Summary
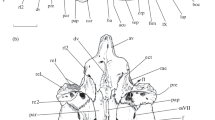
A muscle receptor organ is present in the mandible of macruran decapods. The mandibular muscle receptor organ (Mand. MRO) of Homarus gammarus (L.) consists of a ribbon of muscle innervated at its ventral insertion by 10–20 multiterminal sensory neurones. The sensory cells have a small number of dendritic processes.
The receptor muscle exhibits some structural properties of both fast and slow muscle. The mean sarcomere length is similar to that of the slow abdominal MRO but the receptor muscle in cross section has a punctate distribution of myofibril bundles more typical of fast muscle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandrowiez, J. S.: Muscle receptor organs in the abdomen of Homarus vulgaris and Palinurus vulgaris. Quart. J. mic. Sci. 92, 163–199 (1951).
Alexandrowiez, J. S.: Receptor elements in the thoracic muscles of Homarus vulgaris and Palinurus vulgaris. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 93, 315–346 (1952).
Alexandrowiez, J. S.: Receptor elements in the muscles of Leander serratus. J. marine biol. Ass. 35, 129–144 (1956).
Alexandrowiez, J. S.: Further observations on proprioceptors in crustacea and a hypothesis about their function. J. marine biol. Ass. 37, 379–396 (1958).
Alexandrowiez, J. S.: Receptor organs in the coxal region of Palinurus vulgaris. J. marine biol. Ass. 47, 415–432 (1967a).
Alexandrowiez, J. S.: Receptor organs in thoracic and abdominal muscles of crustacea. Biol. Rev. 42, 288–326 (1967b).
Alexandrowiez, J. S., Whitear, M.: Receptor elements in the coxal region of Decapoda Crustacea. J. marine biol. Ass. 36, 603–628 (1957).
Bodian, D., Bergman, R. A.: Muscle receptor organs of crayfish: functional-anatomical correlations. Bull. Johns Hopk. Hosp. 110, 78–106 (1962).
Borradaile, L. A.: On the function of the mouthparts of the common prawn. Proc. Camb. phil. Soc. biol. Sci. 19, 56 (1917).
Bullock, T. H., Horridge, G. A.: Structure and function in the nervous systems of invertebrates, vol. 2, p. 1603. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman and Company 1965.
Clarac, F.: Proprioceptor anatomy of the ischiopodite-meropodite region in legs of the crab Carcinus mediterraneus. Z. vergl. Physiol. 61, 203–223 (1968).
Clarac, F., Masson, C.: Anatomie comparée des propriocepteurs de la région basiischio-méropodite chez certains crustacés decapodes. Z. vergl. Physiol. 65, 242–273 (1969).
Cloney, R. A., Florey, E.: Ultrastructure of cephalopod chromatophore organs. Z. Zellforsch. 89, 250–280 (1968).
Cohen, M. J.: Muscle fibres and efferent nerves in a crustacean receptor muscle. Quart. J. micr. Sci. 104, 551–559 (1963a).
Cohen, M. J.: The crustacean myochordotonal organ as a proprioceptive system. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 8, 223–243 (1963b).
Dando, M. R., Laverack, M. S.: A mandibular proprioceptor in the lobster, Homarus vulgaris. Experientia (Basel) 24, 931 (1968).
Eyzaguirre, C., Kuffler, S. W.: Processes of excitation in the dendrites and in the soma of single isolated sensory nerve cells of the lobster and crayfish. J. gen. Physiol. 39, 87–119 (1955).
Fahrenbach, W. H.: The fine structure of fast and slow crustacean muscles. J. Cell Biol. 35, 69–79 (1967).
Florey, E., Florey, E.: Microanatomy of the abdominal stretch receptors of the crayfish (Astacus fluviatilis L.). J. gen. Physiol. 39, 69–85 (1955).
Jahromi, S. S., Atwood, H. L.: Correlation of structure, speed of contraction and total tension in fast and slow abdominal muscle fibres of the lobster. J. exp. Zool. 171, 25–38 (1969).
Jansen, J. K. S., Njå, A., Walløe, L.: Inhibitory control of the abdominal stretch receptors of the crayfish. 1. The existence of a double inhibitory feedback. Acta physiol. stand. 80, 420–425 (1970).
Kennedy, D., Takeda, K.: Reflex control of abdominal flexor muscles in the crayfish. 1. The twitch system. J. exp. Biol. 43, 211–228 (1965).
Krnjevie, K., Gelder, N. M. van: Tension changes in crayfish stretch receptors. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 159, 310–325 (1961).
Laverack, M. S., Dando, M. R.: The anatomy and physiology of mouthpart receptors in the lobster, Homarus vulgaris. Z. vergl. Physiol. 61, 176–195 (1968).
Moulins, M., Dando, M. R., Laverack, M. S.: Further studies on mouthpart receptors in decapod crustacea. Z. vergl. Physiol. 69, 225–248 (1970).
Nadol, J. B., Darin de Lorenzo, A. J.: Observations of the dendritec processes and receptor terminations in the abdominal muscle receptor organ of Homarus. J. comp. Neurol. 137, 19–57 (1969).
Netz, W.: Das Skelett des Flußkrebses (Potamobius astacus, Leach). Thesis, Universität Marburg, Germany (1917).
Pantin, C. F. A.: Notes on microscopical technique for zoologists. Cambridge: University Press 1948.
Pasztor, V. M.: The neurophysiology of respiration in decapod crustacea. II. The sensory system. Canad. J. Zool. 47, 435–441 (1969).
Pringle, J. W. S.: Proprioception in arthropods. The cell and the organism, p. 256–282, Ramsay, J. A., Wigglesworth, V. B., eds. Cambridge: University Press 1961.
Ripley, S. H., Bush, B. M. H., Roberts, A.: Crab muscle receptor which responds without impulses. Nature (Lond.) 218, 1170–1171 (1968).
Schmidt, W.: Die Muskulatur von Astacus fluviatilis (Potamobius astacus L.). Z. wiss. Zool. 113, 165–251 (1915).
Snodgrass, R. E.: Comparative studies on the jaws of mandibulate arthropods. Smithson. mist. Collns. 116, 1–85 (1950).
Snodgrass, R. E.: A textbook of arthropod anatomy. New York: Cornell University Press 1952.
Wales, W., Clarac, F., Dando, M. R., Laverack, M. S.: Innervation of the receptors present at the various joints of the pereiopods and third maxilliped of Homarus gammarus (L.) and other Macruran Decapods (Crustacea). Z. vergl. Physiol. 68, 345–384 (1970).
Wales, W., Laverack, M. S.: Sensory activity of the mandibular muscle receptor organ of Homarus gammarus (L.). I. Response to receptor muscle stretch. Mar. Behav. Physiol. (in press, 1972).
Whitear, M.: The fine structure of crustacean proprioceptors. II. The thoracicocoxal organs in Carcinus, Pagurus and Astacus. Phil. Trans. B 248 437–456 (1965).
Wiersma, C. A. G., Pilgrim, R. L. C.: Thoracic stretch receptors in crayfish and rocklobster. Comp. Riochem. Physiol. 2, 51–64 (1961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by Science Research Council grants B/SR/1871 and BR/G/585.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wales, W., Laverack, M.S. The mandibular muscle receptor organ of Homarus gammarus (L.) (crustacea, decapoda). Z. Morph. Tiere 73, 145–162 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280773
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00280773