Summary
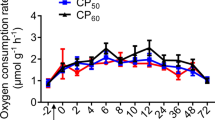
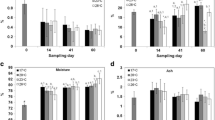
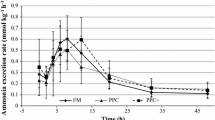
Rates of protein synthesis and oxygen consumption (\(\dot M\)O2) in cod were compared in both fasted and refed animals. During a 14-day fast both protein synthesis and respiration rates fell to stable values after 6 days. When a meal of whole sandeel at 6% body weight was fed to fish fasted for 6 days, protein synthesis and (\(\dot M\)O2) increased to a maximum at between 12 and 18 h after feeding. Peak (\(\dot M\)O2) was about twice the pre-feeding values, while whole animal protein synthesis increased four-fold. There were differences between tissues in the timing of maximum protein synthesis; the liver and stomach responded faster than the remainder of the body. Maximum protein synthesis rates in the liver and stomach occurred at 6 h after feeding, at which time their calculated contribution to total (\(\dot M\)O2) was 11%. Similar calculations suggested that the integrated increment in whole animal protein synthesis contributed between 23% and 44% of the post-prandial increase in (\(\dot M\)O2). It was concluded that protein synthesis is an important contributor to increased (\(\dot M\)O2) after feeding in cod.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A s :
-
absolute rate of protein synthesis
- ASDA:
-
apparent specific dynamic action
- ATP:
-
adenosine triphosphate
- k s :
-
fractional rate of protein synthesis
- k s/RNA:
-
amount of protein synthesized per unit RNA
- (\(\dot M\)O2):
-
oxygen consumption
- PCA:
-
perchloric acid
- RNA:
-
ribonucleic acid
References
Aoyagi Y, Tasaki I, Okumura J-I, Murumatsu T (1988) Energy cost of whole-body protein synthesis measured in vivo in chicks. Comp Biochem Physiol 91A:765–768
Ashworth A (1969) Metabolic rates during recovery from proteincaloric malnutrition: the need for a new concept of specific dynamic action. Nature 223:407–409
Axelsson M, Nilsson S (1986) Blood pressure control during exercise in the Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua. J Exp Biol 126:225–236
Beamish FWH (1964) Influence of starvation on standard and routine oxygen consumption. Trans Am Fish Soc 93:103–107
Beamish FWH (1974) Apparent specific dynamic action of largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides. J Fish Res Board Can 31:1763–1769
Beamish FWH, MacMahon PD (1988) Apparent heat increment and feeding strategy in walleye, Stizostedion vitreum vitreum. Aquaculture 68:73–82
Beamish FWH, Hilton JW, Niimi E, Slinger SJ (1986) Dietary carbohydrate and growth, body composition and heat increment in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Fish Physiol Biochem 1:85–91
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Brett JR, Zala CA (1975) Daily pattern of nitrogen excretion and oxygen consumption of sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) under controlled conditions. J Fish Res Board Can 32:2479–2486
Brown CR, Cameron NJ (1991) The relationship between specific dynamic action (SDA) and protein synthesis rates in the channel catfish. Physiol Zool 64:298–309
Edwards RRC, Finlayson DM, Steele JH (1972) An experimental study of the oxygen consumption, growth and metabolism of the cod (Gadus morhua L.). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 8:299–309
Farrell AP, MacLeod KR, Chancey B (1986) Intrinsic mechanical properties of the perfused rainbow trout heart and the effects of catecholamines and extracellular calcium under control and acidotic conditions. J Exp Biol 125:319–346
Fauconnaeu B, Breque J, Bielle C (1989) Influence of feeding on protein metabolism in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 79:29–36
Garlick PJ, McNurlan MA, Preedy VR (1980) A rapid and convenient technique for measuring protein synthesis in tissues by injection of [3H]-phenylalanine. Biochem J 192:719–723
Grisolia S, Kennedy J (1966) On specific dynamic action, turnover and protein synthesis. Perspect Biol Med 9:578–585
Houlihan DF, Hall SJ, Gray C, Noble BS (1988) Growth rates and protein turnover in Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 45:951–964
Houlihan DF, McMillan DN, Laurent P (1986) Growth rates, protein synthesis and protein degradation rates in rainbow trout: effects of body size. Physiol Zool 59:482–493
Houlihan DF, Waring CP, Mathers E, Gray C (1990) Protein synthesis and oxygen consumption of the shore crab, Carcinus maenas, following a meal. Physiol Zool 63:735–756
Jobling M (1981) The influences of feeding on the metabolic rate of fishes: a short review. J Fish Biol 18:385–400
