Summary
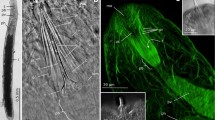
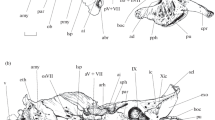
The lung of the deep diving Weddell Seal is characterized by an unusually well developed periacinar dense collagenous connective tissue, and a thick coat of smooth musculature particularly in the distal bronchioli. Both, collagen and smooth musculature appear to be functionally interrelated, the first serving presumably as site of origin or attachment for the latter. The orientation of the bronchiolar smooth muscle cells is complex: there exists a basic pattern of two crisscrossing helical bundles that wind in opposite direction. In addition, longitudinal bundles are frequent both at the inside and the outside of the muscular coat. Furthermore, more or less complete ringshaped bundles occur as well as groups of muscle fibres running radially into the collagenous tissue of the surroundings of a bronchiolus. This complex architecture presumably allows active adjustment to various physiological needs of the Weddell Seal including as extremes both closing and widening of the bronchiolar lumen. Isometric contractions of the smooth musculature may stiffen the wall of the distal airways while diving. In the Crabeater Seal which dives for shorter durations and by far less deeply than the Weddell Seal, both periacinar collagen and bronchiolar smooth musculature are of similar arrangement, however, occur in considerably reduced amounts. A rich supply of autonomie nerve fibres with abundant varicosities controls the smooth muscle cells, which are interconnected by gap junctions and receive their innervation par distance (visceral type of smooth musculature). The majority of varicosities contains small clear vesicles, as is typical for cholinergic nerves, suggesting a strong parasympathetic influence. Other varicosities are presumably of peptidergic type. Mast cells and epithelial endocrine cells may exert additional influence on the musculature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bancroft JD, Stevens A (1982) Theory and practice of histological techniques. Churchill, Livingstone Edinburgh
Belanger LF (1940) A study of the histological structure of the respiratory portion of the lungs of aquatic mammals. Am J Anat 67:437–470
Boshier DP (1974) Structural features in the lung of the Weddell seal, Leptonychotes weddelli, which facilitate deep diving: a light and electron microscope study. J Anat 118:400
Boshier DP, Hill PM (1974) Structural aspects of ventilation and diffusion in the Weddell seal (Leptonychotes weddelli). In: Harrison RJ (ed) Functional anatomy of marine mammals, vol 2. Academic Press, London, pp 197–229
Boyd RB (1973) A gross and microscopic study of the respiratory anatomy of the Antarctic Weddell seal, Leptonychotes weddelli. J Morphol 147:309–336
Burnstock G, Iwayama T (1971) Fine-structural identification of autonomie nerves and their relation to smooth muscle. In: Eränkö O (ed) Progress in brain research, vol 34. Histochemistry of nervous transmission. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 389–404
Denison DM, Kooyman GL (1973) The structure and function of the small airways in pinniped and sea otter lungs. Respir Physiol 17:1–10
Falke KJ, Hill RD, Qvist J, Schneider RC, Guppy M, Liggins GC, Hochachka PW, Elliot RE, Zapol WM (1985) Seal lungs collapse during free diving: evidence from arterial nitrogen tensions. Science 229:556–558
Greef K, Palm P (1987) Einführung in die Pharmakologie des peripheren autonomen Nervensystems. In: Forth W, et al. (eds) Spezielle Pharmakologie und Toxikologie, 5th edn. Bibliographisches Institut, Mannheim, pp 98–102
Harrison RJ, Tomlison JDW (1963) Anatomical and physiological adaptations in diving mammals. In: Carthy JD, Duddington CL (eds) Viewpoints in biology, vol 2. Butterworths, London, pp 115–162
Hayek H von (1953) Die menschliche Lunge. Springer, Berlin Göttingen Heidelberg
King JE, Harrison RJ (1961) Some notes on the Hawaiian monk seal. Pacific Sci 15:282–293
Kooyman GL (1981) Weddell seal: consummate diver. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge New York New Rochelle Melbourne Sydney
Kooyman GL (1989) Diverse divers. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Kooyman GL, Anderson HT (1969) Deep diving. In: Anderson HT (ed) The biology of marine mammals. Academic Press, New York London, pp 65–94
Pizey NCD (1954) The structure of the pinniped lung. J Anat 88:552
Richardson JB (1983) Recent progress in pulmonary innervation. Am Rev Respir Dis,126:65–68
Romeis B (1968) Mikroskopische Technik, 16th edn. Oldenbourg, München
Simpson JG, Gardner MB (1972) Comparative microscopic anatomy of selected marine mammals. In: Ridgway SH (ed) Mammals of the sea, biology and medicine. Charles C Thomas, Springfield, pp 298–418
Sorokin SP (1988) The respiratory system. In: Weiss L (ed) Cell and tissue biology, 6th edn. Urban & Schwarzenberg, Baltimore Munich
Welsch U (1989) Zur Architektur des Bindegewebes in der Lunge der Krabbenfresserund Weddellrobbe. Z. Mikroskop Anat (in press)
Welsch U, Drescher HE (1982) Light and electron microscopical observations on the terminal airways and the alveolar parenchyma of the Antarctic seals Lobodon carcinophagus and Leptonychotes weddelli. Polar Biol 1:105–114
Wetzstein R (1964) Der Uterusmuskel: Morphologie. Arch Gynäk 202:1–13
Zapol WM (1987) Diving adaptations of the Weddell seal. Sci Am 256:80–85
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Welsch, U., Wagner, H., Galm, R. et al. Architecture and functional aspects of the distal airways of Antarctic seals with different habits, the Weddell Seal (Leptonychotes weddellii) and the Crabeater Seal (Lobodon carcinophagus). Polar Biol 10, 187–195 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238494
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238494