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00381367