Jobling M (1983) Towards an explanation of specific dynamic action (SDA). J Fish Biol 23:549–555
Jobling M (1985) Growth. In: Tytler P, Calow P (eds) Fish energetics: new perspectives. Croom Helm, Beckenham, pp 213–230
Jobling M, Davies PS (1980) Effects of feeding on metabolic rate and the specific dynamic action in plaice, Pleuronectes platessa L. J Fish Biol 16:629–638
LeGrow SM, Beamish FWH (1986) Influence of dietary protein and lipid on apparent heat increment of rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 43:19–25
Loughna PT, Goldspink G (1984) The effects of starvation upon protein turnover in red and white myotomal muscle of rainbow trout, Salmo gaidneri Richardson. J Fish Biol 25:223–230
Lowery MS, Somero GN (1990) Starvation effects on protein synthesis in red and white muscle of the barred sand bass, Paralabrax nebulifer. Physiol Zool 63:630–648
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
McMillan DN, Houlihan DF (1988) The effect of refeeding on tissue protein synthesis in rainbow trout. Physiol Zool 61:429–441
Meijer AJ, Lamers WH, Chamuleau RAFM (1990) Nitrogen metabolism and ornithine cycle function. Physiol Rev 70:701–748
Mejbaum W (1939) Über die Bestimmung kleiner Pentosemengen, insbesondere in Derivaten der Adenylsäure. Hoppe-Seyler's Z Physiol Chem 258:204–205
Millward DJ, Garlick PJ, James WPT, Nnanyelugo DO, Ryatt JS (1973) Relationship between protein synthesis and RNA content in skeletal muscle. Nature 241:204–205
Muir BS, Niimi AJ (1972) Oxygen consumption of the euryhaline fish aholehole (Kuhlia sandvicensis) with reference to salinity, swimming and food consumption. J Fish Res Board Can 29:67–77
Munro HN, Fleck A (1966) The determination of nucleic acids. In: Glick D (ed) Methods of biochemical analysis. Wiley, New York, pp 113–176
Pocrnjic Z, Mathews RW, Rappaport S, Haschemeyer AEV (1983) Quantitative protein synthesis rates in various tissues of a temperate fish in vivo by the method of phenylalanine swamping. Comp Biochem Physiol 74B:735–738
Ramnarine IW, Pirie JM, Johnstone ADF, Smith GW (1987) The influence of ration size and feeding frequency on ammonia excretion by juvenile Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua L. J Fish Biol 31:545–559
Randall DJ, Wright PA (1987) Ammonia distribution and excretion in fish. Fish Physiol Biochem 3:107–120
Rao GMM (1968) Oxygen consumption of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) in relation to activity and salinity. Can J Zool 46:781–786
Reeds PJ, Fuller MJ, Nicholson BA (1985) Metabolic basis of energy expenditure with particular reference to protein. In: Garrow GS, Halliday D (eds) Substrate and energy metabolism. John Libbey, London, pp 46–57
Saunders (1963) Respiration of the Atlantic cod. J Fish Res Board Can 20:373–386
Schachterle GR, Pollack RL (1973) A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem 51:654–655
Smith MAK (1981) Estimation of growth potential by measurement of tissue protein synthetic rates in feeding and fasting rainbow trout, Salmo gairneri Richardson. J Fish Biol 19:213–220
Soofiani NM, Priede IG (1985) Aerobic metabolic scope and swimming performance in juvenile cod, Gadus morhua L. J Fish Biol 26:127–138
Tandler A, Beamish FWH (1979) Mechanical and biochemical components of apparent specific dynamic action in largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides Lacepede. J Fish Biol 14:343–350
Tandler A, Beamish FWH (1981) Apparent specific dynamic action (SDA), fish weight and level of caloric intake in largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides Lacepede. Aquaculture 23:231–242
Vahl O, Davenport J (1979) Apparent specific dynamic action of food in the fish Blennius pholis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 1:109–113
Van Waarde A (1983) Aerobic and anaerobic ammonia production by fish. Comp Biochem Physiol 74B:675–684
Weiss RF (1970) The solubility of nitrogen, oxygen and argon in water and seawater. Deep-Sea Res 17:721–735
Wiggs AJ, Henderson EB, Saunders RL, Kutty MN (1989) Activity, respiration and excretion of ammonia by Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) smolt and postsmolt. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 46:790–795
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyndon, A.R., Houlihan, D.F. & Hall, S.J. The effect of short-term fasting and a single meal on protein synthesis and oxygen consumption in cod, Gadus morhua . J Comp Physiol B 162, 209–215 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00357525
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00357525