Abstract
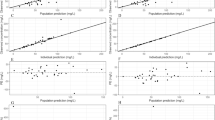
A prospective randomised trial was conducted in critically ill patients to evaluate a computer aided pharmacokinetic method of aminoglycoside dose prediction based on 3 measured plasma concentrations following the loading dose. The ability of this method to achieve therapeutic plasma aminoglycoside concentrations early in the course of treatment was compared with that of a nomogram approach based on creatinine clearance estimated using the formula of Cock-roft and Gault. Ninety-two percent of patients in the computer group achieved peak plasma concentrations within the optimum range of 6–10 mg/l at 48–72 h compared with 21% of control group patients (p=0.0009). The mean peak plasma concentration of 7.45 mg/l at 48–72 h in the computer group was closer to the target concentration of 8 mg/l than was the 5.14 mg/l in the control group (p=0.0004). There was no significant difference between the groups in measured indices of renal function, both groups showing an improvement in mean estimated creatinine clearance from the beginning to the end of the course of treatment. Dosing based on individualised pharmacokinetic data is therefore a more reliable method of achieving therapeutic blood concentrations early in the course of treatment than is nomogram based dosing. Other studies suggest that this should be associated with a reduction in mortality in severe infections.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cockroft DW, Gault MH (1976) Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16:31
Davey PG, Geddes AM, Gonda I (1984) Comparison of methods for estimating gentamicin clearance and retrospective analysis of changes in clearnance with emphasis on patients with normal renal function. Br J Clin Pharmacol 17:147–155
Evans WE, Taylor RH, Feldman S (1980) A model for dosing gentamicin in children and adolescents that adjusts for tissue accumulation with continuous dosing. Clin Pharmacokinet 5:295–306
Sande MA, Mandell HG (1985) Aminoglycosides. In: Goodman, Gilman A et al (eds) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 7th edn. MacMillan, New York, p 1154
Moore RD, Smith CR, Lietman PS (1984) The association of aminoglycoside plasma levels with mortality in patients with gram negative bacteremia. J Infect Dis 149:443–448
Moore RD, Smith CR, Lietman PS (1984) Association of aminoglycoside plasma levels with therapeutic outcome in gram-negative pneumonia. Am J Med 77:657–662
Moore RD, Lietman PS, Smith CR (1987) Clinical response to aminoglycoside therapy: Importance of ratio of peak concentration to minimal inhibitory concentration. J Infect Dis 155:93–99
Oates JA, Wilkinson GR (1987) Clinical pharmacology. In: Braunwald E et al. (eds) Harrison's principles of internal medicine. McGraw Hill, New York, 11th edn, p 347
Sawchuk RJ, Zaske DE, Cipolle RJ (1977) Kinetic model for gentamicin dosing with the use of individual patient parameters. Clin Pharmacol Ther 21:362–365
Summer WR, Michael JR, Lipsky JJ (1983) Initial aminoglycoside levels in the critically ill. Crit Care Med 11:948–950
Zaske DE, Cipolle RJ, Strate RJ (1980) Gentamicin dosage requirements: wide interpatient variations in 242 surgery patients with normal renal function. Surgery 87:164–169
Zaske DE, Bootman JL, Solem LB (1982) Increased burn patient survival with individualised doses of gentamicin. Surgery 91:142–149
Zaske DE, Cipolle RJ, Rotschafer JC (1982) Gentamicin kinetics in 1640 patients: Method for control of serum concentrations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 21:407–411
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hickling, K., Begg, E. & Moore, M.L. A prospective randomised trial comparing individualised pharmacokinetic dosage prediction for aminoglycosides with prediction based on estimated creatinine clearance in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med 15, 233–237 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00271057
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00271057