Summary
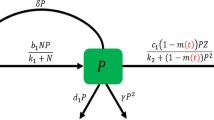
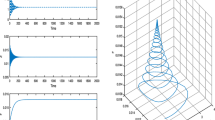
Stability and persistence properties of a family of non-spatial plankton models, each differentiated by its herbivore grazing term, are analytically compared. The dynamic persistence function in the model is shown to operate uniformly even though stability configuration characteristics of the model may be topologically distinct. The persistence threshold for each model indicates that total nutrient is a fundamental biological control. In the parameter space, all of the models studied are structurally unstable; however, an important bifurcation mechanism associated with this instability governs persistence. While, topologically, model transfigurement through parameter modulation is non-continuous, the biological populations evolve in a continuous or a lower semicontinuous manner. A basic conclusion of the paper is that fundamental problems for these marine ecological models remain unresolved since each of the models is a structurally unstable system for a fixed dynamically persistent ecology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht, F., Gatzke, H., Haddad, A., Wax, N.: The dynamics of two interacting populations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 46, 658–670 (1974)
Coddington, E., Levinson, N.: Theory of ordinary differential equations (Ch.15, 16), 429 pp. New York: McGraw-Hill 1955
DiToro, D. M., O'Connor, D. J., Thomann, R. V.: A dynamic model of the phytoplankton population in the Sacramento-San Joaquin delta. Advances in Chemistry. 106, 131–180 (1971)
Frost, B. W.: Feeding processes at lower trophic levels in the pelagic communities. In: ‘The biology of the oceanic Pacific’ (Charles B. Miller, Ed.). pp. 59–77 Corvallis: Oregon State University Press 1974
Hallam, T. G.: On persistence of aquatic ecosystems. In: Oceanic sound scattering prediction (N. Andersen and B. J. Zahuranec, Eds.) pp. 749–766. New York: Plenum 1977
Iverson, R. L., Curl, H. C. Jr., Saugen, J. L.: Simulation model for wind-driven summer phytoplankton dynamics in Auke Bay, Alaska. Marine Biology 28, 169–177 (1974)
Lefschetz, S.: Differential equations: Geometric theory, 2nd Ed., 390 pp. New York: Interscience (1963)
Lotka, A. J.: Elements of mathematical biology, 465 pp. New York: Dover (1925)
May, R. M.: Stability and complexity in model ecosystems, 265 pp. Princeton: University Press 1974
Mullin, M. M., Stewart, E. F., Fuglister, F. J.: Ingestion by planktonic grazers as a function of concentration of food. Limnol. Oceanogr. 20 (2), 259–262 (1975)
O'Brien, J. J., Wroblewski, J. S.: A simulation of the mesoscale distribution of the lower marine trophic levels off West Florida. Invest. Pesq. 37 (2), 193–244 (1973)
Parsons, T. R., LeBrasseur, R. J., Fulton, J. D.: Some observations on the dependence of zooplankton grazing on the cell size and concentration of phytoplankton blooms. J. Oceanogr. Soc. Japan 23, 10–17 (1967)
Sansone, G., Conti, R.: Non-linear Differential Equations, 535 pp. Oxford: Pergamon (1964)
Steele, J. H.: The Structure of Marine Ecosystems, 128 pp. Cambridge: Harvard University Press 1974
Volterra, V.: Variazione e fluttuazione del numero d'individual in specie animali conviventi. Mem. Accad. Nazionale Lincei (Ser. 6) 2, 31–113 (1926)
Walsh, J.: A spatial simulation model of the Peru upwelling ecosystem. Deep Sea Research, 22, 201–236 (1975)
Winter, D. F., Banse, K., Anderson, G. C.: The dynamics of phytoplankton blooms in Puget Sound, a fjord in the Northwestern United States. Marine Biology 29, 139–176 (1975)
Wroblewski, J. S.: The vertically migrating deep scattering layer—Its possible role in the creation of small scale phytoplankton patchiness in the ocean. In: Oceanic sound scattering prediction (N. Andersen and B. J. Zahuranec, Eds.). New York: Plenum 1977
Wroblewski, J. S., O'Brien, J. J.: A spatial model of phytoplankton patchiness. Marine Biology 35, 161–175 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hallam, T.G. Structural sensitivity of grazing formulations in nutrient controlled plankton models. J. Math. Biology 5, 269–280 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276122
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276122